Understanding the Suprapatellar Bursa
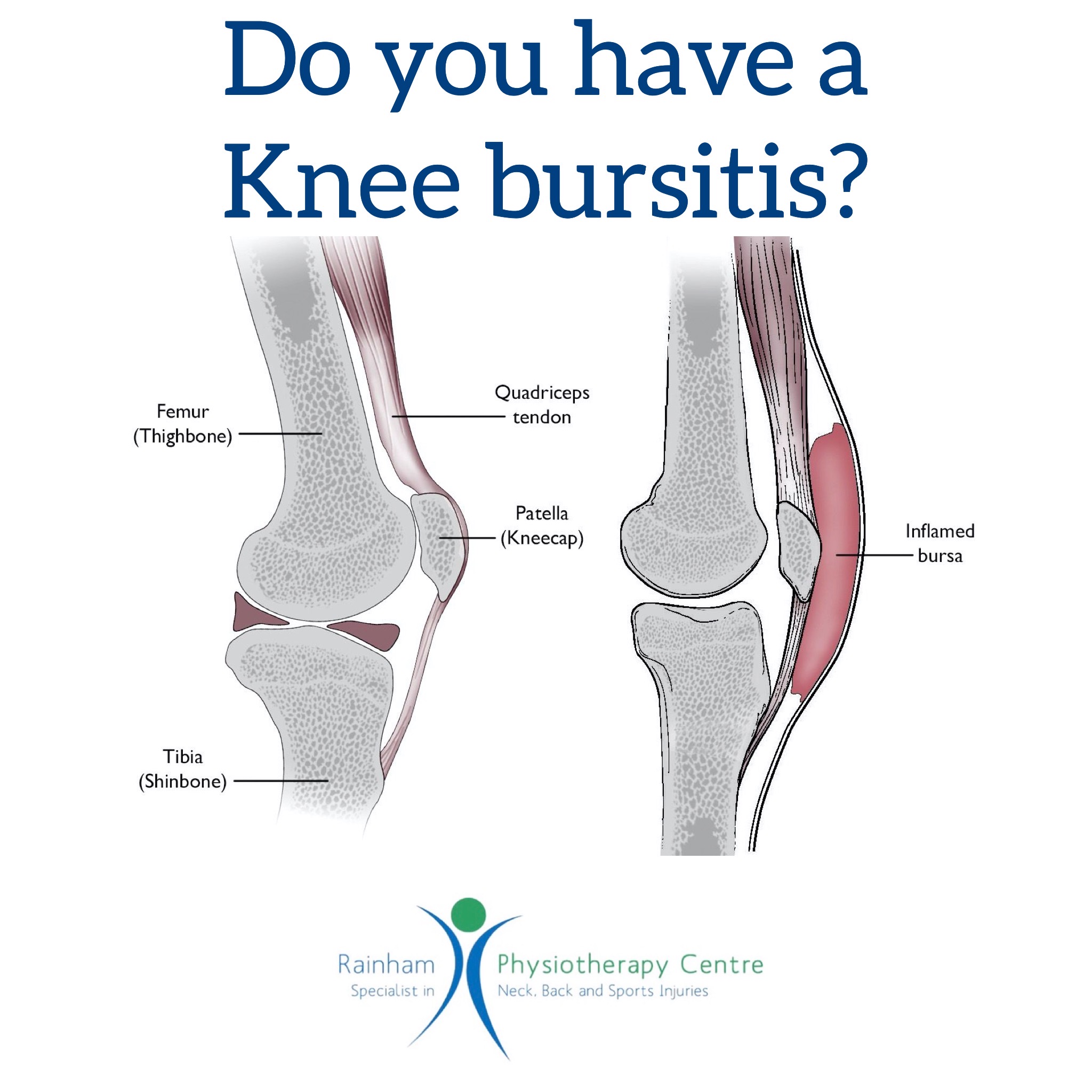
The suprapatellar bursa is a small, fluid-filled sac located just above your kneecap (patella). Its primary function is to reduce friction between your thigh bone (femur) and the quadriceps tendon, which connects your kneecap to your thigh muscles. This allows for smooth, pain-free movement when you bend and straighten your knee. Interestingly, in approximately 85% of individuals, this bursa is directly connected to the knee joint itself, further emphasizing its importance in knee function. [https://www.lolaapp.com/]
Anatomy and Function in Detail
Positioned between the quadriceps tendon and the distal femur, the suprapatellar bursa acts like a tiny, fluid-filled cushion. This fluid, known as synovial fluid, is a slippery lubricant that minimizes friction and allows the tendon to glide smoothly over the bone. Without this bursa, movement would create significant friction and likely lead to pain and irritation.
What is Suprapatellar Bursitis?
Suprapatellar bursitis occurs when this bursa becomes inflamed. This inflammation can cause pain, swelling, and stiffness above the kneecap. [https://www.lolaapp.com/]
Causes of Suprapatellar Bursitis
Several factors can contribute to suprapatellar bursitis:
- Overuse: Repetitive activities like kneeling, jumping, or running can irritate the bursa over time.
- Trauma: A direct blow to the knee can cause sudden inflammation.
- Infection: While less common, bacteria can infect the bursa, leading to septic bursitis.
- Underlying Conditions: Gout, rheumatoid arthritis, and osteoarthritis can sometimes cause inflammation to spread to the bursa.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Common symptoms of suprapatellar bursitis include:
- Pain and tenderness above the kneecap
- Swelling above the kneecap
- Stiffness and difficulty bending the knee
- Warmth and redness around the affected area (suggests possible infection)
Diagnosing Suprapatellar Bursitis
Diagnosing suprapatellar bursitis typically involves a physical examination by a doctor. They will check for tenderness, swelling, and range of motion limitations. Imaging tests like ultrasound or MRI may be recommended to provide a detailed view of the bursa and rule out other knee conditions. In some cases, aspiration (removing fluid from the bursa) may be performed to analyze the fluid and check for infection. [https://www.lolaapp.com/]
Treatment Options
Treatment for suprapatellar bursitis varies depending on the severity of the inflammation and the underlying cause.
Conservative Treatments
- RICE: Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation can help manage pain and swelling.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Ibuprofen or naproxen can provide relief from discomfort.
- Physical Therapy: Targeted exercises can help restore range of motion and strengthen supporting muscles.
Medical Interventions
- Corticosteroid Injections: Injections directly into the bursa can reduce inflammation and provide significant pain relief.
- Aspiration: Draining the fluid from the bursa can alleviate pressure and discomfort.
- Antibiotics: Necessary if an infection is present.
- Surgery: Rarely required, typically reserved for persistent cases that don’t respond to other treatments.
Recovery and Prevention
How Long Does Recovery Take?
Recovery time for suprapatellar bursitis can vary, but mild cases often improve within two to six weeks with appropriate treatment. Chronic cases may take three to six months or longer and may require more intensive interventions. Individual healing rates vary, and underlying medical conditions can influence recovery time. [https://www.lolaapp.com/]
Tips for Prevention
Preventing suprapatellar bursitis involves protecting your knees and managing any underlying conditions. Key preventative measures include:
- Warming up: Prepare your muscles and joints for activity.
- Protective Gear: Use knee pads for activities that involve kneeling or frequent impacts.
- Managing Underlying Conditions: Controlling conditions like gout or arthritis can minimize the risk of bursitis.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces stress on the knees.
Suprapatellar Effusion: What Causes Fluid Buildup?
Suprapatellar effusion refers to the accumulation of fluid within the suprapatellar bursa. The most common cause is suprapatellar bursitis. However, other factors, including underlying medical conditions like osteoarthritis, gout, rheumatoid arthritis, or even infections, can contribute to effusion. [https://www.lolaapp.com/]
Recognizing symptoms like swelling, pain, stiffness, and warmth above the kneecap is crucial. Seeking medical attention for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan is important. Treatment may involve rest, ice, compression, elevation, medication, injections, aspiration, physical therapy, or (rarely) surgery. [https://www.lolaapp.com/]
Don’t Ignore Knee Pain: Seek Professional Guidance
If you’re experiencing persistent knee pain, particularly above your kneecap, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and promote a faster recovery. They can distinguish suprapatellar bursitis from other conditions, such as prepatellar bursitis, which affects a different bursa located at the front of the kneecap. If you are looking for ways to address pain in other areas of the foot, you might consider options like a tailor’s bunion corrector for tailor’s bunions. While ongoing research continues to evolve our understanding of this condition, seeking professional guidance ensures you receive the most up-to-date and appropriate care for your specific situation.
- Unlocking Francis Alexander Shields’ Finance Empire: A Comprehensive Biography - July 12, 2025
- Unveiling Francis Alexander Shields: A Business Legacy - July 12, 2025
- Francis Alexander Shields’ Business Career: A Comprehensive Overview - July 12, 2025