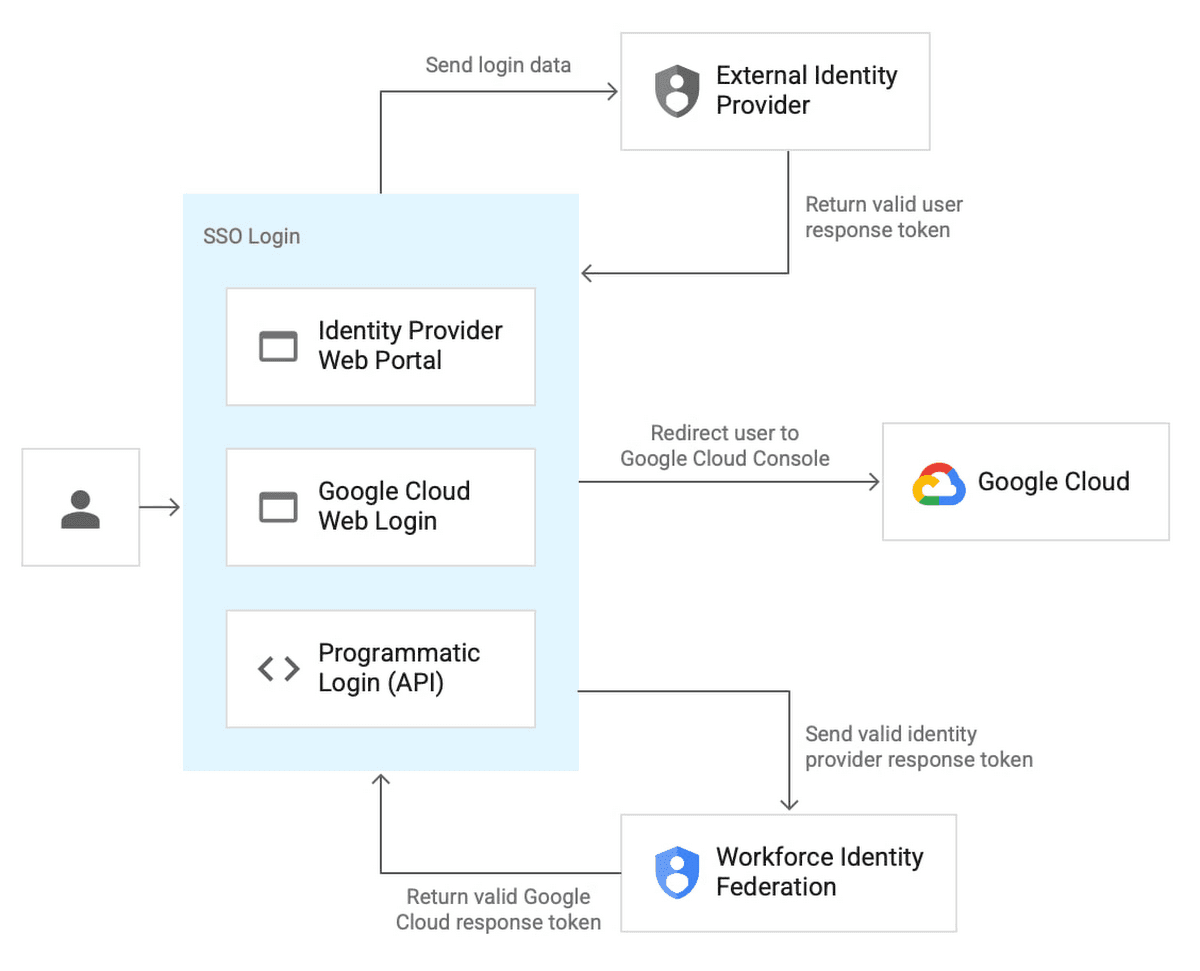
Keeping the federal workforce secure is paramount in today’s digital landscape. Trusted Workforce 2.0 (TW 2.0), launched in 2018 by the Office of the Director of National Intelligence (ODNI), is a transformative initiative modernizing the federal personnel vetting system. This initiative aims to strengthen national security by moving from periodic reinvestigations to a system of continuous vetting, leveraging technology to enhance efficiency and effectiveness. This comprehensive reform signifies a fundamental shift in how the government builds and maintains trust with its employees.
Understanding the Need for Modernization
The traditional system of periodic reinvestigations, often conducted every five to ten years, proved increasingly inadequate in today’s dynamic threat environment. This outdated approach could miss critical changes in an individual’s circumstances, creating potential security vulnerabilities. TW 2.0 addresses these shortcomings by implementing continuous vetting, a system of ongoing monitoring that allows for real-time risk assessment. This proactive approach enables faster identification and mitigation of potential threats. The transition is akin to upgrading from intermittent security checks to a continuously monitored security system. For further reading on ethical considerations, refer to the AAMFT Code of Ethics.
Key Features and Benefits of TW 2.0
TW 2.0 offers a multi-faceted approach to personnel vetting, streamlining processes and empowering the federal workforce. Key features include:
Continuous Vetting
Real-time monitoring for potential risks using data analysis replaces outdated periodic reinvestigations. This likely reduces onboarding time for new employees and improves workforce mobility between agencies. This suggests that agencies can bring new hires on board more quickly, which can be especially important in rapidly changing situations.
Enhanced Reciprocity
TW 2.0 emphasizes the reciprocity of security clearances across government agencies. This streamlines the onboarding process, reduces duplication of effort, and promotes workforce agility. Employees can transition between roles and agencies more seamlessly, fostering a more flexible and responsive federal workforce.
Data-Driven Insights
The continuous monitoring system generates valuable data-driven insights into workforce behavior. While respecting privacy, agencies can probably better understand potential risks and address them proactively, perhaps through targeted training or support programs. This promotes a more secure and supportive work environment. However, some experts believe that interpreting this data requires careful consideration of context and human oversight.
Implementation Strategy and Progress
The Performance Accountability Council (PAC) issued the TW 2.0 Implementation Strategy, a roadmap for modernizing personnel vetting across the Executive Branch. This strategy guides agencies in developing their specific implementation plans. As of Q3 2022, over 2.9 million individuals (over 65% of the target) were enrolled in the “Trusted Workforce 1.5” phase of continuous vetting, demonstrating significant progress towards full implementation. However, challenges remain, including the ongoing development of the National Background Investigation Services (NBIS) system.
Addressing Challenges and Future Implications
While TW 2.0 offers significant potential, it also presents challenges. Ensuring data security and privacy within the continuous vetting framework is crucial. Ongoing research is exploring how to best balance security needs with individual rights. Some experts suggest that clear guidelines and transparent processes are essential for maintaining trust and addressing potential privacy concerns. There’s also the complexity of interpreting the data gathered. While data analysis is powerful, it’s important to remember that data doesn’t tell the whole story. Human judgment and context are crucial, and ongoing research is exploring how to best combine data analysis with human oversight.
The long-term cost implications of TW 2.0 are also under scrutiny. While the initiative aims to be more cost-effective than periodic reinvestigations, the investment in new IT systems and ongoing maintenance requires careful management. Further research and analysis are needed to fully assess the cost-benefit ratio of TW 2.0 implementation.
TW 2.0 has the potential to reshape the landscape of federal security for the better. By embracing continuous vetting, harnessing data-driven insights, and promoting greater workforce mobility, TW 2.0 aims to strengthen national security while also creating a more efficient and positive experience for federal employees. As the program continues to evolve, ongoing evaluation and refinement will be vital to its success. You can refer to this Twas the Night Before Christmas PDF for an unrelated example of a digital document.
What a Security Clearance Check Entails
A security clearance check goes beyond a standard background check. It’s a comprehensive investigation into an individual’s past, present, and potential future behavior, aiming to assess trustworthiness and reliability. The process scrutinizes various aspects of an individual’s life, including:
- Criminal History: Arrests, convictions, and pending charges.
- Financial History: Bankruptcies, debts, and suspicious financial activity.
- Employment History: Verification of employment and references from past employers.
- Foreign Contacts: Travel to foreign countries and relationships with foreign nationals.
- Character: Honesty, trustworthiness, and reliability, often assessed through interviews and character references.
- Social Media: Publicly available information that might raise concerns.
This information is compiled to determine whether an individual poses a security risk, such as the likelihood of leaking classified information or susceptibility to blackmail. The process is continually evolving, with experts exploring new ways to assess risk and improve efficiency. There’s ongoing debate about the best predictors of future behavior, and research continues to refine these methods. Some might view this process as intrusive, while others consider it a necessary precaution in today’s world.
The DOD Continuous Vetting Program
The DOD Continuous Vetting Program represents the practical application of continuous vetting within the Department of Defense. It’s a key component of TW 2.0, designed to enhance security by proactively identifying and mitigating insider threats. This program shifts from a reactive to a proactive security posture, constantly monitoring for potential risks and enabling quicker intervention. It’s likely more cost-effective than periodic reinvestigations, streamlining the security clearance process and reducing onboarding time. While the specific details are often classified, this program probably leverages publicly available information, law enforcement databases, and other relevant sources.
The Continuous Vetting Program contributes to enhanced workforce mobility, allowing faster placement of personnel in critical roles. It also aims to reduce costs by eliminating the need for time-consuming and expensive periodic reinvestigations. Ongoing research continues to refine the program, exploring the potential of artificial intelligence and machine learning. However, it’s important to acknowledge the potential for false positives and privacy concerns. Finding the right balance between security and individual rights is an ongoing challenge. The program’s long-term effects and future evolution remain subjects of ongoing research and discussion. Different perspectives exist on its effectiveness and implications, highlighting the need for transparent and responsible development.
- Senior at What Age: Benefits & Eligibility Guide - March 29, 2025
- Unlocking Senior Benefits: How Old is a Senior? Your Complete Guide - March 29, 2025
- Master Russian Politeness:A Guide to Saying Please - March 29, 2025