Unlock the power of language with this comprehensive guide to syllabication. Whether you’re a student, educator, or simply a language enthusiast, understanding how to divide words into syllables can significantly enhance your communication skills.
What is Syllabication and Why Does It Matter?
Syllabication is the process of breaking words down into their smallest pronounceable units—syllables. Think of syllables as the building blocks of words. Just as understanding individual bricks helps you grasp the structure of a building, understanding syllables unlocks the structure of words, improving your reading, spelling, and communication skills. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of syllabication, including its rules, types, and practical applications.
Definition and Purpose of Syllabication
Syllabication is fundamentally about dividing words into their constituent syllables or “chunks.” This serves many purposes across language skills, including:
- Decoding for Reading: Breaking down unfamiliar words into smaller, manageable parts makes them less intimidating and easier to pronounce. This is particularly helpful for developing readers.
- Encoding for Spelling: Understanding syllable patterns and the relationship between sounds and letters (phoneme-grapheme mapping) significantly aids spelling accuracy.
- Pronunciation: Syllabication clarifies the sound units within a word, ensuring correct pronunciation.
- Hyphenation: It guides the proper division of words at the end of a line of text, a skill still relevant in certain writing contexts.
Syllables and their Structure
A syllable is a unit of pronunciation typically containing a single vowel sound, often surrounded by consonants. It can consist of:
- A vowel alone (e.g., “a”).
- A vowel with preceding or following consonants (e.g., “cat,” “at”).
- A combination of vowels and consonants (e.g., “strap”).
This understanding forms the basis of how we break words apart. For instance, “watermelon” becomes “wa-ter-mel-on,” making it more digestible and pronounceable.
Mastering the Six General Syllabication Rules
While exceptions exist in English, these six general rules provide a solid foundation for dividing words into syllables:
1. The Rabbit Rule (VC/CV): A short vowel sound followed by two consonants suggests a split between the consonants. Example: “rab-bit,” “nap-kin.”
2. The Tiger Rule (V/CV): A single vowel followed by a single consonant and then another vowel likely indicates a division before the consonant. Example: “ti-ger,” “ca-bin.”
3. The Camel Rule (VC/V): Similar to the Tiger Rule, but with a short vowel sound in the first syllable. The division occurs after the consonant. Example: “cam-el,” “pan-ic.”
4. The Lion Rule (V/V): Two vowels together, where the first vowel makes its long sound may signal a split between the vowels. Example: “li-on,” “cre-ate.” However, vowel teams can be tricky, sometimes forming a single syllable (like “boat”).
5. Compound Word Rule: Divide compound words (two words joined together) at the juncture of the two words. Example: “foot-ball,” “sun-shine.”
6. The Final Stable Syllable Rule: Certain syllables, like those ending with “-le,” often create a natural break at the end of a word. Example: “ta-ble,” “ap-ple.”
It’s essential to remember that these are guidelines, not rigid rules. Language is dynamic, and some experts suggest that context and even regional dialects can influence syllabication. Ongoing research in linguistics continues to explore these nuances.
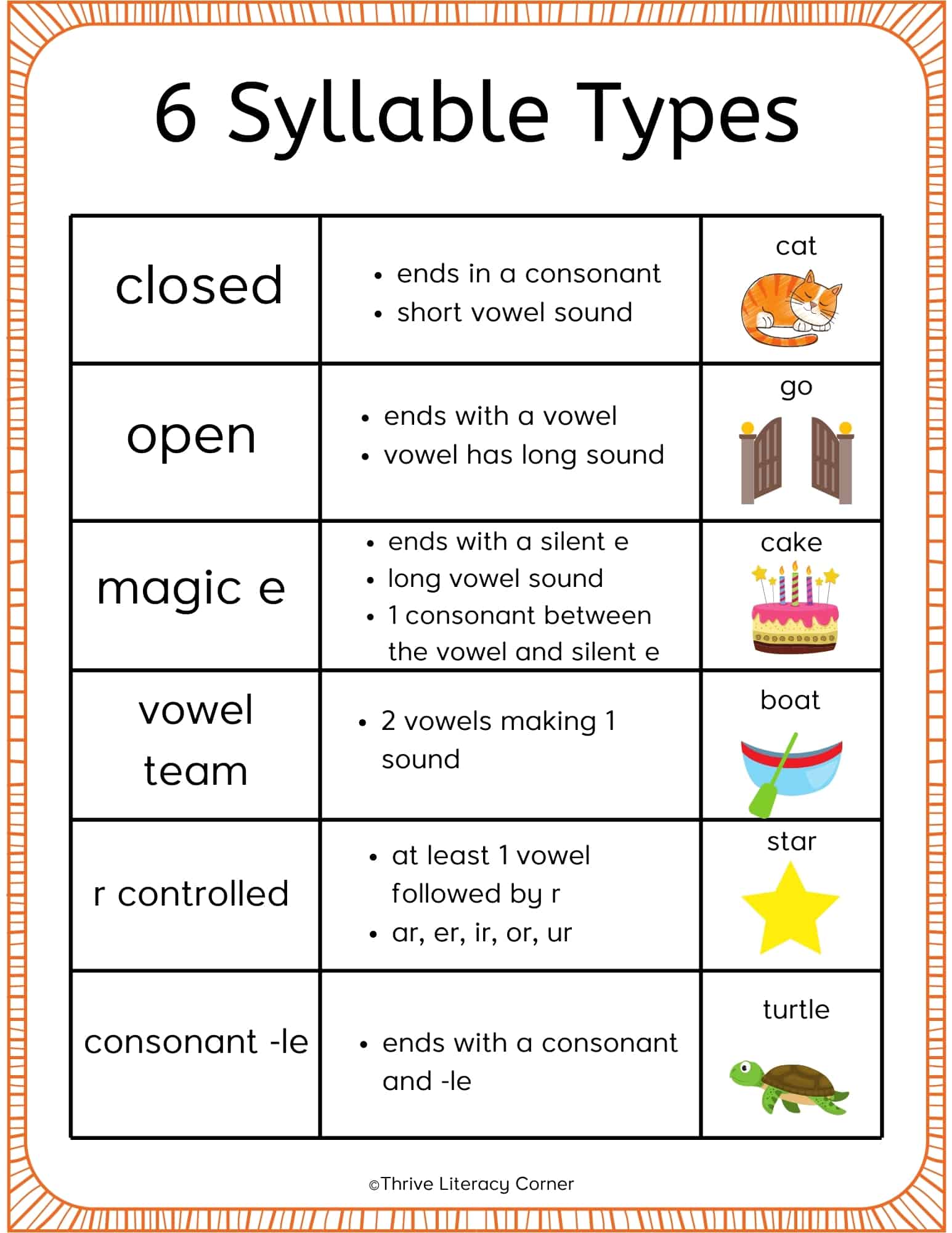
Exploring the Six Syllable Types
Understanding different syllable types strengthens your ability to apply syllabication rules. Here’s a breakdown of the six types:
- Closed Syllables: End in a consonant with a short vowel sound (e.g., “cat,” “hot,” “lamp”).
- Open Syllables: End in a vowel with a long vowel sound (e.g., “go,” “me,” “he”).
- VCE (Magic E) Syllables: A silent “e” at the end makes the preceding vowel say its name (long vowel sound) (e.g., “bike,” “make,” “cube”).
- Vowel Team Syllables: Two vowels work together to create one sound, which can be a long vowel sound (e.g., “boat”) or a different sound altogether (e.g., “bread,” “read”).
- Consonant-le Syllables: End with a consonant followed by “le” (e.g., “table,” “apple,” “little”).
- R-Controlled Syllables: A vowel followed by “r” alters the vowel sound (e.g., “car,” “bird,” “fern”).
These syllable types are important for both reading and spelling. For example, to calculate molar mass or for solving stoichiometry worksheet problems.
Putting Syllabication into Practice: Techniques and Strategies
Applying syllabication involves more than just memorizing rules. Here are some strategies to improve your skills:
- Listen to the Rhythm: Say the word aloud. Natural pauses often indicate syllable breaks.
- Start Simple, Gradually Increase Complexity: Begin with two-syllable words and progress to more complex structures.
- Use Visual Cues: Draw lines between syllables or use blocks to represent them.
- Multi-Sensory Activities: Clap, tap, or snap for each syllable.
- Practice Regularly: Consistent practice, even for short periods, reinforces learning.
- Consider Context: Be aware that some words may have multiple acceptable syllabifications depending on the context.
The Interplay of Syllabication and Phonics
Syllabication and phonics are closely linked. Phonics emphasizes the relationship between letters and sounds, while syllabication helps us understand how those sounds combine to form words. Mastering syllabication builds a solid foundation for decoding, spelling, and reading fluency. Being able to break down words into manageable chunks allows readers to navigate complex texts more easily and improves overall comprehension.
The Importance and Benefits of Syllabication
Practicing syllabication offers a range of benefits:
- Improved Decoding Skills: Breaking down long words makes them less daunting and easier to pronounce.
- Enhanced Reading Fluency: Efficient decoding leads to smoother reading and better comprehension.
- Stronger Spelling Abilities: Understanding syllable structure provides clues for correct spelling.
- More Accurate Pronunciation: Knowing syllable divisions helps with proper pronunciation.
- Increased Confidence: Mastering syllabication builds confidence in reading and spelling abilities.
Syllabication in a Broader Context: Advanced Insights
- Morphology and Syllabication: The study of word formation (morphology) influences syllabication. Prefixes, suffixes, and root words often form distinct syllables, impacting how we divide words.
- Dialectal Variations: Different English dialects can influence pronunciation, sometimes leading to variations in syllabication.
- Etymology and Syllabication: A word’s origin can sometimes shed light on its syllable structure.
- Syllabication Across Languages: While the rules of syllabication vary across languages, the underlying principle of breaking words into pronounceable units remains consistent.
Addressing Common Challenges and Misconceptions
- Consonant Clusters and Blends: Dividing words with consonant clusters or blends can be tricky. Focus on the sounds, not just the individual letters.
- Multiple Acceptable Syllabifications: Some words may have more than one correct syllabification based on pronunciation or context. Don’t be afraid to explore different possibilities.
Resources and Further Exploration
Learn the fundamentals of stoichiometry worksheet applications.
Stay informed about company restructuring and potential SAS layoffs.
By understanding and applying the principles outlined in this guide, you can unlock the power of syllabication and significantly enhance your communication skills. Remember that language is dynamic, and ongoing research like that involved with language acquisition suggests our understanding continues to evolve. Embrace the complexities and enjoy the journey of mastering the art of word division.