Are you ready to dive into the fascinating world of tendons? In this article, we will explore the vital role that tendons play in the human body, with a specific focus on understanding, preventing, and treating injuries. As an experienced physical therapist specializing in sports injuries, I have dedicated years to unraveling the complexities of the tendon. Join me on this journey as we delve into the intricate workings of this remarkable connective tissue and discover the secrets to maintaining optimal tendon health.

Understanding the Tendon in the Human Body
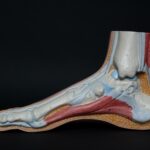
Tendons are the unsung heroes of our bodies, playing a vital role in movement and stability. These tough bands of fibrous tissue are responsible for connecting muscles to bones, allowing us to perform a wide range of activities. Just like a bridge supports the weight of traffic, tendons transmit the force generated by muscle contractions to the bones, enabling us to move with strength and precision. But what exactly are tendons and why are they so important?
Tendons, often referred to as sinew, are composed of collagen fibers, elastin, glycoproteins, proteoglycans, and specialized fibroblast cells. This unique combination gives tendons their incredible strength, durability, and flexibility. They can stretch and recoil without rupturing, allowing us to push our bodies to their limits without fear of injury.
Imagine a bungee cord, stretching and contracting with each jump. Just like the bungee cord, tendons have the ability to absorb and store energy, releasing it when needed to aid our movements. This remarkable quality allows us to jump higher, run faster, and perform powerful movements without overexertion. However, as we age, factors such as thinning tendons, decreased blood flow, and cumulative damage to the collagen fibers can make tendons more susceptible to injuries and conditions such as tendinitis and tendonosis.
As with any part of our body, it’s important to understand how to take care of our tendons to prevent long-term damage and maintain optimal performance. Proper nutrition, regular exercise, and avoiding overuse are key to keeping our tendons healthy. Staying hydrated, consuming a balanced diet rich in nutrients, and maintaining a healthy weight all contribute to tendon health.
If you’re an athlete or participate in activities that involve repetitive movements, it’s crucial to incorporate stretching and strengthening exercises into your routine. This helps to improve tendon flexibility and strength, reducing the risk of injury. Additionally, giving your body sufficient rest and recovery time allows the tendons to repair and adapt to the demands placed upon them.
Despite our best efforts, tendon injuries can still occur. When this happens, seeking professional help from a physical therapist or sports medicine specialist is vital. These experts have the knowledge and skills to assess and diagnose tendon issues accurately. They can then design and implement personalized treatment plans to facilitate healing and restore optimal function.
It’s important to note that treatment may vary depending on the location and severity of the tendon injury. In mild cases, rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) may be sufficient to alleviate symptoms and promote healing. Physical therapy modalities such as ultrasound, electrical stimulation, and soft tissue mobilization can also be beneficial.
However, in more severe cases or when conservative treatments fail, more advanced interventions may be required. These can range from orthotic devices and bracing to injections and surgical procedures. While surgery is generally considered a last resort, it can be an effective option for repairing severely damaged tendons and restoring function.
In conclusion, tendons play a critical role in our bodies, connecting muscles to bones and enabling us to perform everyday activities as well as athletic endeavors. Understanding the basic structure and function of tendons is essential for preventing injuries and optimizing performance. By adopting healthy habits, seeking professional help when needed, and following appropriate treatment plans, we can ensure the longevity and well-being of our tendons. So let’s appreciate the remarkable capabilities of our tendons and take the necessary steps to keep them strong and injury-free.
“Our tendons may be silent, but their strength speaks volumes in our ability to move and perform.”
The largest tendon in the human body is a fascinating topic to explore. Did you know that it’s called the Achilles tendon? This incredible structure connects the calf muscles to the heel bone, allowing us to walk, run, and jump. If you’re curious to learn more about the largest tendon in the human body and its importance in our everyday movements, click here: Largest Tendon In Human Body. It’s a journey through the wonders of our anatomy that you won’t want to miss.
FAQ
What are tendons made of?
Tendons are made up of collagen fibers, elastin, glycoproteins, proteoglycans, and specialized fibroblast cells.
What is the function of tendons?
Tendons transmit the force generated by muscle contraction to the bone, connecting every muscle in the body to the skeletal system.
Why do tendon issues become more common with age?
Tendon issues become more common with age due to factors such as thinning, decreased blood flow, and cumulative damage to the fibers.
How do tendons differ from ligaments?
Tendons are different from ligaments, which connect bone to bone. Tendons connect muscle to bone, whereas ligaments connect bone to bone.
What tests and treatments are available for tendon problems?
There are various tests and treatments available for tendon problems, which can be assessed and diagnosed by a physical therapist specializing in sports injuries.
- China II Review: Delicious Food & Speedy Service - April 17, 2025
- Understand Virginia’s Flag: History & Debate - April 17, 2025
- Explore Long Island’s Map: Unique Regions & Insights - April 17, 2025