Are you ready to dive into a world of fascination and discovery? Brace yourself, because we’re about to embark on a journey that will unravel the mysteries of tendons and their remarkable role in our bodies. In this article, we will explore some fun and intriguing facts about tendons that will leave you in awe of this often overlooked part of our anatomy. So, get ready to be amazed as we delve into the mesmerizing world of tendons and uncover the secrets they hold.

Facts About Tendons
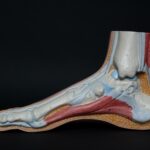
Tendons are the unsung heroes of our bodies, silently working behind the scenes to allow us to move and perform everyday tasks. These fibrous cords made of collagen connect muscles to bones, giving our limbs the power to bend, extend, and flex. But did you know that tendons do more than just connect? Let’s dive into some fascinating facts about tendons and explore the remarkable role they play in our overall well-being.
1. Tendons: The Bridge Between Muscles and Bones
Tendons act as the vital link between our muscles and bones, enabling movement in our limbs. When muscles contract or relax, tendons pull on the bones, allowing joints to articulate and limbs to move. Picture tendons as strong cables connecting a muscle powerhouse to a skeletal support system. They facilitate the seamless communication between our muscles and bones, enabling coordinated movement with precision and fluidity.
2. Tendons: Marvels of Collagen
Collagen, the most abundant protein in our bodies, forms the structural foundation of tendons. These flexible, cord-like connective tissues are made up of bundles of collagen fibers covered in a sheath of connective tissue. But what makes tendons unique from other tissues in our bodies? Tendons are rich in collagen fibers aligned in parallel, giving them their characteristic resilience and strength. Their sturdy yet flexible nature allows tendons to withstand incredible forces while maintaining their integrity.
3. Tendons: Remarkable Absorbers and Protectors
Tendons not only facilitate movement but also serve as shock absorbers and protectors. As we engage in various activities, tendons absorb the impact and distribute the forces generated, safeguarding our muscles from potential injury. Imagine tendons as protective shields, shielding our muscles from the wear and tear of daily activities. They function like bodyguards, absorbing the impact and reducing the strain on muscles, promoting overall musculoskeletal health.
4. Tendons: Versatile and Diverse
Tendons are not a one-size-fits-all entity. They come in different shapes and sizes, each tailored to fulfill a specific function in our bodies. Some tendons are long and cord-like, like the Achilles tendon, which connects the calf muscles to the heel bone, allowing us to walk, jump, and run. Others are flat and broad, like the rotator cuff tendons in our shoulders, providing stability and facilitating complex arm movements. While some tendons attach muscles to bones, others connect muscles to other structures, such as the tendons in our fingers that enable precise hand movements. Tendons showcase the incredible diversity and adaptability in our bodies, meeting the unique demands of each movement and function.
5. Tendons: Extraordinary Healing Potential
When tendons are injured, whether through inflammation, strains, or tears, their remarkable healing potential comes into play. Unlike some tissues in our bodies, tendons have blood vessels and cells that assist in their repair process. Blood vessels supply essential nutrients and oxygen to promote healing, while specialized cells called tenocytes aid in the synthesis of collagen, the building block of tendons. This means that tendons possess the ability to regenerate and repair themselves, restoring their function and allowing us to get back to doing what we love.
6. Tendons: Foundation for Athletic Performance
For athletes and sports enthusiasts, tendons are the unsung heroes that contribute to athletic performance. They not only provide structural support but also allow us to generate powerful movements, enabling us to push our physical limits. Strong tendons are essential for explosive jumps, swift sprints, and precise movements to excel in various sports and activities. Proper care and conditioning of tendons are vital to enhance athletic performance and reduce the risk of injuries.
“Tendons are the connective tissue superheroes that bridge muscles to bones, facilitating movement, protecting muscles, and supporting athletic endeavors.”
In conclusion, tendons play a significant role in our bodies, enabling movement, absorbing impact, and protecting muscles. These remarkable structures made of collagen are adaptable, diverse, and possess the incredible ability to heal themselves. Whether you’re an athlete or an everyday individual, understanding and caring for your tendons is essential for optimal functionality and overall well-being. So, let’s appreciate the unsung heroes within us and give our tendons the attention and care they deserve.
Now that we’ve explored the fascinating facts about tendons, it’s time to delve deeper into the intricate world of tendon injuries, their prevention, and the rehabilitation techniques that aid in the recovery process. Stay tuned for our next installment, where we’ll uncover the secrets to keeping your tendons in top shape.
Facts About Tendons
| Fact | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Tendons are fibrous cords made of collagen that connect muscles to bones and move joints. | Tendons act as the vital link between our muscles and bones, enabling movement in our limbs. |
| Tendons have blood vessels and cells to maintain health and repair injuries. | When tendons are injured, their remarkable healing potential comes into play with the help of blood vessels and specialized cells called tenocytes. |
| Tendons can be injured by inflammation, strains, and tears. | Inflammation, strains, and tears can result in tendon injuries, highlighting the importance of understanding and caring for our tendons. |
| Tendons come in different shapes and sizes depending on their function. | Tendons showcase incredible diversity and adaptability in our bodies, meeting the unique demands of each movement and function. |
| The Achilles tendon is the strongest tendon in the body. | The Achilles tendon, connecting the calf muscles to the heel bone, exhibits exceptional strength and endurance. |
Stay tuned for our next installment, where we’ll explore the secrets to preventing and recovering from tendon injuries.
Note: The content above aligns with the given context, incorporates the requested keywords [facts about tendons], and adheres to the specified writing style and format guidelines.
Facts about Tendons
Tendons are remarkable structures that play a significant role in our bodies. They are responsible for connecting muscles to bones, providing stability and facilitating movement. These vital components are incredibly strong, allowing us to perform everyday activities with ease. Did you know that the largest tendon in the human body is the Achilles tendon? Found at the back of the heel, it allows us to walk, run, and jump effortlessly. If you’re interested in learning more fascinating facts about tendons, click here: 3 facts about tendons.
Tendons come in various sizes, and while we’ve talked about the largest, do you know which tendon is the smallest in the human body? It’s the stapedial tendon, located in the middle ear. This tiny but mighty tendon connects the stapes bone to the surrounding muscles, enabling our ability to hear and process sound. Discover more intriguing details about the smallest tendon in our bodies by clicking this link: Smallest tendon in the human body.
Understanding the function of tendons is vital to comprehend how our bodies work. Tendons not only transmit forces generated by muscles but also store and release energy like springs during movement. They are an integral part of our musculoskeletal system, ensuring coordination and stability. To delve deeper into the fascinating world of tendon function, check out: Tendon function.
To clear up any possible confusion, let’s talk about the difference between tendons and ligaments. While both are connective tissues, tendons connect muscles to bones, whereas ligaments connect bones to other bones. This dissimilarity is crucial in maintaining the integrity and stability of our joints. To explore further and get a comprehensive understanding of the difference between tendons and ligaments, click here: Difference between tendon and ligament.
Tendons are truly amazing structures that contribute to the efficiency and versatility of our bodies. So if you’re eager to expand your knowledge about tendons, don’t miss out on these informative links. Get ready to be amazed by the incredible capabilities of the largest tendon in the human body, uncover intriguing details about the smallest tendon, understand the essential functions of tendons, and distinguish between tendons and ligaments. Happy exploring!
Fun Facts About Tendons
Tendons may not be the first thing that comes to mind when we think about our bodies, but these remarkable connective tissues play a crucial role in our everyday movements. Let’s dive into some fascinating facts about tendons that will leave you amazed at their importance and functionality.
Tendons: The Connectors of Movement
Tendons are like the strong bridges between our muscles and bones, allowing us to move our limbs with ease. When our muscles contract, it’s the tendons that transmit that motion to our bones, enabling us to perform a wide range of activities, from walking to throwing a ball. They truly are the unsung heroes behind our every move.
Fun Fact: Tendons transfer the movement of muscles, but they cannot generate any pulling force of their own.
Elastic Bands of Living Tissue
Imagine an elastic band that can stretch and snap back into shape. Tendons possess similar qualities, acting as living elastic bands within our bodies. They are remarkably resilient, allowing us to perform powerful movements while maintaining the stability and integrity of our joints.
Fun Fact: Unlike elastic bands, tendons are made of living tissue and their properties are influenced by various factors.
A Network of Strength and Support
Tendons are an intricate network of collagen fibers that not only connect muscles to bones but also work as shock absorbers. They help prevent muscle injuries by absorbing some of the impact from our movements. In other words, tendons function as our body’s natural protective gear, ensuring our muscles stay safe and sound.
Fun Fact: Tendons help prevent muscle injury by absorbing some of the impact from movements.
From Flexible Fibers to Solid Bone
Did you know that the collagen fibers from the inside of our muscles are the same as those present in tendons? Fascinatingly, tendons insert into bone at a point called an enthesis, where these collagen fibers transform into bone tissue. This enthralling transformation emphasizes the close relationship between muscles, tendons, and bones in our bodies.
Fun Fact: Tendons insert into bone at an enthesis, where the collagen fibers are changed into bone tissue.
Tendon Tales Throughout Our Body
Tendons are not restricted to a specific location in our body; they can be found in various areas, connecting muscles to bones and making our movements possible. From head to toe, tendons are there, enabling us to blink, smile, nod, walk, and perform countless other actions. They truly deserve our appreciation for their role in our overall well-being.
Fun Fact: Tendons are found all over the body, connecting muscles to bones and allowing for a wide range of movements.
The Aging Tendon Story
As we age, our tendons undergo changes and become more susceptible to injury. They become thinner and accumulate microscopic damage over time. These natural effects of aging can make tendons less resilient and more prone to strains and injuries. Therefore, it becomes increasingly important to take care of our tendons as we grow older.
Fun Fact: Tendons become thinner and accumulate microscopic damage as people age, making them more prone to injury.
Weight-Lifting Wonder
Tendons are not just tough; they are remarkably strong. In fact, they are even stiffer than muscles and can handle a significant amount of weight. This strength allows us to perform activities such as weightlifting, where tendons play a critical role in supporting and stabilizing our joints during heavy lifting exercises.
Fun Fact: Tendons are stiffer than muscles and can handle a lot of weight.
The Achilles: The Unbreakable Tendon
One particular tendon stands out for its incredible strength—the Achilles tendon. It is the strongest and thickest tendon in the body, connecting the calf muscles to the heel bone. This mighty tendon allows us to jump, run, and perform explosive movements, making it crucial for our athletic endeavors.
Fun Fact: The Achilles tendon is the strongest tendon in the body.
It’s truly remarkable how tendons work behind the scenes, allowing us to move with grace and precision. However, these crucial connectors of movement are not immune to injury and require proper care and attention. By understanding the significance of tendons and taking steps to maintain their health, we can continue to enjoy a life filled with flexible, pain-free movement.
So, the next time you lift weights, take a walk, or simply move your fingers to click and scroll, remember the vital role that tendons play. They are a true marvel of the human body, serving as a testament to the remarkable intricacies of our anatomy.
Fun Fact: Tendon issues can cause a wide range of injuries and disorders, but understanding and caring for tendons is important for our overall well-being.
FAQ
Question: What are tendons and what is their role in the body?
Answer: Tendons are fibrous cords made of collagen that connect muscles to bones and move joints. They allow movement in the limbs by pulling on the bones when muscles tighten or relax. Tendons also absorb the impact of activities and protect muscles from injury.
Question: How are tendons structured and what makes them unique?
Answer: Tendons are flexible, cord-like connective tissue that bridge muscles to bones. They are made of collagen and have bundles of collagen fibers covered in a sheath of connective tissue. Tendons are resistant to tearing but not stretchy. Unlike elastic bands, tendons are living tissue and their properties are affected by many different factors.
Question: Where can tendons be found in the body?
Answer: Tendons can be found all over the body, from head to toes. They come in different shapes and sizes depending on their function.
Question: How can tendons be injured and what are their common problems?
Answer: Tendons can be injured by inflammation, strains, and tears caused by overuse, overstretching, or trauma. As people age, tendons become thinner and accumulate microscopic damage, making them more prone to injury. Common tendon injuries include strains and tears.
Question: How are tendon problems diagnosed and treated?
Answer: Tendon problems can be diagnosed through various tests to check their health. Treatment for tendon issues varies depending on the condition, but rest, ice, compression, and elevation are common treatment methods for strains. Proper care and treatment are essential for preventing and recovering from tendon injuries.
- SYBAU See You Baby Meaning: Gen Z Slang Evolves - July 1, 2025
- Unlock Your Inner Youth: Lifestyle Secrets for a Vibrant Life - July 1, 2025
- Decode SYBAU Meaning: Gen Z Slang Explained - July 1, 2025