Are you ready to embark on a journey to unravel the mysteries of the human body? In this captivating article, we will delve into the fascinating world of tendons – those remarkable connective tissues that hold our muscles and bones in perfect harmony. Brace yourself for a ride filled with discoveries as we go deep into the composition and structure of tendons, shedding light on their vital role in preserving our physical capabilities. So, get ready to be amazed as we unveil the wonders and answer the pressing question: What are tendons made of? Let’s dive right in!

What are tendons made of?
Tendons are truly remarkable structures that play a crucial role in our ability to move. But have you ever wondered what tendons are made of? Let’s dive into the fascinating composition and structure of tendons, shedding light on their incredible properties.
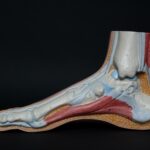
At the core of tendons lies collagen, a type of protein that forms the main structural framework of our bodies. Collagen fibers in tendons are flexible yet strong, making them resistant to impact. Imagine them as tiny cables woven together, providing stability and support.
These collagen fibers are arranged in neat bundles, giving tendons a structure akin to a fiberoptic cable or rope. This organized arrangement allows tendons to efficiently transmit the force generated by muscle contraction to the bones, enabling movement. It’s like a high-quality cable connecting a powerful engine to a mighty anchor, ensuring smooth and precise coordination.
However, it’s important to note that tendons are not elastic like a rubber band. They lack the ability to stretch and snap back into place. Think of them more like a strong rope that can only handle so much tension before it may fray or even tear.
Tendons can be found throughout the body, from larger joints like the knee to smaller ones like the jaw. They serve a crucial role in creating tension in muscles for movement and providing support and stability to various body structures, allowing us to perform everyday tasks and activities.
Unfortunately, tendon injuries are not uncommon. Athletes and individuals who engage in repetitive activities or sudden, excessive physical exertion are particularly susceptible. The Achilles tendon, tibialis posterior tendon, and patellar tendon are some of the commonly affected areas.
As we age, tendons undergo changes as well. They become thinner and weaker, which can increase the risk of injury. Understanding the composition and structure of tendons is crucial in preventing and managing tendon injuries, as well as maintaining our physical abilities as we grow older.
To summarize, tendons are primarily made up of collagen fibers that provide flexibility and strength. They resemble fiberoptic cables or ropes, transmitting the force of muscle contraction to the bones. However, they are not elastic and can tear if stretched too far. Tendons have multiple functions, including creating tension in muscles for movement and providing support and stability to different body structures.
Intriguingly, tendons truly are wonders of the human body. Now that we’ve unraveled what tendons are made of, let’s explore further to appreciate the incredible complexity and resilience of these connective tissues.
“Tendons, the woven anchors of our bodies, rely on collagen fibers to provide the strength and flexibility needed for movement and stability.”
Tendons are an essential part of our bodies, playing a crucial role in connecting muscles to bones and allowing for movement. If you’re curious to learn more about these fascinating connective tissues, we’ve got you covered. Discover three intriguing facts about tendons by clicking here: 3 facts about tendons. Prepare to be amazed as you delve into the intricate world of tendons and gain a deeper understanding of their importance. Don’t miss out on this opportunity to expand your knowledge and marvel at the wonders of the human body.
FAQ
Question 1: What are tendons primarily made of?
Answer: Tendons are primarily made of collagen, which is a type of dense, regular connective tissue.
Question 2: Why are collagen fibers in tendons strong and flexible?
Answer: Collagen fibers in tendons are strong and flexible, making them resistant to impact, due to their composition.
Question 3: What is the role of tendons in the body?
Answer: Tendons connect muscles to bones and transmit the force generated by muscle contraction to the bones. They also create tension in muscles for movement and provide support and stability to body structures.
Question 4: What is the structure of tendons?
Answer: Tendons have a structure similar to a fiberoptic cable or rope, with small collagen fibers arranged in bundles.
Question 5: Can tendons stretch?
Answer: Tendons are not elastic and may tear if stretched too far. They do not have the same stretching capacity as muscles.
- Georgia Platform: A Southern Strategy, 1850s - March 31, 2025
- How many weeks is 40 days: Quick Conversion Guide for Accurate Results - March 31, 2025
- How many feet is 300 meters? 984 Feet: Understand Length Conversions Easily - March 31, 2025