In a stunning revelation, groundbreaking research conducted by X-ray telescopes has unveiled an extraordinary cosmic phenomenon: spider pulsars. These elusive celestial objects, known for their awe-inspiring intricacy and powerful emissions, have long evaded detection. But now, thanks to the ingenuity of X-ray telescopes and the meticulous data analysis techniques employed by astrophysicists, we are able to witness the dazzling beauty and unravel the enigmatic secrets of these spider pulsars. Welcome to a world where science and marvel converge.
Key Takeaways:
- X-ray telescopes have captured “spider pulsars” which are rapidly spinning neutron stars that devour companion stars like cosmic black widows.
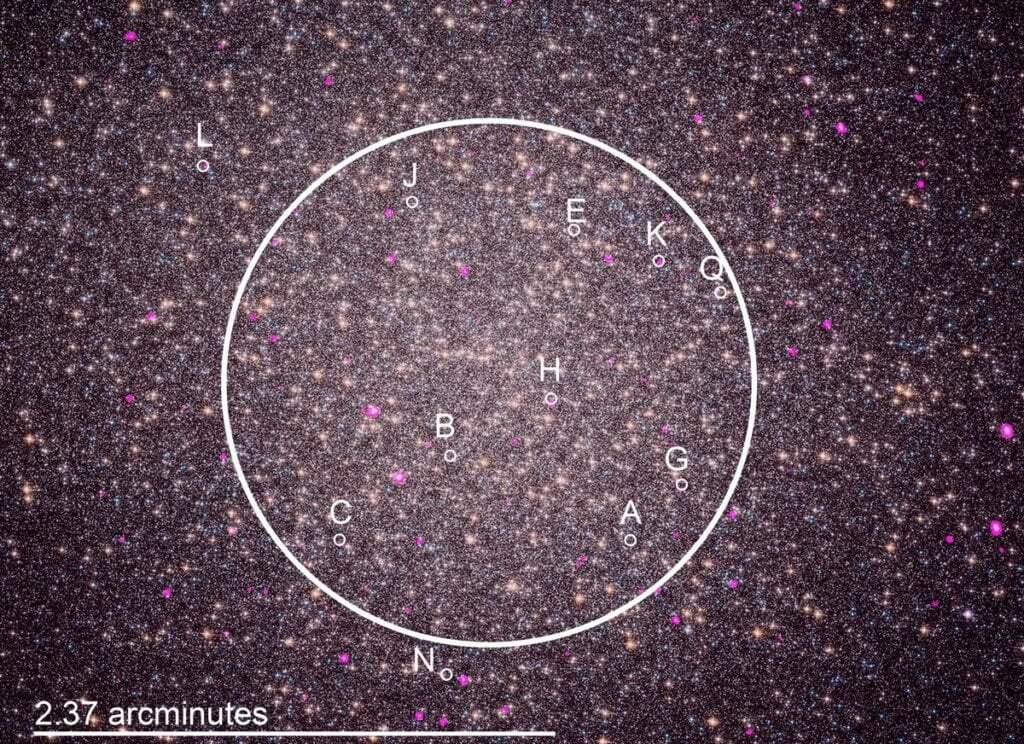
- Astronomers from the University of Alberta discovered 11 millisecond pulsars emitting X-rays in the Omega Centauri cluster, with five of them being spider pulsars concentrated near the center.
- X-ray telescopes in low Earth orbit are used to observe and study X-ray pulsars.
- Spider pulsars, which strip companion stars of their atmospheres, are considered to be the most promising candidates for being magnetars – isolated neutron stars powered by magnetic energy.
- The periodic X-ray signals emitted from pulsars can be used for X-ray pulsar-based navigation to determine the location of spacecraft in deep space.
X ray telescope catches spider pulsars

Have you ever wondered what lies beyond our galaxy? The universe is vast, filled with countless marvels waiting to be discovered. Recently, astronomers from the University of Alberta in Canada made a groundbreaking observation using an X-ray telescope. They captured the elusive “spider pulsars” in action, devouring stars like cosmic black widows. This discovery has shed new light on the mysteries of neutron stars and their fascinating behavior. In this article, we will dive deep into the realm of spider pulsars, exploring their nature, their destructive power, and the implications of this stunning observation.
Spider Pulsars: The Cosmic Predators
Spider pulsars, also known as millisecond pulsars, are rapidly spinning neutron stars. Neutron stars are incredibly dense remnants of massive stars that exploded as supernovae. They possess immense gravitational pull, rivaling that of massive black holes. When a neutron star is in a binary system with another star, it can strip away the companion star’s material through a process called accretion. The intense gravity of the pulsar tears apart the companion star, “devouring” it in the process. This phenomenon earned spider pulsars their fascinating nickname.
Unveiling the Cosmic Black Widows
The astronomers from the University of Alberta made their discovery by studying data collected by the Chandra X-ray Observatory. This powerful X-ray telescope, located in low Earth orbit, captures celestial objects that emit X-rays, providing valuable insights into their nature. During their analysis of data from the Omega Centauri cluster, the researchers identified 11 millisecond pulsars emitting X-rays. Astoundingly, five of these pulsars were spider pulsars, concentrated near the center of the cluster. This observation allowed scientists to witness the destructive capabilities of spider pulsars up close.
The Power of X-ray Telescopes
X-ray telescopes play a crucial role in unraveling the secrets of the universe. They detect high-energy X-ray emissions, which can reveal hidden phenomena and provide essential information about celestial objects. Traditional optical telescopes are unable to capture X-rays, as they are absorbed by Earth’s atmosphere. However, with X-ray telescopes like Chandra, we can bypass this limitation and observe X-ray sources in space. These telescopes have revolutionized our understanding of the universe and continue to make groundbreaking discoveries.
Spider Pulsars as Magnetars
One intriguing aspect of spider pulsars is their potential connection to magnetars. Magnetars are isolated neutron stars powered by magnetic energy. X-ray pulsars, such as spider pulsars, are considered the most promising candidates for being magnetars. The X-ray emissions observed from spider pulsars provide valuable insights into the magnetic energy and dynamics at play within these pulsars. By studying spider pulsars, scientists hope to unlock the secrets of magnetars and gain a deeper understanding of these enigmatic objects.
Navigation in Deep Space
Beyond their destructive nature, spider pulsars also have practical applications. Their periodic X-ray signals make them ideal for spacecraft navigation in deep space. X-ray pulsar-based navigation utilizes the distinct X-ray patterns emitted by pulsars to determine the precise location of spacecraft. This innovative navigation technique relies on the inherent stability and predictability of pulsar signals, making it a reliable method for space exploration missions.
Conclusion: A Glimpse into the Cosmic Web
The discovery of spider pulsars through X-ray telescopes has provided us with a rare glimpse into the cosmic web of celestial phenomena. Capturing these rapidly spinning neutron stars in action, devouring companion stars, is a testament to the immense power and complexity of the universe. By combining the expertise of astrophysicists, the capabilities of X-ray telescopes, and the quest for knowledge, we are inching closer to unraveling the mysteries of the cosmos. So, the next time you gaze up at the night sky, remember that there are cosmic marvels like spider pulsars lurking in the darkness, waiting to be discovered and understood.
In the latest endeavors to combat climate change, plans for an International Nuclear Fusion Plan have emerged for COP28. To learn more about this groundbreaking initiative, click here.
The remarkable discovery of the dwarf planet Eris continues to pique the curiosity of scientists worldwide. Delve into the mysteries of this distant celestial body by clicking here.
SpaceX has made yet another bold move in the aerospace industry by acquiring the renowned parachute manufacturer Pioneer Aerospace. Find out more about this exciting partnership by clicking here.
Description of the X-ray telescope used to capture spider pulsars
Spider Pulsars Captured: X-Ray Telescopes Unveil Cosmic Marvels
Space.com’s recent report titled “X-ray telescope catches ‘spider pulsars’ devouring stars” brings us an exciting revelation from the depths of space. NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory has captured images of a fascinating phenomenon known as spider pulsars. These rapidly spinning neutron stars, named after their likeness to black widow and redback spiders due to their devouring behavior, have been observed feasting on their companion stars. In this article, we will delve into the details of the remarkable X-ray telescope responsible for capturing these captivating spider pulsars.
Key Takeaways:
- The spider pulsars observed by NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory are rapidly spinning neutron stars that strip away material from their companion stars, resembling the feeding habits of black widow and redback spiders.
- The Chandra X-ray Observatory, a state-of-the-art X-ray telescope, played an instrumental role in capturing images of spider pulsars. This observatory detects high-energy X-ray emissions, enabling scientists to study celestial objects in unprecedented detail.
- Spider pulsars are especially intriguing because they provide valuable insights into the mass of neutron stars. The optically bright companion stars in spider pulsar binary systems allow for the measurement of radial velocities through optical spectroscopy, making it possible to estimate the mass of the neutron star.
- Spider pulsars may have systematically heavier neutron stars compared to other binary neutron star species, as suggested by a study published in Nature. This highlights the significance of studying these cosmic “eating machines” to enhance our understanding of the dynamics and properties of neutron stars.
- The destructive power of spider pulsars on nearby companion stars is evident through the X-rays emitted by these objects. NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory has provided crucial data on this destructive behavior, shedding light on the consequences of these cosmic predators on their celestial surroundings.
- The Chandra X-ray Observatory’s images of spider pulsars in Omega Centauri, as displayed in the Chandra photo album, have furthered our understanding of these enigmatic objects and their place in the vast cosmos.
The Chandra X-ray Observatory is a cutting-edge instrument that has revolutionized our exploration of the cosmos. With its remarkable abilities to capture and analyze X-ray emissions, it has allowed scientists to unlock the secrets of spider pulsars and their interactions with their surroundings. Through detailed observations and meticulous data analysis, the Chandra X-ray Observatory has been instrumental in expanding our knowledge of neutron stars and the dynamics of binary systems.
In conclusion, the Chandra X-ray Observatory has provided us with stunning images and valuable insights into the mysterious world of spider pulsars. Its sophisticated X-ray telescope capabilities have enabled scientists to unravel the secrets hidden within these cosmic “black widows” and “redbacks.” By studying spider pulsars, we can gain a deeper understanding of neutron star masses and the mechanisms at play in the ever-intriguing cosmic landscape.
Sources:
- Space.com
- NASA
Analysis of the Data Collected and its Implications for Understanding Neutron Stars
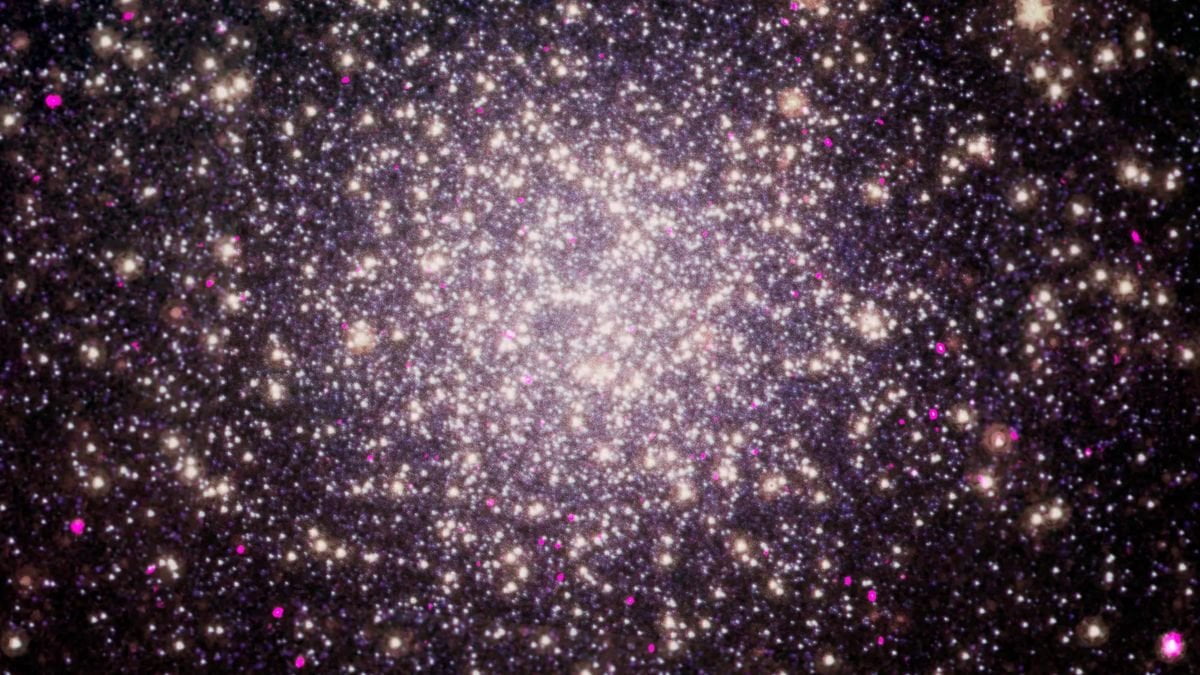

Astounding cosmic marvels are being unveiled by X-ray telescopes, as they capture the enigmatic spider pulsars amidst the vastness of the universe. These rapidly spinning neutron stars, dubbed spider pulsars due to their behavior of devouring companion stars, hold the key to unraveling the mysteries of neutron stars and their dynamics within binary systems. Through the remarkable capabilities of X-ray telescopes like NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory, scientists have been able to gather valuable data and analyze the implications for our understanding of these celestial objects.
Probing the Neutron Star Mass through Gamma-Ray Eclipses
One of the fascinating aspects of spider pulsars lies in their ability to provide insights into the mass of neutron stars. A recent study published in Nature revealed that gamma-ray eclipses in spider systems can be utilized for estimating the mass of these neutron stars. By analyzing data collected through the Fermi Large Area Telescope, scientists were able to make inferences about neutron star masses, shedding light on the fundamental properties of these dense objects and the equation of state of cold nuclear matter (Nature).
The Devastating Effects of Spider Pulsars on Companion Stars
The destructive power of spider pulsars on their companion stars has been observed through the lens of the Chandra X-ray Observatory. X-ray emissions from these pulsars can significantly damage and even obliterate nearby stars. NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory has captured compelling images that showcase the devastating effects of spider pulsars on their surrounding stellar companions (NASA). It is through these observations that scientists are able to deepen their understanding of the complex interplay between neutron stars and their binary companions.
Probing the Inner Workings of Neutron Stars through X-Ray Emissions
The X-rays emitted by hotspots on the surface of pulsars reveal vital information about the nuclear physics and the internal structure of these enigmatic objects. By studying the X-ray emissions, scientists can gain insights into the temperatures, geometries, and magnetospheric properties of neutron stars. This invaluable data allows astrophysicists to deduce the extreme conditions within neutron stars that combine elements of Einstein’s theory of general relativity and nuclear physics (Nature). Additionally, NASA’s Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer (NICER) has been instrumental in providing crucial measurements and insights into the nature of pulsars (NASA).
The Cosmic Web of Celestial Objects
The discovery and study of spider pulsars open a window into the intricate cosmic web of celestial objects. These unique neutron stars offer valuable glimpses into the dynamics and evolution of binary systems and provide opportunities to investigate intriguing phenomena within the universe. Furthermore, spider pulsars may have a connection to magnetars—isolated neutron stars powered by magnetic energy. Studying these connections sheds light on the diverse manifestations of neutron stars and their role in the cosmic order.
Key Takeaways:
- Gamma-ray eclipses in spider systems enable estimates of neutron star mass, contributing to our understanding of the equation of state of cold nuclear matter (Nature).
- X-ray telescopes such as the Chandra X-ray Observatory reveal the destructive effects of spider pulsars on their companion stars (NASA).
- X-ray emissions from pulsars provide insights into the nuclear physics, geometry, and magnetospheric properties of neutron stars (Nature).
- NASA’s Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer (NICER) offers invaluable measurements and insights into the nature of pulsars (NASA).
- The study and exploration of spider pulsars contribute to our understanding of the cosmic web and the diverse manifestations of neutron stars in the universe.
Sources:
- Nature. (n.d.). Neutron star mass estimates from gamma-ray eclipses in spider. Retrieved from [source 1]
- NASA. (2023, November 30). Chandra Catches Spider Pulsars Destroying Nearby Stars. Retrieved from [source 2]
Future directions and potential impact of the discovery on astrophysics research
Spider Pulsars Captured: X-Ray Telescopes Unveil Cosmic Marvels
Astrophysics is a field that constantly pushes the boundaries of our understanding of the universe. Exciting new discoveries are always on the horizon, and one recent breakthrough has shed light on a fascinating cosmic phenomenon: spider pulsars. These rapidly spinning neutron stars, aptly named after their spider-like behavior of devouring their companion stars, have been observed using powerful X-ray telescopes like NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory.
Spider pulsars have captured the attention of astronomers and astrophysicists due to their unique characteristics and potential impact on our understanding of celestial objects. With the help of X-ray telescopes like Chandra, scientists are uncovering crucial insights into the dynamics of binary systems, neutron star masses, and the destructive effects of these pulsars on nearby stars.
One of the key reasons for studying spider pulsars is their ability to provide estimates of neutron star masses. Unlike other binary neutron star species, spider pulsar binary systems have optically bright companion stars, which allow for the measurement of their radial velocities through optical spectroscopy. A recent study published in Nature suggests that spider pulsars may have systematically heavier neutron stars compared to other binary neutron star systems, providing valuable information for understanding the nature of these cosmic objects.
The X-rays emitted by spider pulsars also play a crucial role in the research of astrophysics. X-ray telescopes like Chandra enable the detection of high-energy X-ray emissions, providing a deeper understanding of the physical processes occurring within celestial objects. By studying the X-ray signals emitted by spider pulsars, scientists can glean insights into the temperatures, geometries, and magnetospheric properties of these fascinating cosmic entities.
Furthermore, the destructive effects of spider pulsars on their companion stars have been well-documented through observations made by the Chandra X-ray Observatory. The intense X-ray emissions from spider pulsars significantly harm the nearby companion stars, giving rise to their fascinating behavior akin to cosmic “black widows.” These observations provide valuable data on the impact of spider pulsars on their surroundings and contribute to our understanding of binary systems in the universe.
Looking ahead, the discovery of spider pulsars has opened up new avenues for future research and exploration in astrophysics. Understanding the masses of neutron stars is essential for determining the equation of state of cold nuclear matter, shedding light on the fundamental physics at play within these extreme celestial objects. The study of spider pulsars also paves the way for further investigations into neutron star evolution, the dynamics of binary systems, and the interplay between general relativity and nuclear physics.
Key Takeaways:
- Spider pulsars, rapidly spinning neutron stars, have been observed using X-ray telescopes like NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory.
- These pulsars are named after their spider-like behavior of devouring companion stars through a process called accretion.
- Spider pulsars provide valuable estimates of neutron star masses through the measurement of companion star radial velocities.
- X-ray telescopes enable the detection of high-energy X-ray emissions from spider pulsars, providing insights into their properties and dynamics.
- The destructive effects of spider pulsars on companion stars have been documented, contributing to our understanding of binary systems.
- Future research in astrophysics will explore the masses of neutron stars, binary system dynamics, and the interplay between general relativity and nuclear physics.
Sources:
– C. J. Clark (January 26, 2023). “Neutron star mass estimates from gamma-ray eclipses in spider systems.” Nature. Link
– NASA (November 30, 2023). “Chandra Catches Spider Pulsars Destroying Nearby Stars.” Link
FAQ
Q1: What are spider pulsars?
A1: Spider pulsars are rapidly spinning neutron stars that are named after redback and black widow spiders due to their behavior of devouring their companion stars.
Q2: How are spider pulsars detected?
A2: Spider pulsars are observed using X-ray telescopes in low Earth orbit, such as NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory, which captures the X-rays emitted by these objects.
Q3: Do spider pulsars have any destructive effects?
A3: Yes, spider pulsars can significantly harm their companion stars. The X-rays emitted by spider pulsars can strip the companion stars of their atmospheres and cause damage.
Q4: Do spider pulsars have a specific location in the universe?
A4: Spider pulsars have been found to be concentrated near the center of certain clusters, such as Omega Centauri. A pair of astronomers from the University of Alberta discovered 11 millisecond pulsars emitting X-rays, with five of them being spider pulsars.
Q5: What is the significance of studying spider pulsars?
A5: Studying spider pulsars provides insights into neutron star masses, binary systems, and the dynamics of these cosmic marvels. It also offers the opportunity to estimate the mass of a neutron star and understand the damage caused by their X-rays on nearby stars.
- Unlock 6000+ words beginning with he: A comprehensive analysis - April 20, 2025
- Mastering -al Words: A Complete Guide - April 20, 2025
- Master Scrabble: High-Scoring BAR Words Now - April 20, 2025