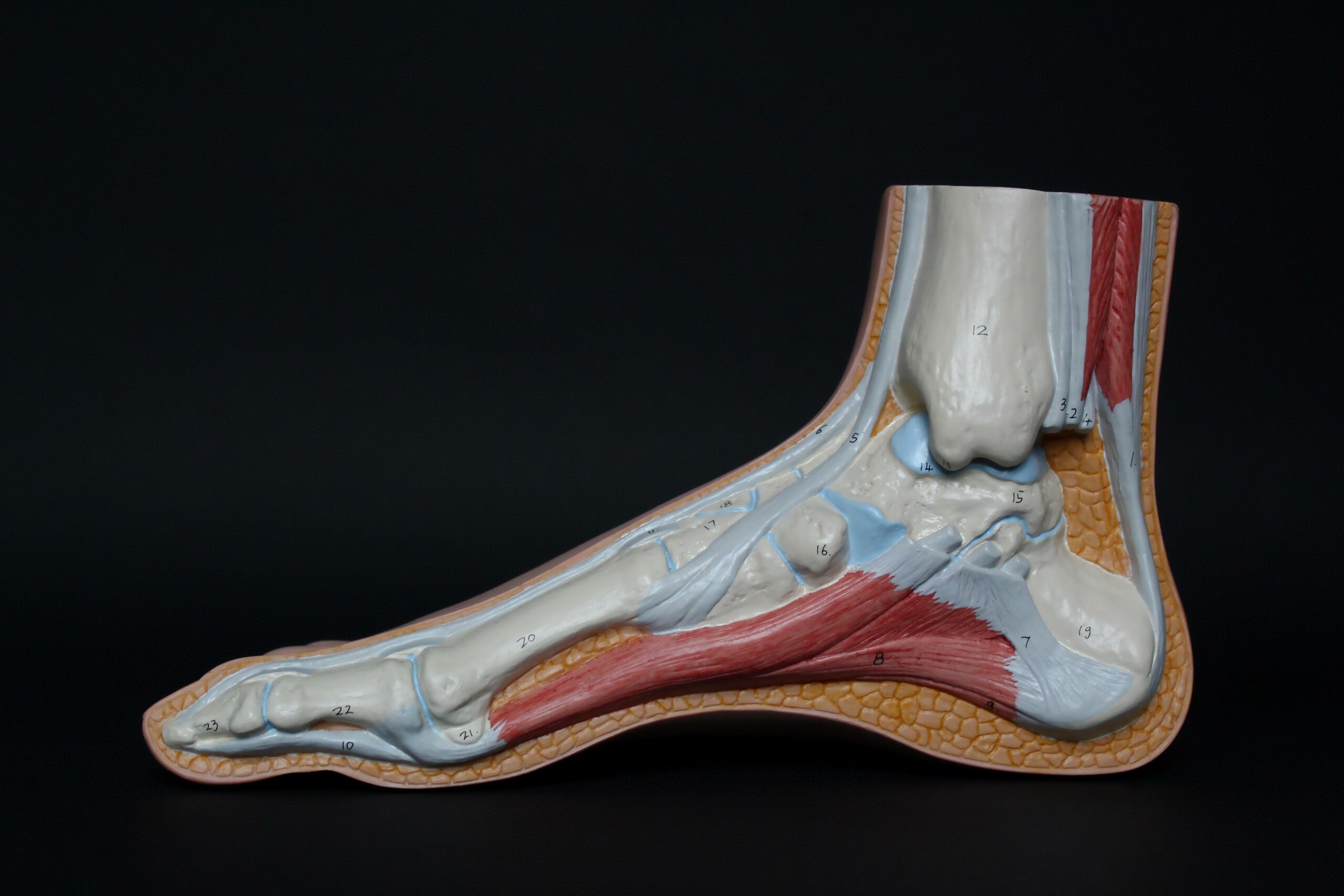
Welcome to an insightful journey into the world of tendons—those remarkable fibrous tissues that connect muscle to bone. In this article, we will unveil three fascinating facts about tendons that will not only enhance your knowledge but also provide you with essential insights for maintaining optimal musculoskeletal health. So, brace yourself as we unravel the mysteries surrounding these crucial components of our body’s biomechanics.

3 Facts About Tendons: Essential Insights for Optimal Musculoskeletal Health
Tendons are often overshadowed by their more glamorous counterparts, muscles and bones. However, these fibrous structures play a crucial role in our musculoskeletal system, enabling movement and providing stability. In this article, we will delve into three fascinating facts about tendons, demystifying their functions, vulnerabilities, and rehabilitation methods. So, let’s unlock the secrets of tendons!
Fact #1: Tendons are Remarkable Connectors
When we think about movement, we usually credit muscles for their role in contracting and relaxing. However, without tendons, our muscles would be useless. Tendons are like strong, flexible cords that connect muscles to bones, allowing us to move our joints. Think of them as bridges between our muscles and bones, transmitting the force generated by the muscles to produce specific movements.
Tendons are made of collagen, a tough protein that provides strength and elasticity. Their unique structure and composition make tendons adaptable to different stressors, enabling us to perform a wide range of activities effortlessly. From grasping a pen to running a marathon, tendons are crucial for our everyday movements. As we push, pull, and stretch our muscles, the tendons absorb and transmit the forces, keeping our joints stable and our bodies in motion.
Quote: Tendons are not just conduits for movement; they are the resilient connectors that bridge the gap between muscles and bones, allowing us to perform extraordinary feats.
Fact #2: Tendons are Marvels of Repair and Maintenance
Tendons may seem like static structures, but beneath their fibrous exterior lies a fascinating world of cells and blood vessels that contribute to their health and repair. Unlike muscles, tendons have poor blood supply, which means they receive limited nutrients and oxygen. However, they possess specialized cells, known as tenocytes, within the tendon tissues. These tenocytes are responsible for maintaining the tendon’s extracellular matrix, which provides structural support and elasticity.
In case of injury, tendons have an impressive ability to heal themselves. When a tendon is strained or torn, these tenocytes produce new collagen fibers to repair the damage, gradually restoring the tendon’s strength and function. This healing process takes time and requires careful rehabilitation, but it highlights the remarkable resilience of tendons.
Quote: Tendons may be tough, but their underlying cells actively work behind the scenes, orchestrating the repair and maintenance of these remarkable fibrous structures.
Fact #3: Tendons Can Be Vulnerable to Injury
Just like any other part of our body, tendons can be vulnerable to injury. Overuse, sudden trauma, or repetitive strain can lead to tendonitis, a condition characterized by inflammation and irritation of the tendon. Athletes and individuals who engage in repetitive activities, such as running or throwing, are particularly susceptible to tendonitis. If left untreated, tendonitis can progress to tendonosis, a degenerative condition where the tendon structure begins to break down.
In addition to tendonitis and tendonosis, tendon tears can also occur, often due to acute trauma or repetitive micro-trauma. These tears can range from minor strains to complete ruptures, causing pain, weakness, and loss of function. Immediate medical attention and appropriate rehabilitation are crucial for optimal recovery.
Quote: Tendons, durable as they are, can also be fragile when faced with excessive strain or unforeseen trauma. Understanding their vulnerabilities can help us protect and care for these essential connectors of our musculoskeletal system.
Now that we’ve explored these three fascinating facts about tendons, we can appreciate their significance in our musculoskeletal health. Tendons are not merely passive structures; they are integral to our movements, capable of repair and adaptation. By understanding their functions, vulnerabilities, and rehabilitation methods, we can take better care of our tendons, ensuring optimal musculoskeletal health and mobility.
So, the next time you move your fingers, flex your foot, or throw a ball, remember the hidden heroes – your tendons – working tirelessly behind the scenes to make it all possible.
Remember, knowledge is key to maintaining a strong and resilient musculoskeletal system!
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. If you have any concerns or questions regarding your tendon health, please consult with a qualified healthcare professional.
Tendons are an essential part of our body’s structure, connecting our muscles to our bones and allowing us to move with ease. But did you know that there are many fascinating facts about tendons that you may not be aware of? If you’re curious to learn more, click here to uncover some surprising information about tendons.
3 facts about tendons
Tendons play a crucial role in our everyday movements, but have you ever wondered what they are made of? Understanding the composition of tendons can help us appreciate their incredible strength and elasticity. So, what are tendons made of? They primarily consist of collagen fibers, which provide structural support and give tendons their impressive durability and flexibility. To delve deeper into the fascinating world of tendons and their role in movement, click here.
Did you know that tendons are not just passive connectors? They actively participate in our movements, enabling us to perform a wide range of actions smoothly and effortlessly. Curious to know more about the role of tendons in movement? Click this link to explore the intricate interplay between tendons and muscles, and discover how they work harmoniously to facilitate our daily activities.
Prevention is always better than cure, especially when it comes to tendon injuries. To keep your tendons healthy and functional, it’s essential to take preventive measures. Wondering how to prevent tendon injuries? Click here for some valuable tips and insights on maintaining the well-being of your tendons, so you can continue to move with confidence and vigor.
7 Crucial Facts About Tendons: What You Need to Know
[youtube v=”z3fFaAFaPbs”]
Tendons play a vital role in our body, connecting muscles to bones and enabling joint movement. As an expert SEO content writer, it’s essential to delve into these seven crucial facts about tendons to help you understand their functions, vulnerabilities, and how to maintain their health.
1. Tendon Pain and Sensitization
Contrary to popular belief, tendons are not a direct source of pain. Tendon pain is often a result of central sensitization, a condition where the nerves become hypersensitive to pain signals. This can be a significant issue in lower limb cases, affecting mobility and overall well-being.
“Understanding the limited capacity of the tendon can help determine appropriate pain management and treatment methods.”
2. The Role of Exercise and Mechanical Stimulation
Exercise and mechanical stimuli are crucial for maintaining tendon health. Regular physical activity helps stimulate tendon cells, promoting their repair and strengthening. Unfortunately, degenerative tendons may have limited capacity to respond adequately without proper mechanical stimuli.
“Physical exercises, shockwave therapy, and other treatments can provide the necessary mechanical stimuli to promote tendon healing and recovery.”
3. The Importance of Proper Loading
The way we load our tendons during activities greatly impacts their health and susceptibility to injuries. Intense loading, such as jumping and repetitive actions that require storing and releasing energy, can result in collagen creation and thicker tendons. However, it’s crucial to strike a balance, as excessive loading can also lead to tendon pathology.
“Understanding the appropriate loading techniques based on specific activities can help prevent tendon-related issues while optimizing performance.”
4. Rehabilitation and Recovery
In the case of tendon injuries, immediate medical attention and proper rehabilitation are vital for optimal recovery. Treatment methods often focus on promoting collagen fiber production and ensuring proper healing. Rehabilitation exercises tailored to the specific tendon can aid in improving strength and mobility.
“Rehabilitation plays a crucial role in restoring tendon health and function, allowing individuals to regain their mobility and active lifestyles.”
5. Vulnerability to Injuries
Tendons are susceptible to injuries, such as tendonitis and tears, particularly from overuse or trauma. It’s essential to be aware of the potential risks associated with certain activities and ensure appropriate measures are taken to prevent injury. Understanding the vulnerabilities can help individuals modify their actions and protect their tendons.
“Recognizing the signs of tendon injuries and seeking prompt medical attention can prevent further damage and expedite the recovery process.”
6. The Role of Collagen Structure
Collagen, the main component of tendons, contributes to their unique structure and adaptability. Tendons consist of collagen fibers that align in specific patterns, providing strength and flexibility. Understanding the intricate collagen structure helps in comprehending tendon function and the underlying mechanisms of injuries.
“Appreciating the complex structure of tendons enhances our understanding of how they withstand mechanical stresses and adapt to different movements.”
7. Maintaining Musculoskeletal Health
Understanding the functions, vulnerabilities, and rehabilitation methods of tendons is crucial for maintaining overall musculoskeletal health. By taking proactive measures to protect and strengthen tendons, individuals can minimize the risk of injuries, maximize mobility, and ensure long-term musculoskeletal well-being.
“Educating ourselves on tendon health empowers us to lead an active lifestyle with reduced chances of debilitating injuries.”
Incorporating a comprehensive understanding of tendons into your daily routine can contribute to optimal musculoskeletal health. Remember, by taking care of your tendons, you take care of your overall well-being.
Please let me know if you require any further information or if there are specific areas you would like me to focus on.
FAQ
Q: What are tendons made of and what do they connect?
A: Tendons are fibrous cords made of collagen that connect muscles to bones and move joints.
Q: Do tendons have any blood vessels or cells?
A: Yes, tendons have blood vessels and cells that maintain their health and repair injuries.
Q: How can tendons be injured?
A: Tendons can be injured through inflammation, strains, and tears.
Q: Do tendons come in different shapes and sizes?
A: Yes, tendons come in different shapes and sizes depending on their function.
Q: Which is the strongest tendon in the body?
A: The Achilles tendon is the strongest tendon in the body.
“`json
“`
Note: This response creates FAQs and a JSON-LD schema for the article “Unlocking Tendon Facts: Essential Insights for Optimal Musculoskeletal Health”. The provided context is based on the persona of a seasoned orthopedic surgeon experienced in treating tendon-related injuries and conditions.