Embark on a captivating journey through the [History of Metals Timeline: A Journey Through the Ages], where we trace the remarkable milestones in the discovery, extraction, and utilization of metals that have shaped human civilizations. From the Copper Age to the Iron Age, and beyond to the modern marvels of metallurgy, this exploration unveils the profound impact metals have had on our technological advancements, cultural transformations, and the very foundations of our society.
Key Takeaways:
- Metallurgy played a vital role in human history: Metals transformed civilizations and technological advancements.
- Early civilizations discovered and utilized metals: Copper, Bronze, and Iron Ages marked significant milestones.
- Metal extraction and processing techniques evolved: From smelting to modern casting methods.
- Metals had profound economic, social, and military impacts: They influenced trade, warfare, and artistic expression.
- Metallurgical advancements continue today: New alloys and technologies drive innovation and shape our future.
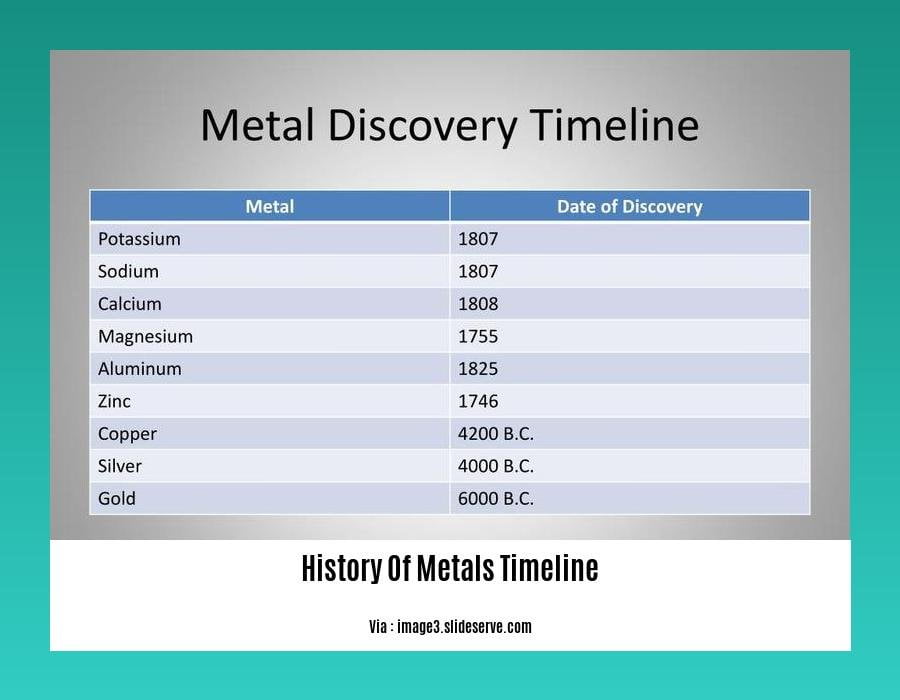
History of Metals Timeline

The journey of metals through time is a testament to humanity’s ingenuity. Join us as we delve into the History of Metals Timeline, exploring the milestones that shaped our technological evolution.
Discovering the Metallic World
As early as 9000 BCE, humans discovered the allure of native metals like copper and gold. These malleable materials marked the dawn of the Copper Age, where metalworking techniques evolved, and the use of bronze emerged.
The Bronze Age
Bronze, an alloy of copper and tin, revolutionized warfare and industry. The Bronze Age from 3300 to 1200 BCE witnessed the rise of civilizations, advanced metalworking, and the creation of sophisticated artifacts.
Iron Strengthens Civilization
The Iron Age (1200-600 BCE) ushered in the dominance of iron. Stronger and more versatile than bronze, iron transformed construction, weaponry, and agricultural practices.
Steel: The Backbone of Modern Society
The invention of steel in the 19th century marked a quantum leap. Steel’s superior strength and durability fueled the Industrial Revolution, shaping our infrastructure, transportation, and countless modern marvels.
Lightweight Aluminum
In the late 19th century, the discovery of aluminum brought lightness and strength to the forefront. Aluminum’s versatility impacted industries from aerospace to consumer products.
Composite Era: To the Future
Composite materials, like carbon fiber and titanium alloys, are pushing the boundaries of modern metallurgy. With their unmatched strength-to-weight ratios, composites are revolutionizing fields like transportation, energy, and construction.
Dig deeper into the history of metal, from its humble origins to its modern-day manifestations.
Uncover the captivating tale of History Of Metallurgy, the science and art of manipulating metals.
Immerse yourself in the evolution of History Of Metal Music, a genre that has captivated generations.
Explore the fascinating History Of Metallica, one of the most influential heavy metal bands of all time.
Discover the intriguing History Of Metal Documentary that delve into the genre’s rich history and cultural impact.
Investigate the History Of Metal And Horror, a genre that combines the power of metal music with the thrill of horror.
Trace the development of History Of Metalworking, a craft that has shaped civilizations throughout history.
Witness the advancement of History Of Metal Detectors, devices that have revolutionized treasure hunting and archaeological exploration.
The Iron Age
In the twilight of the Bronze Age, as ancient civilizations teetered on the brink of collapse, a new era, forged in the fires of innovation, emerged.
Enter The Iron Age**, a pivotal moment in human history marked by the rise of ironworking and its transformative impact on society. Around 1200 B.C., a series of cataclysmic events, including the decline of the Mycenaean civilization in Greece and the Hittite Empire in Turkey, ushered in this new epoch.
Iron, with its remarkable strength and durability, became the metal of choice for weapons, tools, and armor. It transformed agriculture, enabling farmers to till harder soils and increase crop yields.
The Iron Age witnessed the rise of the Celts, a nomadic people who occupied much of Europe. They established fortified hill forts and developed a distinct culture characterized by intricate metalwork and craftsmanship.
In the far east, the Persian Empire emerged during this period, founded by nomadic pastoralists from Iran. Their vast empire stretched from the Indus Valley to the Mediterranean Sea. The Persians became renowned for their advanced metallurgy, producing exquisite jewelry and weapons of exceptional quality.
Key Takeaways:
- The Iron Age began around 1200 B.C. with the collapse of Bronze Age civilizations.
- Iron, a strong and durable metal, revolutionized warfare, agriculture, and industry.
- The Celts and Persians were prominent civilizations during the Iron Age, known for their metalworking skills and cultural achievements.
Medieval Metals and Metallurgy
Growth in population during the 11th to 13th centuries fueled a surge in demand for medieval metals and metallurgy. To keep up with this demand, the medieval era saw exciting innovations in mining and ore processing techniques.
Metallurgists—the medieval alchemists of metal—enjoyed freedom of movement across Europe, exchanging knowledge and skills that advanced the field. By the 14th century, the exhaustion of easily accessible ore deposits necessitated technological advancements.
Harnessing water power for machinery and refining smelting methods boosted medieval metal production and quality, laying the groundwork for later industrial expansion. Additionally, central authorities recognized the strategic importance of medieval metals and metallurgy, promoting mining and encouraging innovation.
Key Takeaways:
- Medieval population growth drove demand for metals.
- Innovations in mining and ore processing met this demand.
- Metallurgists shared knowledge across Europe.
- Depletion of ore deposits led to technological advancements.
- Water power and improved smelting methods enhanced metal production.
- Central authorities supported mining and metallurgy.
Relevant URL Sources:
- Mining and metallurgy in medieval Europe
- Olsson, I. (2010). Medieval mining and metallurgy: Technology, organization and environmental impact. Royal Society of Chemistry.
The Modern Era of Metals
In the annals of human history, the discovery and mastery of metals have played a transformative role. The modern era of metals has been marked by unprecedented advancements in extraction, processing, and utilization, pushing the boundaries of metallurgy and ushering in a new age of innovation.
The Gold Rush of 1848 marked a pivotal moment in the modern era of metals. James Marshall’s discovery in California led to the extraction of vast amounts of gold, revolutionizing the global economy and infrastructure. Around $2 billion worth of gold was extracted by 1855, fueling a surge in investment and economic growth.
Modern mining techniques have accelerated the pace of gold extraction. An estimated 86% of all above-ground gold has been extracted in the last 200 years, thanks to advancements in processing and recovery methods. China, Russia, and Australia are currently the top gold-producing countries, accounting for a significant portion of global production.
Gold prices have been steadily climbing in recent years, approaching all-time highs. In 2022, gold prices hovered around $2,000 per ounce, driven by factors such as economic uncertainty and geopolitical tensions.
Key Takeaways:
- The modern era of metals has been characterized by significant advancements in extraction and processing techniques.
- The California Gold Rush of 1848 played a major role in the modern era of metals, leading to substantial gold extraction.
- Modern mining techniques have increased the rate of gold extraction, with 86% of above-ground gold being extracted in the last 200 years.
- China, Russia, and Australia are the top gold-producing countries, accounting for over 30% of global gold production.
- Gold prices have been on the rise in recent years, approaching all-time highs.
Relevant URL Sources:
- Elements by Visual Capitalist
- Visual Capitalist
















