The origins and significance of the ancient world’s first dagger have long fascinated historians and enthusiasts alike. In this exploration, we delve into the captivating tale of this groundbreaking weapon, unearthing its cultural, practical, and symbolic implications with precision and depth. From meticulous analysis of historical records, archaeological findings, and ethnographic research, we unveil the history and importance of the first dagger in human history.
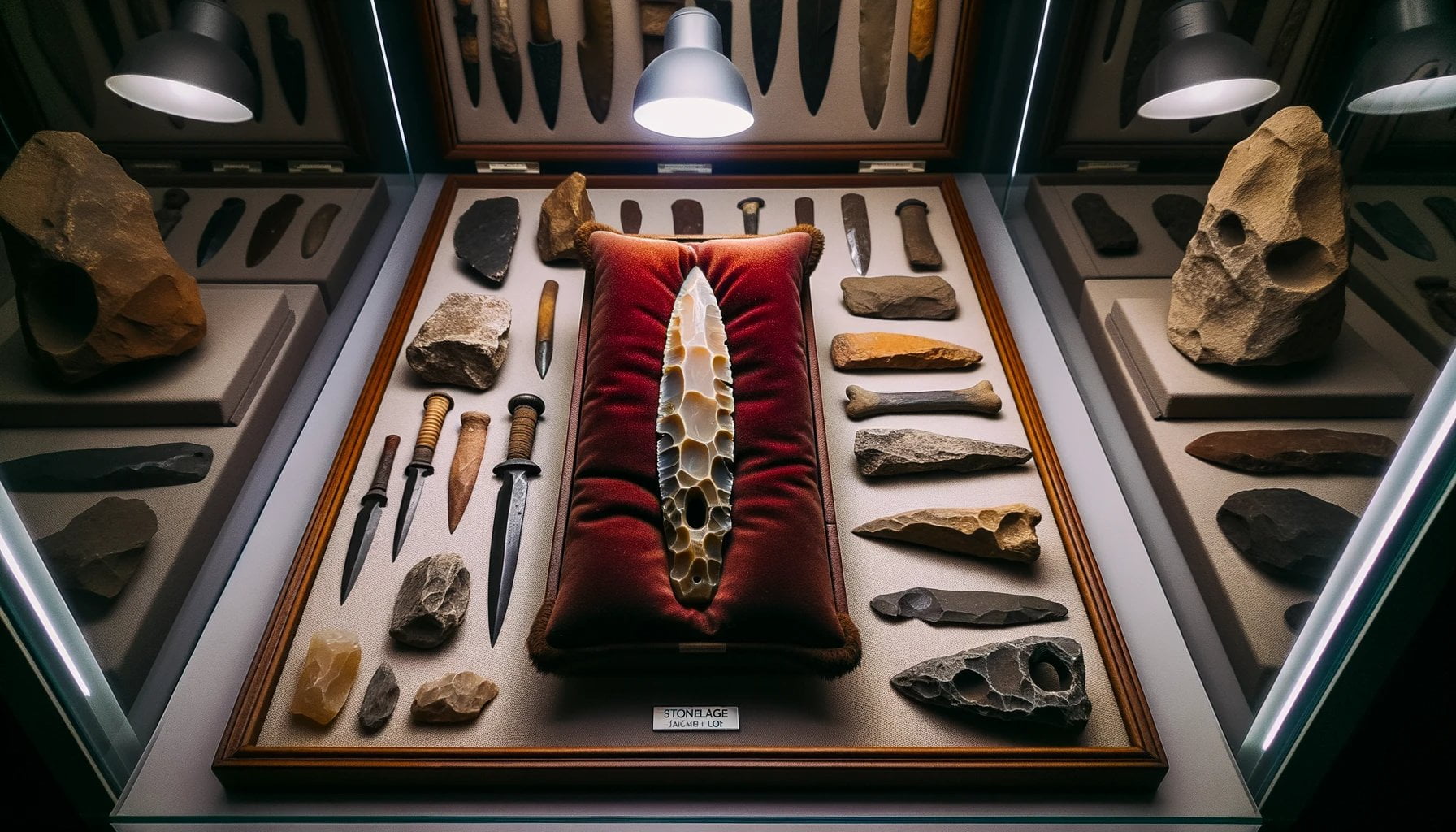

What was the first dagger in history?
In the vast expanse of human history, the humble dagger holds a significant place as one of the earliest weapons used by our ancestors. But what exactly was the first dagger in history? Let’s embark on a journey through time to unveil the origins, significance, and implications of this iconic weapon.
Origins of the Dagger
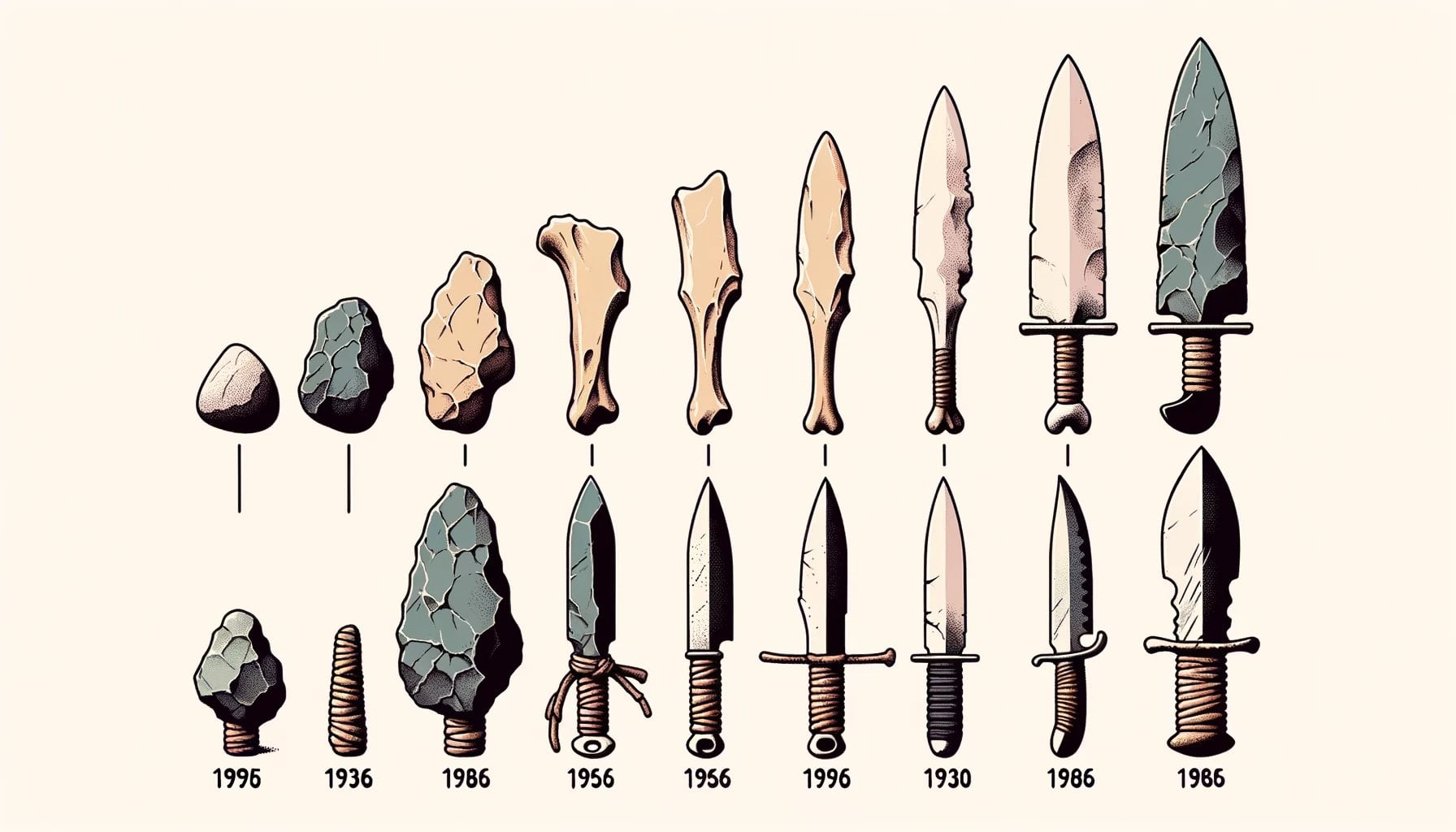
To understand the first dagger in history, we must delve into the ancient past. In the early Bronze Age, around the 3rd millennium BC, copper daggers made their appearance. These early daggers were crafted with great precision and skill using the smelting and refining process of copper ore.
The island of Crete, specifically the archaeological site of Knossos, reveals insights into the early development of daggers. Here, during the Early Minoan III period (2400-2000 BC), copper daggers have been discovered, shedding light on the craftsmanship and innovation of the ancient world.
Materials and Techniques
In the ancient world, daggers were constructed from various materials. During the Neolithic period, daggers were fashioned out of flint, ivory, or bone. However, as the Bronze Age dawned, copper became the primary metal used for crafting daggers.
The process of making copper daggers involved smelting and refining the ore, resulting in a strong and durable weapon. Additionally, other metals such as bronze, known for its superior strength, were also used in the creation of daggers.
Symbolism and Practicality
Daggers held great significance in multiple cultures throughout history. They symbolized courage and daring in combat for some warrior societies, while others utilized them in ritual and ceremonial contexts. The distinctive shape and historic usage of daggers have made them iconic and deeply symbolic objects.
While the dagger has a rich history imbued with cultural meaning, it cannot be ignored that it was primarily a practical weapon. Daggers were indispensable in close combat confrontations throughout human history. Their uniquely designed short blade, sharply tapered point, and dual cutting edges ensured their effectiveness in combat.
The Dark Side
Regrettably, not all associations with daggers are positive. Due to their historical use as weapons, daggers have become associated with assassination and murders. As a result, legislation in many places restricts their manufacture, sale, possession, transport, or use.
The Enduring Legacy
Despite their ancient origins, daggers continue to capture our fascination in the modern world. From the pages of history to the gripping tales of warriors, these weapons have left an indelible mark on human culture.
As we reflect on the first dagger in history, we uncover a story of innovation, skill, symbolism, and survival. It reminds us of the journey our ancestors embarked upon, equipping themselves with tools to navigate the challenges of their time. The first dagger serves as a testament to the ingenuity and resourcefulness of humankind.
So, the next time you come across a dagger, take a moment to appreciate the rich tapestry of history it represents. It is more than a mere weapon; it is an artifact that connects us to our ancient past and reminds us of the valuable lessons learned along the way.
Conclusion
The first dagger in history holds a captivating tale that intertwines cultural, practical, and symbolic dimensions. From its humble beginnings in the early Bronze Age to its enduring legacy, the dagger has remained an iconic and potent symbol throughout human history.
As we unveil the mysteries of the first dagger, we gain insight into our ancestors’ innovative spirit, their resourcefulness in crafting weapons, and their complex relationship with combat. It is through understanding the origins, significance, and implications of the first dagger that we can fully appreciate its enduring allure.
Ancient daggers have always fascinated historians and collectors alike. Explore the intriguing world of these historical weapons with our collection of ancient daggers. Discover more about their origins, craftsmanship, and the stories they hold, at Ancient Daggers.
Early Examples of Blade Materials and Designs
Daggers have been a fundamental tool and weapon throughout human history, and their evolution is intricately connected to the development of civilization itself. In this article, we will delve into the earliest examples of blade materials and designs, exploring how they influenced the ancient world and continue to captivate our fascination today.
The Birth of Daggers and the Rise of Copper
Around 5,000 years ago, during the early Bronze Age, the first daggers in history emerged as essential implements. These early daggers were typically forged from reheating metal ores, with copper being the primary material used. Through the smelting and refining process of copper ore, ancient craftsmen shaped these daggers with precision, creating tools of both practical and symbolic significance.
Copper daggers served as versatile substitutes for axes and javelins in ancient times. However, they had their limitations. Copper daggers were less durable compared to their predecessors, and their edges required constant sharpening. Nonetheless, their introduction represented a significant leap forward in the ancient world’s tool-making technology.
The Ancient Splendor of Bronze Daggers
Following the utilization of copper, the discovery of bronze revolutionized dagger craftsmanship. The benefits of bronze as a material were manifold. Its durability and ability to hold a sharp edge for a more extended period made bronze daggers highly desired in the ancient world.
Bronze daggers, like their copper predecessors, were made by heating and shaping metal ores. Bronze itself is an alloy composed primarily of copper, blended with tin or other metals depending on the specific desired properties. This alloy enhanced the durability and strength of the daggers, enabling them to withstand rigorous usage in both combat and everyday tasks.
Design Innovations and Cultural Influence
Dagger designs underwent significant transformations throughout history, driven by both practical and cultural factors. Early examples of daggers were often honed on both ends, enhancing their cutting and thrusting abilities. They were frequently crafted from a single piece of metal, enabling a seamless transition between the blade and hilt.
As societies developed, so did the prominence of daggers. This prominence influenced their designs, leading to the creation of sharper, more durable blades and the incorporation of elaborate patterns. Medieval dagger hilts, for example, were made from various materials such as metal, wood, bone, and horn, showcasing the intricate craftsmanship and reflecting societal values and aesthetics.
The ubiquitous nature of daggers meant that they served multiple purposes. They were commonly used as backup weapons in combat and were also employed for routine tasks like chopping food. Their presence in both practical and ceremonial contexts imbued them with cultural and symbolic significance. Daggers represented courage, combat prowess, and even featured in ritualistic practices across different societies.
The Implications and Enduring Legacy
The development and evolution of daggers played a vital role in the history of weaponry. From their humble beginnings as simple copper tools to the sophisticated designs of the medieval era, daggers tell a captivating tale of innovation, skill, and human resourcefulness.
Daggers, despite having ancient origins, continue to fascinate us in the modern world. They serve as reminders of our ancestors’ journey and the challenges they faced. These blades connect us to our ancient past and teach us valuable lessons about ingenuity and perseverance.
In conclusion, the first daggers in history emerged during the early Bronze Age, crafted from copper and later bronze. These blades represented a significant technological advancement, offering increased durability and sharper edges. Their designs evolved to reflect cultural values and practical needs, resulting in more sophisticated and versatile weapons. Today, as we examine ancient daggers, we uncover not only their historical significance but also timeless lessons about the resilience and creativity of our ancestors.
Exploration of the First Known Dagger in History
Unveiling the origins, significance, and implications of the earliest weapon
The first known dagger in history holds a captivating tale that takes us back to the ancient world. This exploration delves into the origins, significance, and implications of this remarkable weapon, shedding light on its cultural, practical, and symbolic implications.
The Journey Begins: Neolithic Times
In the depths of Neolithic times, our ancestors crafted the earliest daggers from materials like flint, ivory, and bone. These rudimentary weapons served as tools for survival, enabling our early human predecessors to navigate a world teeming with challenges.
A Glimpse into the Past: The Early Bronze Age
As time pressed on, the early Bronze Age emerged, bringing forth a new era of dagger craftsmanship. Copper daggers made their grand entrance, with fine examples unearthed at Knossos in ancient Minoan civilization (2400–2000 BC). Through the smelting and refining process of copper ore, our ancestors honed their skills, crafting daggers with precision and elegance.
Daggers in Ancient Egypt: A Royal Splendor
In ancient Egypt, daggers held a prominent place in society. They were predominantly fashioned from copper or bronze, while those bestowed upon royalty gleamed with the luster of gold. These majestic weapons symbolized power, authority, and protection in the realm of pharaohs.
Unraveling the Crafting Techniques
To unleash the lethal potential of daggers, our ancestors employed various techniques to sharpen the blade. Grinding or honing the edges with meticulous precision became essential practices, ensuring that these weapons could penetrate the opposition’s defenses with devastating efficacy.
Courage and Symbolism: Daggers in Culture
For many cultures and military organizations, the dagger symbolized courage and daring in combat. It became emblematic of strength and resilience, serving as a reminder of the warriors’ unwavering commitment to protect their people.
A Marvel of Metalwork: Crafting Daggers
Daggers were crafted through various methods, each contributing to their unique design and functionality. Forging and shaping the metal, our ancestors honed their skills to create blades of unparalleled sharpness and durability. The artistry and craftsmanship behind each dagger reflected the ingenuity and resourcefulness of our ancient predecessors.
A Plethora of Designs: The Diversity of Daggers
Throughout history, numerous types of daggers emerged, each tailored to meet specific needs and cultural preferences. The European rondel dagger, with its distinctive round hilt, and the Afghan pesh-kabz, characterized by its curved blade, showcase the breadth and diversity of dagger designs across different regions and eras.
The Practical Weapon: Close Combat and Self-Defense
Daggers primarily served as weapons for close combat and self-defense. Their compact size and maneuverability made them ideal for swift strikes and parries, enabling fighters to engage in hand-to-hand combat with precision and agility.
A Dark History: The Associations with Assassination
Throughout history, daggers have unfortunately been associated with nefarious deeds. The dark reputation of these weapons stems from their historical use in assassinations and murders. Consequently, knife legislation now restricts the manufacture, sale, possession, transport, and use of daggers in many places.
As we explore the history and significance of the first known dagger in human history, we gain a deeper understanding of our ancient past. These weapons connect us to the challenges faced by our ancestors, reminding us of their resourcefulness, innovation, and the lessons we can learn from their journey.
Daggers continue to captivate our fascination in the modern world. Their story embodies innovation, skill, symbolism, and human resourcefulness. By unveiling the origins and implications of the first known dagger, we embark on a journey back in time, discovering the remarkable weaponry that shaped our history.
Significance and Impact of the First Dagger in Human History
In the vast tapestry of human history, one artifact stands out as a testament to our ancient ancestors’ resourcefulness and ingenuity. The first dagger, crafted during the Neolithic period, captivates us with its origins, significance, and profound implications. This article delves into the story behind this groundbreaking weapon and explores its cultural, practical, and symbolic dimensions.
Origins: Unveiling Ancient Ingenuity
The journey towards the first dagger begins in the Neolithic period, a time when our ancestors were transitioning from hunter-gatherer societies to settled agricultural communities. As they faced new challenges and opportunities, they honed their skills in crafting tools and weapons that would shape their destiny.
The first daggers emerged during this period, crafted from materials like flint, bone, and ivory. These early prototypes showcased our ancestors’ ability to transform simple objects into deadly weapons. With each strike of their primitive tools, they unknowingly set in motion a legacy that would impact generations to come.
Practicality: A Weapon Designed for Warriors
In the realm of weaponry, the dagger occupies a unique space. It was conceived as a short stabbing weapon, ideal for close-quarters combat where larger swords were impractical. Warriors needed a weapon that could be easily carried and deployed when the situation demanded it.
The dagger’s design evolved over time, influenced by cultural and practical factors. For example, the shape of the eastern dagger was inspired by the curve of a cow’s horn. These adaptations ensured that the dagger became a versatile and effective tool, providing warriors with an edge in battle.
Symbolism and Culture: A Blade with Deeper Meanings
Beyond its practical utility, the dagger held immense cultural and symbolic significance. It became more than just a weapon; it embodied courage, combat prowess, and even featured in ritual and ceremonial contexts.
However, the dagger’s symbolic associations are not without their dark side. Throughout history, it has often been linked to assassination and murder, leading to restrictions on its manufacture, sale, possession, transport, and use. This duality of symbolism highlights the complex nature of the dagger and its enduring impact on human society.
Evolution and Legacy: From Artifacts to Inspiration
Over time, the ancient craftsmen refined their techniques, transitioning from wooden and bone daggers to more durable metal versions. In the Bronze Age, copper and bronze daggers emerged as substitutes for axes and javelins, revolutionizing the craftsmanship of these weapons.
The legacy of the first dagger extends far beyond its practical applications. It has inspired countless artistic representations, from intricate medieval hilt designs to modern-day depictions in literature and film. The dagger serves as a reminder of our ancestors’ journey, their resilience, and the challenges they faced.
Residue Analysis: Unraveling the Dagger’s Purpose
To truly understand the significance and impact of the first dagger, historians and archaeologists have turned to residue analysis. By examining traces of organic materials left on ancient daggers, researchers gain insights into their function and purpose. This meticulous analysis unravels the mysteries of the past, shedding light on the practical considerations and cultural contexts that shaped the first dagger’s existence.
In Conclusion: A Journey into the Ancient Past
The first dagger in human history stands as a testament to our ancestors’ resourcefulness and adaptability. Its significance and impact extend beyond the realm of weaponry, highlighting cultural and symbolic dimensions that continue to captivate our fascination in the modern world.
As we explore the origins, practicality, symbolism, and evolution of the first dagger, we gain a deeper understanding of our ancient past and the valuable lessons it imparts. Let us cherish this artifact, for it connects us to our heritage and reminds us of the remarkable journey that has led us to this point in history.
FAQ
Q1: What materials were the earliest daggers made of?
A1: The earliest daggers were made of materials such as flint, ivory, or bone in Neolithic times.
Q2: When did copper daggers first appear in history?
A2: Copper daggers first appeared in the early Bronze Age, around the 3rd millennium BC.
Q3: What materials were daggers made of in ancient Egypt?
A3: In ancient Egypt, daggers were typically made of copper or bronze, while royalty had gold weapons.
Q4: How were copper daggers sharpened?
A4: Copper daggers were sharpened using techniques such as grinding or honing.
Q5: What did daggers symbolize for some cultures and military organizations?
A5: Daggers symbolized courage and daring in combat for some cultures and military organizations.
Q6: What are the different types of daggers?
A6: There are different types of daggers, such as the European rondel dagger and the Afghan pesh-kabz.
Q7: What were daggers primarily used for?
A7: Daggers were used primarily as weapons for close combat and self-defense.
Q8: What are the associations with daggers and assassination?
A8: Daggers have associations with assassination and murders due to their historical use.
Q9: What restrictions exist for daggers?
A9: Knife legislation in many places restricts the manufacture, sale, possession, transport, or use of daggers.
Q10: What materials were medieval dagger hilts made from?
A10: Medieval dagger hilts were made from various materials, including wood, bone, horn, and metal.
- Sept 31 Myth: Unveiling Calendar Secrets - March 18, 2025
- How Long & Till December 18, 2025: Accurate Countdown Guide - March 18, 2025
- Discover Japanese Artists: A Complete History - March 18, 2025
















