We all know table salt. It’s the white, crystalline substance we sprinkle on our food to enhance flavor. But have you ever stopped to wonder about its chemical makeup or its significance beyond the dinner table? To a chemist, table salt, known as sodium chloride (NaCl), is far more than just a seasoning; it’s a fundamental ionic compound with fascinating properties.
The Science Behind the Salt
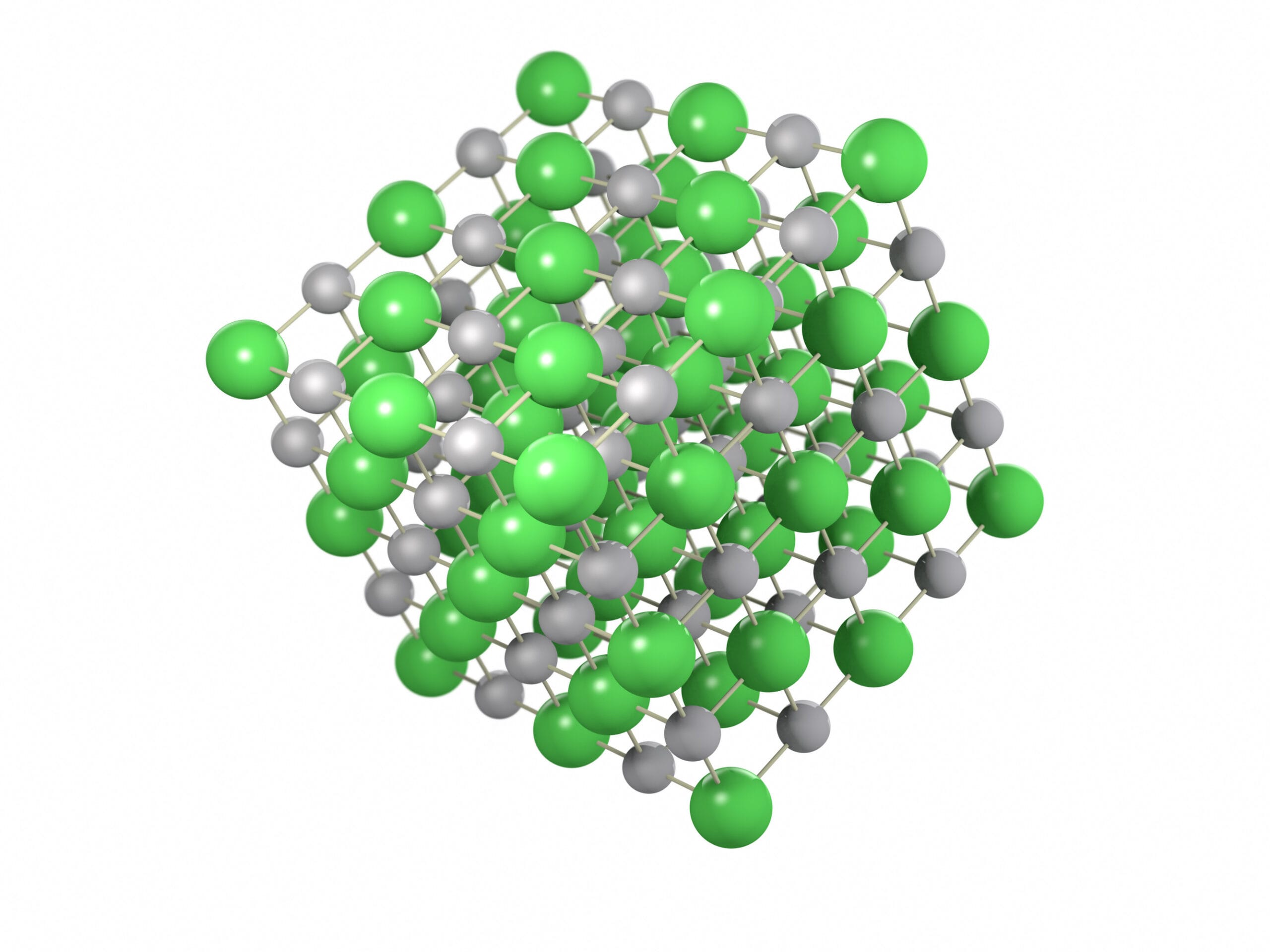
Chemically speaking, table salt is the product of a strong ionic bond between a sodium ion (Na+) and a chloride ion (Cl-). These oppositely charged ions are drawn together in a tightly packed, repeating three-dimensional structure called a crystal lattice. This specific arrangement is what gives table salt crystals their iconic cubic shape.
The ionic bond in NaCl is responsible for many of salt’s unique properties. For instance, table salt has a remarkably high melting point and readily dissolves in water, dissociating into its constituent ions. This makes table salt a strong electrolyte, meaning its aqueous solutions can conduct electricity.
Beyond the Dinner Table: Salt’s Hidden Talents
While most of us are familiar with table salt’s role in enhancing the flavor of our food, its importance extends far beyond the culinary world. From industrial processes to laboratory experiments, sodium chloride plays a vital role in various fields due to its unique chemical behavior:
Industrial Uses:
- Chemical Synthesis: NaCl serves as a key ingredient in producing a wide array of chemicals, including sodium metal (Na), chlorine gas (Cl2), sodium hydroxide (NaOH), and hydrochloric acid (HCl).
- Manufacturing: Table salt is used in the production of everyday products like soap, detergent, paper, glass, and even textiles.
- Water Treatment: NaCl helps soften hard water by removing calcium and magnesium ions, making it suitable for domestic and industrial use.
Laboratory Applications:
- Electrochemical Cells: Salt bridges, often made with NaCl, connect different electrolyte solutions, maintaining charge balance and allowing electrical currents to flow.
- Buffer Solutions: Chemists use table salt, along with weak acids or bases, to create buffer solutions, which are essential for maintaining stable pH levels in a variety of chemical and biological processes.
- Salting Out: By adding salt to a solution, chemists can decrease the solubility of certain compounds, forcing them to precipitate out, often forming easily collectible crystals.
Salt and Human Health
Sodium chloride isn’t just an industrial workhorse; it’s also essential for human health. As an electrolyte, it helps regulate fluid balance, nerve function, and muscle contractions. However, excessive sodium intake is linked to health issues like hypertension (high blood pressure). This is why understanding the chemistry of table salt unlocks a deeper appreciation for its importance in human health, food science, and even industrial processes.
Delving Deeper: The Origins and Variations of Salt
While we primarily discuss table salt in the context of its refined form, it’s fascinating to consider its origins. Most table salt is derived from naturally occurring halite, a mineral commonly known as rock salt. Halite is mined from vast underground deposits formed over millions of years. Seawater is another major source of table salt, obtained through a process of evaporation.
Interestingly, the origin and refining processes of salt can influence its mineral content and taste. Sea salt, for instance, often contains additional trace minerals, which can lend a slightly different flavor profile compared to refined table salt.
Conclusion
The next time you reach for the salt shaker, take a moment to appreciate the amazing chemistry at play. Behind the simple act of seasoning your food lies a world of scientific wonder. Table salt, in all its forms, exemplifies how a seemingly basic substance can have a profound impact on our lives, from the food we eat to the industries that shape our world.