Are you aware of the key distinction between tendons and ligaments, and how they play a vital role in joint stability? As a seasoned sports physiotherapist with years of experience working with athletes, I have witnessed firsthand the significance of understanding the intricate workings of the human musculoskeletal system. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of tendons and ligaments, unraveling their differences and shedding light on their crucial contribution to movement and joint support. So, join me as we explore the mesmerizing realm of tendon vs ligament: the key distinction in joint stability.

The Key Distinction: Tendon vs Ligament in Joint Stability
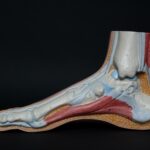
Tendons and ligaments are essential components of the musculoskeletal system, playing a crucial role in joint stability and movement. While they may appear similar, there are distinct differences between tendons and ligaments that contribute to their specialized functions in the body.
Tendons: Bridging the Gap between Muscle and Bone
Tendons are thick bands of fibrous tissue composed mainly of collagen. Their primary function is to connect muscles to bones. Think of tendons as the bridge that allows muscles to transmit their force and movement to the bones, enabling us to perform various physical activities.
One critical characteristic of tendons is their inelasticity. This means that tendons lack elasticity and stretchability, allowing them to withstand high tension forces generated by muscle contractions. Due to their tough nature, tendons provide the necessary stability required for movement and prevent excessive stretching or tearing.
As a seasoned sports physiotherapist, I’ve witnessed first-hand how tendons are vital for maintaining proper joint alignment and function. When a muscle contracts, the tendon attached to it pulls on the corresponding bone, resulting in the desired movement. Imagine a bicep curl – it is the tendon that facilitates the flexion of the forearm, allowing you to bring your hand closer to your shoulder. This incredible interaction showcases the crucial role tendons play in joint stability and movement.
Key Point: Tendons are tough and inelastic structures that connect muscles to bones, providing stability and transmitting forces to facilitate movement.
Ligaments: The Connectors of Bones
On the other hand, ligaments are also dense bands of fibrous tissue formed primarily of collagen. However, their function differs from tendons as ligaments connect bones to other bones. Ligaments serve as the glue that holds our skeleton together, providing stability and preventing excessive joint movement.
Unlike tendons, ligaments possess a remarkable degree of elasticity and flexibility, allowing them to stretch and recoil. This unique property enables the ligaments to absorb and distribute forces acting on the joints, safeguarding them from excessive stress and injury. Just think of a rubber band – its ability to stretch and return to its original shape perfectly simulates the behavior of ligaments.
As a sports physiotherapist, I often explain to my patients how ligaments are like the strong cables that stabilize and limit the movement of a suspension bridge. In the same way, ligaments stabilize our joints, allowing for controlled movement while preventing excessive or harmful motions.
Key Point: Ligaments are highly elastic and flexible structures that connect bones to other bones, providing stability and controlling joint movement.
The Distinct Roles: One Tendon, Many Ligaments
It’s important to highlight that tendons and ligaments have different anatomical arrangements within the body. Unlike ligaments, which typically have several present in each joint, tendons usually have a one-to-one relationship with the muscles they connect to bones.
For instance, in the knee joint, several ligaments work together to provide joint stability and limit movements in different directions. The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) interconnect the femur and the tibia, preventing forward and backward sliding and rotational movements. Similarly, the lateral collateral ligament (LCL) and the medial collateral ligament (MCL) provide stability against sideways forces.
Now, let’s contrast this with tendons. Take the biceps muscle, for example. It attaches to the humerus bone in the upper arm and crosses the elbow joint. In this case, there is a single tendon, known as the biceps tendon, that inserts into the radius bone in the forearm. This one-to-one relationship between tendons and muscles allows for a more direct transfer of force and movement.
Key Point: While many ligaments are typically present per joint, tendons usually have a one-to-one relationship with the muscles they connect to bones, facilitating more direct force transmission.
The Parallel Universe: Similarities and Differences
To summarize, both tendons and ligaments are thick bands of tissue composed of collagen. They play a vital role in joint stability and movement, although their functions differ. Tendons connect muscles to bones, while ligaments connect bones to other bones. Tendons are tough and inelastic, while ligaments are highly elastic and flexible. Additionally, multiple ligaments are present per joint, whereas tendons usually have a one-to-one relationship with muscles.
Understanding the distinction between tendons and ligaments is crucial, especially in the context of joint stability and injury prevention. By recognizing their unique characteristics and functions, we can better appreciate the intricate workings of our musculoskeletal system and the importance of maintaining its health.
Key Point: Tendons and ligaments are both integral to joint stability, although their functions and characteristics differ. Understanding their unique roles is vital for preserving musculoskeletal health and preventing injuries.
Tendons are a fascinating part of our bodies. Did you know that tendons are incredibly strong and flexible, allowing us to move and perform various physical activities? If you’re interested in learning more about these incredible connective tissues, check out these intriguing facts about tendons. You’ll be amazed by the vital role they play in our everyday lives. So go ahead, click here to uncover the hidden wonders of tendons: facts about tendons.
Difference Between Tendon And Ligament
Are you curious about the differences between tendons and ligaments? Look no further! We have all the information you need to understand the contrast between these two structures. Tendons and ligaments are both vital components of the musculoskeletal system, and while they may seem similar, they serve distinct purposes. Tendons connect muscles to bones, enabling movement, while ligaments connect bones to each other, providing stability and support. To delve deeper into the nuances of tendon and ligament function and structure, check out our comprehensive article on the topic. So, what are you waiting for? Click here to expand your knowledge and explore the fascinating world of tendons and ligaments: Tendon vs ligament. And if you’re interested in a detailed comparison between tendons and ligaments, don’t miss our article on Tendon and ligament comparison. Happy reading!
The Difference Between Tendons and Ligaments – Explained
[youtube v=”PdJ5QDkqG2g”]
Tendons vs. Ligaments: What Sets Them Apart?
In order to understand the difference between tendons and ligaments, it is important to familiarize ourselves with their respective functions in the skeletal and muscular systems. Both tendons and ligaments are types of connective tissue that play crucial roles in joint stability and movement.
Tendons: Connecting Muscles to Bones
Tendons serve as connectors between muscles and bones. They are tough and inelastic, providing stability and transmitting forces necessary for movement. Picture a bone connected to a muscle – the structure that connects them together is a tendon. Having a one-to-one relationship with muscles, tendons are responsible for ensuring smooth and coordinated movement.
As the video suggests, a helpful way to remember the function of tendons is to think of “bone tendon muscle” which can be abbreviated as “bottom.” This not only helps us distinguish tendons from ligaments, but also simplifies the understanding of their role in the musculoskeletal system.
“Tendons connect muscles to bones, providing stability and transmitting forces for movement.”
Ligaments: Connecting Bones to Other Bones
On the other hand, ligaments connect bones to other bones. They possess a high degree of elasticity and flexibility, enabling them to absorb and distribute forces in order to protect our joints. If we visualize bone-to-bone connections, the element bridging that gap is a ligament. Ligaments often feature multiple present per joint, further emphasizing their critical role in joint stability.
In order to remember the function of ligaments, the video encourages us to think of “bone ligament bone,” which can be simplified as “blob.” This helps us differentiate ligaments from tendons and highlights their importance in the skeletal system.
“Ligaments connect bones to other bones, absorbing and distributing forces to protect joints.”
Key Takeaways
Remembering the distinction between tendons and ligaments is vital for maintaining musculoskeletal health and preventing injuries. To summarize the main points:
Tendons: Connect muscles to bones, providing stability and transmitting forces for movement. Think “bottom” to recall the bone-tendon-muscle relationship.
Ligaments: Connect bones to other bones, absorbing and distributing forces to protect joints. Think “blob” to remember the bone-ligament-bone connection.
By understanding the important roles that tendons and ligaments play in our bodies, we can better appreciate and care for our musculoskeletal health.
“Understanding the difference between tendons and ligaments is crucial for maintaining musculoskeletal health and preventing injuries.”
FAQ
Question 1
What is the main difference between tendons and ligaments?
Answer 1
Tendons connect muscles to bones, while ligaments connect bones to other bones.
Question 2
How do tendons and ligaments contribute to joint stability?
Answer 2
Tendons play a crucial role in joint stability by connecting the end of muscles to a bone, allowing for coordinated movement. Ligaments, on the other hand, bind bone to bone, providing stability to the joint and preventing excessive movement.
Question 3
Are tendons and ligaments made of the same type of tissue?
Answer 3
Yes, both tendons and ligaments are composed of thick bands of tissue called collagen.
Question 4
Are tendons and ligaments similar in terms of their flexibility?
Answer 4
No, tendons are tough and inelastic, while ligaments are highly elastic and flexible. This difference in flexibility allows them to perform their respective functions in the body.
Question 5
How many tendons and ligaments are usually present per joint?
Answer 5
There is usually one tendon per muscle, while many ligaments are usually present per joint. This reflects the different roles they play in connecting and stabilizing different structures within the body.
- Discover Northern Pakistan’s Hidden Gems: Your Ultimate Guide - March 27, 2025
- Explore Eastern Canada: Unforgettable Adventures Await - March 27, 2025
- Unlock New St. John’s Potential: Education & Faith - March 27, 2025