It’s not just Mount St. Helens and Pompeii we need to worry about. Volcanoes are a sneaky natural hazard that can strike anywhere, anytime. They might be dormant for centuries, but when they wake up, they can cause catastrophic damage. In this article, I’ll break down the science of volcanic eruptions and give you practical tips on how to keep your community safe from volcanic threats.
Volcanic Hazards and Risks: A Closer Look
Volcanoes are awe-inspiring natural wonders, but they come with a darker side: the potential for destruction. Volcanic hazards and risks pose a significant threat to human populations and infrastructure.
What’s the Difference?
- Volcanic hazards: The dangerous processes that can occur during an eruption, such as lava flows and ash clouds.
- Volcanic risks: The potential for harm or damage caused by these hazards to people, property, and the environment.
The Wrath of Volcanoes
Volcanoes erupt in various ways, unleashing a range of hazards:
- Lava Flows: Sizzling rivers of molten rock that burn everything in their path.
- Pyroclastic Flows: Deadly clouds of hot gas, ash, and rocks that race down slopes like avalanches.
- Lahars: Devastating mudflows that form when volcanic debris mixes with water.
- Volcanic Gases: Toxic fumes that can cause respiratory problems, especially when inhaled during air travel.
Protecting Ourselves
To minimize the risks posed by volcanoes, we need to understand these hazards and take steps to mitigate their impact:
- Monitoring and Hazard Assessment: Scientists keep a close eye on volcanic activity, identifying potential hazards and predicting their likely consequences.
- Early Warning Systems: When an eruption is imminent, warning systems provide timely alerts to give people enough time to evacuate and prepare.
- Land-Use Planning: Governments restrict construction and development in areas at high risk of volcanic activity, ensuring that people aren’t putting themselves in harm’s way.
- Education and Public Awareness: Communities need to be educated about volcanic hazards, their early warning signs, and what to do in the event of an eruption.
Working Together
Volcanic hazards don’t stay within national borders. They can affect entire regions, so international cooperation is crucial. Countries share data, resources, and expertise to ensure that all populations are protected.
Conclusion
By understanding volcanic hazards and risks, and by taking proactive steps to mitigate them, we can significantly reduce the devastation they cause. Through science, collaboration, and community preparedness, we can safeguard our lives and livelihoods from the awesome power of volcanoes.
Do you know about the famous volcanoes that spew ash and lava? Or the types of volcanoes that exist? Read about the famous volcanic eruptions in history that left a lasting impact. Explore the connection between volcanoes and climate change and learn about volcano tourism and safety. Discover the volcanic islands and archipelagos that were formed by volcanic eruptions. Get insights into the volcanic rocks and minerals that are unique to volcanic environments. Explore the potential of geothermal energy from volcanoes and learn about the fascinating volcanoes on other planets. Finally, delve into the volcano monitoring and prediction techniques that help us understand and mitigate volcanic risks.
What are the different types of volcanic hazards?
Picture this: You’re chilling at home, sipping your coffee, when suddenly, your peaceful morning is interrupted by a volcanic eruption! It’s like nature’s version of a surprise party, but with a lot more destruction and chaos.
Volcanoes are impressive, but they can also be a bit of a handful, unleashing a range of hazards that can make your day go from relaxing to downright terrifying. Let’s dive into the different types of volcanic hazards and see what they’re all about.
Direct Hazards: The Hot and Heavy Stuff
These hazards are like the rowdy guests at the party, causing immediate and serious threats:
- Lava flows: Imagine a river of molten rock flowing towards you, destroying everything in its path like a giant, fiery bulldozer.
- Pyroclastic flows: These are like super-heated clouds of gas, ash, and rocks that race across the land, burning everything they touch. It’s like a volcanic version of a firestorm!
- Lahars: These mudflows are formed when volcanic debris mixes with water. They’re like messy, volcanic hurricanes, leaving a trail of destruction in their wake.
- Ballistic projectiles: Picture this: huge rocks and bombs flying through the air like cannonballs. Not exactly the ideal way to spend your afternoon!
- Ash clouds: These fine particles can travel for miles, blocking out the sun and causing breathing problems. It’s like having a volcanic smog cloud hanging over your head.
Indirect Hazards: The Sneaky Side Effects
These hazards are more like the quiet guests at the party, but don’t be fooled, they can still cause some serious trouble:
- Tsunamis: When a volcano explodes or collapses, it can send giant waves crashing towards coastal areas. These waves can be devastating, causing widespread damage and flooding.
- Climate change: Volcanoes release gases and ash into the atmosphere, which can affect the climate. Sometimes it gets colder, sometimes it gets warmer, but it’s never good news for those who like predictability.
- Famine: Volcanic ash and gases can damage crops and disrupt food chains, leading to food shortages and famine. It’s like a volcanic version of a food crisis.
- Habitat destruction: Volcanoes can destroy vegetation and ecosystems, leaving behind a barren landscape. It’s like a volcanic wasteland, not exactly the best place to go for a picnic.
Key Takeaways:
- Volcanic hazards come in two flavors: direct and indirect. Direct hazards hit you head-on, while indirect hazards mess with the environment and sneak up on you.
- Understanding these hazards is like having a volcanic preparedness plan. You know what to expect and can take steps to stay safe when the volcano starts to act up.
So, there you have it, the different types of volcanic hazards. They can be scary, but don’t panic! By knowing what to look out for, you can take precautions and avoid becoming a casualty of a volcanic party gone wrong.
How can we assess volcanic risks?
Volcanic eruptions can be like angry giants, unleashing their fury and posing threats to our homes and lives. That’s why scientists have put their thinking caps on and come up with smart ways to predict these fiery outbursts before they wreak havoc.
Let’s Dive into the Volcanic Risk Assessment Toolkit
1. Digging into the Past:
Just like detectives solving a mystery, scientists analyze historical records and geological clues to learn about a volcano’s past behavior. They look at how often it’s erupted, how big those eruptions were, and what kind of nasty tricks it pulled off.
2. Keeping a Watchful Eye with Gadgets:
Scientists don’t just rely on old stories; they’ve got high-tech gadgets to keep an eye on volcanoes in real-time. They measure how the ground shakes, how it puffs its chest, and what gases it breathes out. By studying these signs, they can guess when a volcano’s about to break loose.
3. Modeling the Magma Monster:
Scientists use computers to create virtual volcanoes. They feed the computers historical data and real-time info to predict how a volcano might act up in the future. This helps them map out where the lava will flow, how far the ash will spread, and if it will send out those fiery pyroclastic flows.
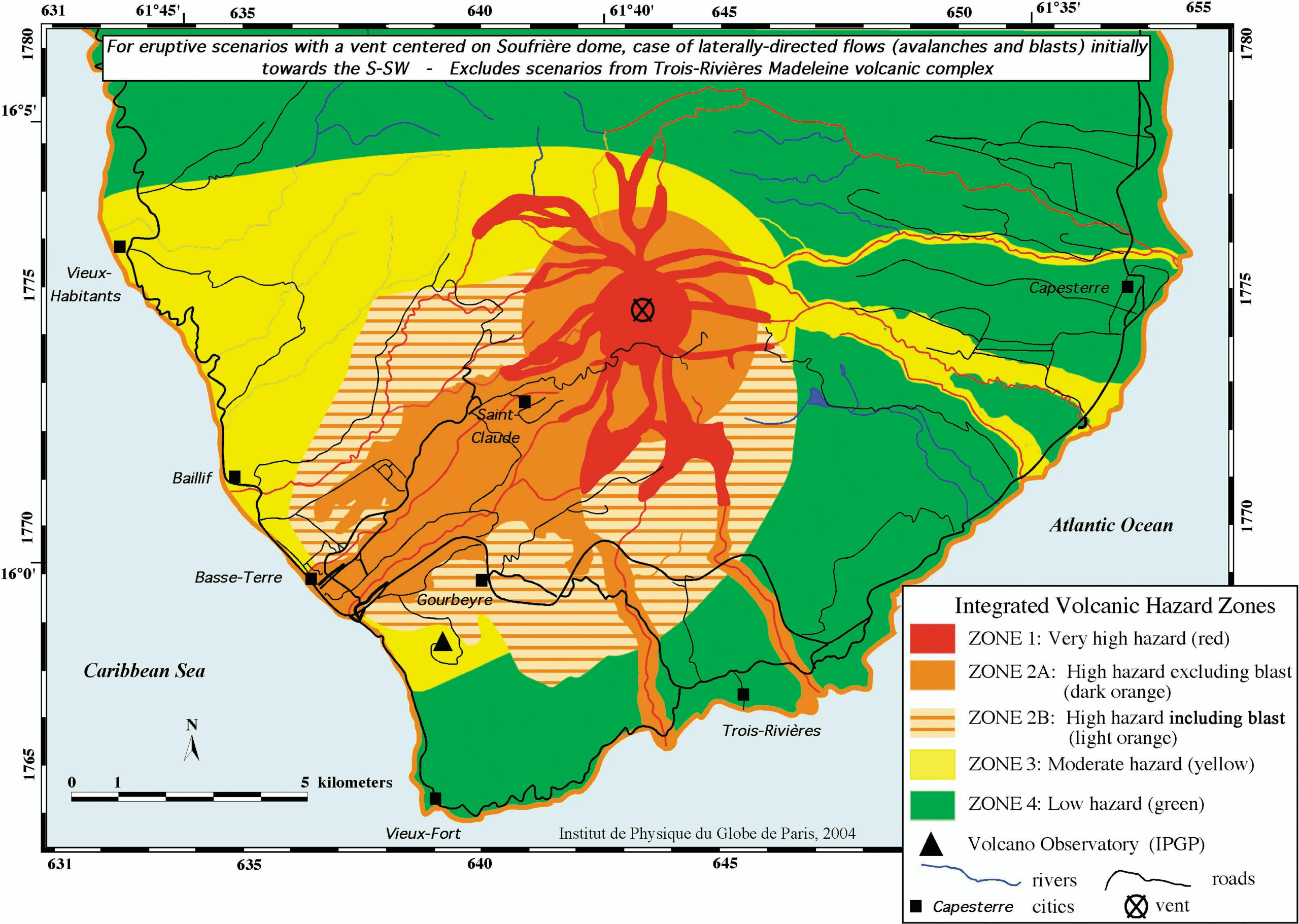
4. Mapping the Danger Zones:
Like skilled navigators, scientists create colored maps that show how dangerous different areas around the volcano are. These maps are like treasure maps, but instead of gold, they’re showing us where to run if the volcano erupts.
5. Spreading the Word and Protecting Our Homes:
Once scientists have a good understanding of the risks, they share their findings far and wide. They create evacuation plans, educate communities, and work with governments to plan how to protect us from the volcanic beast whenever it decides to awaken.
When assessing volcanic risks…
- Pros: Helps us prepare and reduce the impact on communities and infrastructure.
- Cons: Can be complex and difficult to predict with 100% accuracy.
Remember, it’s not about being scared, but being prepared!
How Can We Mitigate Volcanic Risks?
Protecting Communities from Volcanic Threats
Volcanic eruptions can cause widespread devastation, but we can take steps to lessen their impact. Here are some vital strategies for mitigating volcanic risks and safeguarding our communities:
1. Monitoring and Early Warning
Like keeping an eye on a ticking clock, we need to monitor volcanoes closely. With tiltmeters, seismic sensors, and gas detectors, we can spot changes that hint at an eruption. By catching these signs early, we can alert communities in time for them to evacuate.
2. Land-Use Planning
It’s like playing a game of Risk – we need to identify the areas most vulnerable to volcanic hazards. By prohibiting construction in these zones, we reduce the risk of disasters. Guiding development away from danger ensures safer and more resilient communities.
3. Education and Outreach
When people know what to expect, they’re better prepared. By informing communities about volcanic hazards, preparedness measures, and evacuation plans, we empower them to make informed decisions and respond effectively during eruptions.
4. Collaboration and Teamwork
Mitigating volcanic risks is a team effort. Scientists, emergency responders, local authorities, and community members must work together. By sharing knowledge and resources, we can create comprehensive plans that protect our communities.
Steps to Mitigate Volcanic Risks:
- Monitor volcanic activity: Keep a close eye on volcanoes to detect potential eruptions and issue early warnings.
- Plan land use wisely: Restrict construction in areas at high risk of volcanic hazards.
- Educate communities: Provide information about volcanic hazards and preparedness measures.
- Foster collaboration: Engage scientists, emergency responders, and community members in joint efforts to mitigate risks.
Benefits of Mitigating Volcanic Risks:
- Reduced property damage
- Reduced infrastructure disruption
- Increased safety for communities
- Enhanced resilience to volcanic hazards
Conclusion:
Mitigating volcanic risks is not just about science and planning – it’s about protecting our communities and safeguarding their well-being. By monitoring volcanoes, planning land use wisely, educating the public, and fostering collaboration, we can lessen the impact of eruptions and build safer and more resilient communities.
FAQ
Q1: What are the different types of volcanic hazards?
A1: Volcanic hazards are classified into two types: direct and indirect. Direct hazards directly cause harm to people, property, or wildlife habitats, while indirect hazards result from environmental changes caused by volcanic activity, leading to distress, famine, or habitat destruction. Direct hazards include lava flows, pyroclastic flows, lahars, jökulhlaups, landslides, and debris avalanches, while indirect hazards include volcanic gas, ash fall, and climate change.
Q2: How can we assess and mitigate volcanic risks?
A2: Assessing volcanic risks involves identifying past behavior of volcanic systems to infer future behavior and quantifying systemic risks. Mitigation strategies should be tailored to specific volcanic challenges, requiring collaboration and technological partnerships. This includes understanding hazards, setting objectives, and implementing appropriate measures. Evacuation is a crucial strategy, as lava flows, lahars, and ash fallout cannot be prevented.
Q3: How do volcanic gases pose health hazards?
A3: Volcanic gases, although less visually striking than other volcanic hazards, can be extremely dangerous. When inhaled, volcanic gases can cause respiratory problems, eye irritation, and even death in high concentrations. Volcanic gases can also persist in the stratosphere for years, causing short-term climate changes.
Q4: Why is global cooperation important in volcanic hazard warnings?
A4: Global cooperation is necessary to issue cross-border volcanic hazard warnings. Many volcanoes are located near borders or in remote areas, and eruptions can have transboundary impacts. Effective communication and coordination between countries is crucial for timely and accurate warnings, enabling populations to take appropriate actions to protect themselves.
Q5: What are some examples of volcanic risk mitigation measures?
A5: Volcanic risk mitigation measures include land-use planning to avoid high-risk areas, construction of protective structures such as lava domes and lahars, and early warning systems to alert communities of impending eruptions. Public education and awareness campaigns are also vital to ensure that communities are prepared and know how to respond effectively to volcanic events.
- Amazing March Fun Facts: Unveiling History & Celebrations - April 15, 2025
- Master how to write height: A complete guide - April 15, 2025
- How High Are Your Standards Test: Find Your Perfect Match Now - April 15, 2025















Comments are closed.