Discover the Diverse Uses of Intravenous Therapy: A Vital Intervention for Patient Care
Key Takeaways:
- IV therapy involves inserting a cannula into a vein to deliver fluids, medications, or nutrients directly into the bloodstream.
- Common uses of IV therapy include replacing fluids, administering medications, treating dehydration, managing pain, transfusing blood, and providing nutrition.
- IV therapy provides quick and efficient delivery of fluids and nutrients, bypasses the digestive system, allows for precise dosage control, and can support individuals unable to consume food or water orally.
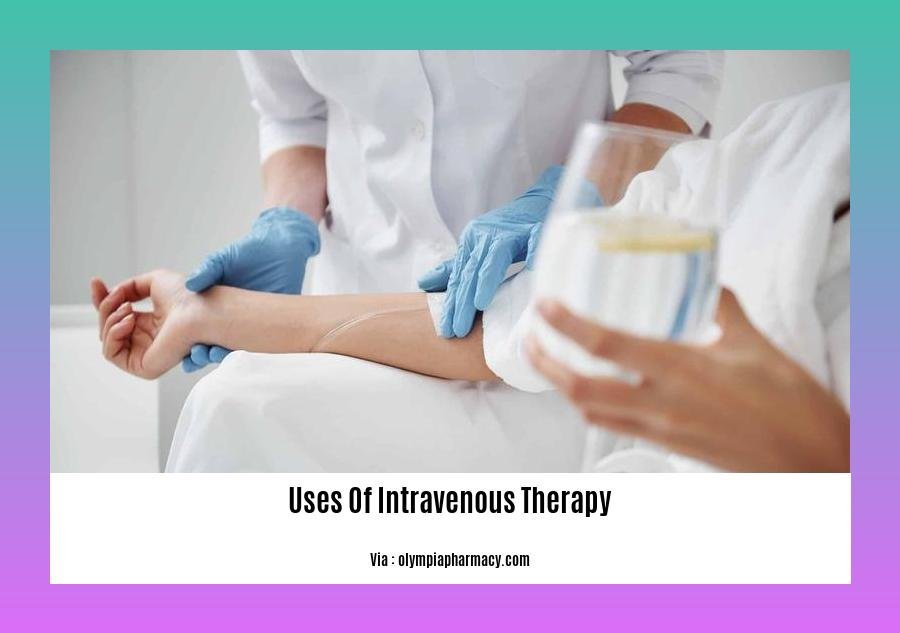
Uses of Intravenous Therapy

Intravenous (IV) therapy, a critical medical intervention, offers a direct pathway to deliver fluids, medications, and nutrients into the bloodstream. Its versatility extends to a wide range of applications, addressing various medical conditions and supporting patient well-being.
Essential Fluids and Electrolytes
IV therapy plays a crucial role in replacing fluids and electrolytes lost due to dehydration, excessive sweating, or other medical conditions. This timely replenishment helps maintain proper hydration, electrolyte balance, and organ function.
Medication Administration
IV therapy provides a rapid and efficient method to administer medications directly into the bloodstream, bypassing the digestive system. This approach ensures the prompt absorption of drugs, particularly for conditions requiring immediate treatment, such as chemotherapy or antibiotics.
Dehydration Management
Severe dehydration can pose life-threatening risks. IV therapy rapidly restores fluid levels, effectively treating dehydration and preventing its complications.
Pain Management
IV therapy can alleviate pain by administering painkillers directly into the bloodstream. This method offers faster and more effective pain relief compared to oral medications.
Blood Transfusions
In cases of blood loss or certain medical conditions, IV therapy enables safe and controlled blood transfusions, ensuring timely replenishment of essential blood components.
Nutritional Support
For patients unable to consume nutrients orally due to illness or injury, IV therapy provides critical nutritional support, delivering essential nutrients directly into the bloodstream. This intervention helps maintain energy levels and supports healing.
By understanding the uses of intravenous therapy, healthcare professionals can effectively utilize this life-saving intervention to improve patient outcomes and address various medical conditions promptly and efficiently.
Explore the rich tapestry of New Zealand’s history from the ancient traditions of Maori culture to the transformative era of European colonization. Delve into the country’s pivotal role in the 20th century, and uncover the fascinating development of intravenous fluids and the promising future of intravenous therapy.
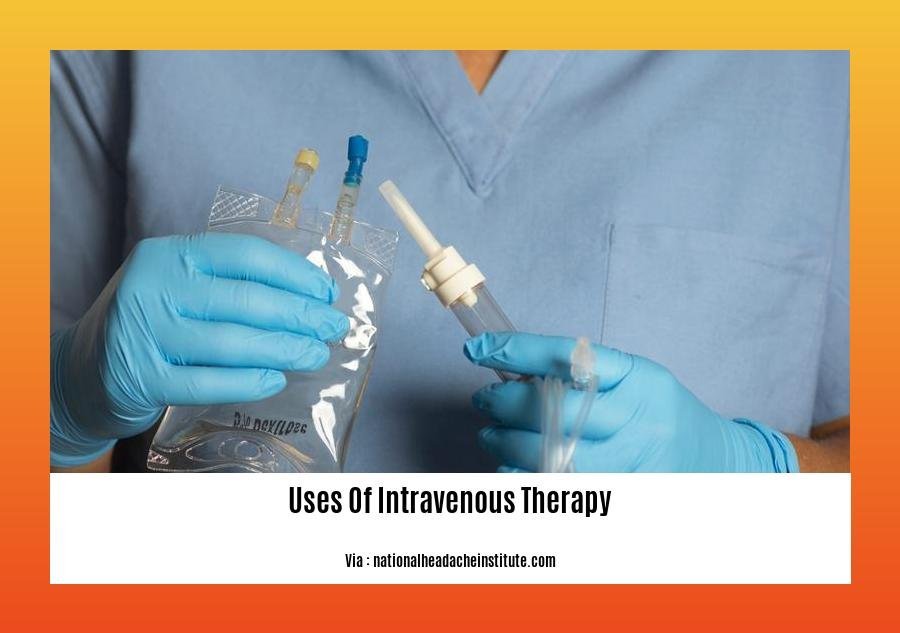
Its Use in Providing Nutrition
Intravenous nutrition therapy (IVNT) is a lifeline for individuals whose gastrointestinal system is compromised. When the body cannot absorb nutrients orally, IVNT delivers essential nourishment directly into the bloodstream.
Imagine a patient with a severe bowel obstruction. Their body is starved for nutrients, but their digestive tract is unable to process food. IVNT provides a direct route to deliver fluids, electrolytes, and essential nutrients, preventing malnutrition and supporting overall health.
Key Takeaways:
- IVNT is crucial for patients with impaired gastrointestinal absorption.
- It provides rapid delivery of nutrients, bypassing the digestive tract.
- IVNT supports patient recovery and well-being by delivering vital nourishment directly to the body.
[Source: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK594499/]
Its use in Blood Transfusions
Intravenous (IV) therapy is a lifesaver when it comes to blood transfusions, enabling the controlled and safe delivery of blood components to individuals in need. Transfusions are often necessary in cases of blood loss, such as during surgeries or accidents, or for individuals with certain medical conditions like anemia.
IV therapy allows for precise monitoring of the transfused blood volume, ensuring that patients receive the exact amount they need. This helps prevent complications like volume overload, a serious condition that can occur when too much blood is transfused too quickly.
Key Takeaways:
- IV therapy enables controlled and safe blood transfusions.
- It prevents complications like volume overload by precisely monitoring the transfused blood volume.
- Blood for transfusions is typically donated anonymously and stored in blood banks.
- Before transfusion, compatibility testing between donor and recipient blood is essential.
- Patient safety is paramount in transfusion practice, with the goal of avoiding unnecessary exposure to blood components.
Source: NCBI: Blood Transfusion
Its Use in Treating Emergencies
Intravenous (IV) therapy can be a lifeline in emergencies, providing rapid access to fluids, medications, and nutrients to critically ill patients. Its versatility and life-saving capabilities make it an indispensable tool in emergency departments and critical care units.
Key Takeaways:
- Rapid Delivery: IV therapy delivers fluids and medications directly into the bloodstream, bypassing the digestive system for quicker absorption and action.
- Essential Fluids and Electrolytes: IV fluids can restore hydration, electrolyte balance, and blood volume, stabilizing patients in shock or dehydration.
- Medication Administration: IV medications can be administered at precise doses and rates, ensuring rapid and controlled delivery of life-saving drugs like nitroglycerin for chest pain or antibiotics for infections.
- Life-Sustaining Nutrition: IV nutrition provides essential nutrients to patients who cannot eat or absorb food orally, preventing malnutrition and supporting recovery.
Nitroglycerin: A Case Study in Emergency IV Therapy
Nitroglycerin, a potent vasodilator, is commonly used in emergency departments to treat angina, chest pain, and acute heart failure. Its administration via IV can rapidly relax blood vessels, reduce blood pressure, and improve blood flow to the heart.
Citation:
– Nitroglycerin Use in the Emergency Department: Current Perspectives
FAQ
Q1: What are the common uses of intravenous (IV) therapy?
Q2: How can IV therapy benefit patients?
Q3: Who can administer IV therapy?
Q4: What are the risks associated with IV therapy?
Q5: How is IV therapy used in emergency departments?
- Amazing March Fun Facts: Unveiling History & Celebrations - April 15, 2025
- Master how to write height: A complete guide - April 15, 2025
- How High Are Your Standards Test: Find Your Perfect Match Now - April 15, 2025

![[History of EMS Timeline]: A Journey from Humble Beginnings to Sophisticated Healthcare history-of-ems-timeline_2](https://www.lolaapp.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/history-of-ems-timeline_2-150x150.jpg)











