Embark on a historical odyssey through [A History of Insurance: Milestones and Advancements in Risk Management]. This article delves into the fascinating evolution of insurance, tracing its roots in ancient civilizations, its pivotal role in medieval trade, and its indispensable contributions to modern risk management. Explore how this industry has continuously adapted to societal and economic shifts, shaping the insurance landscape as we know it today.
Key Takeaways:
- Insurance safeguards assets from unforeseen perils.
- Its origins can be traced to ancient civilizations.
- Early versions centered around maritime trade and responsibility.
- Insurance coverage extended over time to include fire, vehicles, and health.
- Benjamin Franklin played a key role in establishing the first insurance company in the United States in 1752.
History of Insurance
From ancient maritime trade to modern-day health coverage, insurance has a rich and ever-evolving history. It’s a journey marked by innovation, adaptation, and a constant pursuit to safeguard individuals, businesses, and societies against uncertainty.
Ancient Roots: The origins of insurance can be traced back to ancient civilizations. Babylonian traders used “bottomry” contracts to spread the risk of maritime trade around 2000 B.C. Similarly, in ancient Greece, “benevolent societies” provided support to members in times of need.
Maritime Dominance: During the Middle Ages, insurance focused heavily on maritime trade. Merchants and ship owners sought protection against the perils of sea travel, leading to the development of marine insurance contracts. The concept of “general average” emerged, where all parties involved in a sea voyage shared the losses if a ship or cargo was sacrificed for the benefit of the group.
Expansion and Evolution: As societies grew more complex, so did the need for insurance. Fire insurance became prevalent in the 16th and 17th centuries, with the Great Fire of London in 1666 serving as a catalyst. The 18th century saw the rise of life insurance and the establishment of the first specialized insurance companies.
American Ingenuity: In the United States, Benjamin Franklin co-founded the Philadelphia Contributionship for the Insurance of Houses from Loss by Fire in 1752. This was the first insurance company in the colonies and laid the foundation for the insurance industry in the United States.
Modern Advancements: The 19th and 20th centuries witnessed significant advancements in insurance. Automobile insurance emerged with the advent of the automobile, while health insurance gained traction in the mid-20th century. The development of new technologies, such as data analytics and AI, has further transformed the insurance landscape in recent times.
Insurance has come a long way since its humble beginnings. Today, it’s an integral part of our financial system, providing peace of mind and financial protection against a wide range of risks. As the world continues to evolve, insurance will undoubtedly play a vital role in safeguarding our future.
To learn about the numerous coverage options available, check out different types of insurance. If you want to learn more about reputable insurance providers, major insurance companies can help. For a detailed account of the development of the insurance industry, click on the link.
The history of insurance in the Middle Ages

During the Middle Ages, The history of insurance in the Middle Ages blossomed, with insurance becoming an essential aspect of daily life. The growth of trade and commerce led to the development of various forms of insurance, including marine insurance, property insurance, and life insurance.
Marine insurance was one of the earliest forms of insurance to develop during the Middle Ages. As trade between different regions increased, merchants began to seek ways to protect their goods from the perils of the sea. Marine insurance policies covered the loss or damage of goods due to storms, shipwrecks, and piracy.
Property insurance also developed during the Middle Ages to protect homes, businesses, and other property from fire, theft, and other hazards. Property insurance policies were typically written for a period of one year and covered the cost of repairing or replacing damaged property.
Life insurance was another important development during the Middle Ages. Life insurance policies provided a financial benefit to the beneficiaries of the policyholder in the event of the policyholder’s death. Life insurance policies were often used to provide for the financial security of a family in the event of the death of the breadwinner.
The development of insurance during the Middle Ages was a major step forward in the evolution of risk management. Insurance provided a way for individuals and businesses to protect themselves from the financial consequences of unexpected events.
Key Takeaways:
The history of insurance in the Middle Ages is a complex and fascinating one, with roots in ancient civilizations.
The growth of trade and commerce during the Middle Ages led to the development of various forms of insurance, including marine insurance, property insurance, and life insurance.
Insurance provided a way for individuals and businesses to protect themselves from the financial consequences of unexpected events.
Citation:
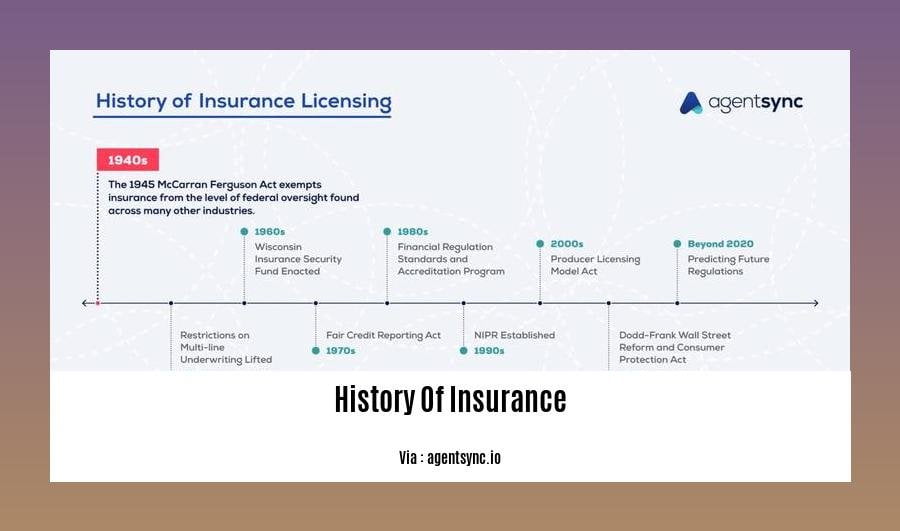
History of Insurance Timeline
Spreading Risk in Dangerous Waters:
Insurance is an indispensable tool for managing risk, an art that has evolved over centuries. From ancient mariners to modern corporations, insurance has evolved to protect against a vast range of perils, ensuring the continuity of commerce, livelihoods, and lives.
Key Takeaways:
- Insurance has its roots in ancient practices designed to mitigate risks associated with maritime trade.
- Early forms of insurance provided coverage for merchants against shipwrecks, storms, and piracy.
- As societies grew more complex, insurance expanded to encompass a wider range of risks, including fire, theft, and liability.
- The rise of merchant guilds in the Middle Ages led to the development of mutual insurance societies, fostering risk-sharing among members.
- Today, insurance is a global industry that plays a vital role in economic development and stability.
Marine Insurance: The Origin of Risk Sharing
The perilous nature of maritime trade in ancient times necessitated the development of Spreading Risk in Dangerous Waters. Merchants faced constant threats from storms, pirates, and other hazards. To mitigate these risks, they pooled their resources and created mutual insurance funds, guaranteeing compensation in the event of a catastrophe.
From Maritime to Modern: The Evolution of Risk Management
Over time, the principles of marine insurance extended to other areas. Guilds established funds for members who suffered losses due to fire, theft, or disability. As societies became more complex, so did the risks faced by businesses and individuals. The Industrial Revolution brought new perils, including workplace accidents and product liability.
The Rise of Insurance Institutions
With the expansion of risk management, dedicated insurance institutions emerged. Lloyd’s of London, established in the 17th century, became a hub for marine insurance and later a center for a wide range of insurance products. The 19th century saw the rise of life insurance companies, providing financial security for families in the event of a breadwinner’s death.
Citation:
FAQ
Q1: When and where was the first insurance contract created?
A1: The earliest known insurance contract dates back to 1750 B.C. in Babylon and is known as the Code of Hammurabi.
Q2: How did insurance help merchants during the Middle Ages?
A2: Insurance provided merchants with financial protection against losses due to disasters like shipwrecks and fires, encouraging trade and commerce.
Q3: What was the impact of the Great Fire of London on the development of insurance?
A3: The Great Fire of London in 1666 led to the rise of fire insurance as a way for property owners to protect themselves from financial ruin.
Q4: How did the industrial revolution influence the insurance industry?
A4: The industrial revolution brought new risks, such as factory accidents and worker injuries, leading to the development of specialized insurance products to address these emerging needs.
Q5: What are some unusual or unexpected forms of insurance that exist today?
A5: Unique insurance policies include falling coconut insurance in Papua New Guinea, pet insurance, and even alien abduction insurance, reflecting the diverse and evolving nature of risks in modern society.
- Senior at What Age: Benefits & Eligibility Guide - March 29, 2025
- Unlocking Senior Benefits: How Old is a Senior? Your Complete Guide - March 29, 2025
- Master Russian Politeness:A Guide to Saying Please - March 29, 2025




![[Brief History of Venice Italy]: A Journey Through Time and Wonders brief-history-of-venice-italy_2](https://www.lolaapp.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/brief-history-of-venice-italy_2-150x150.jpg)