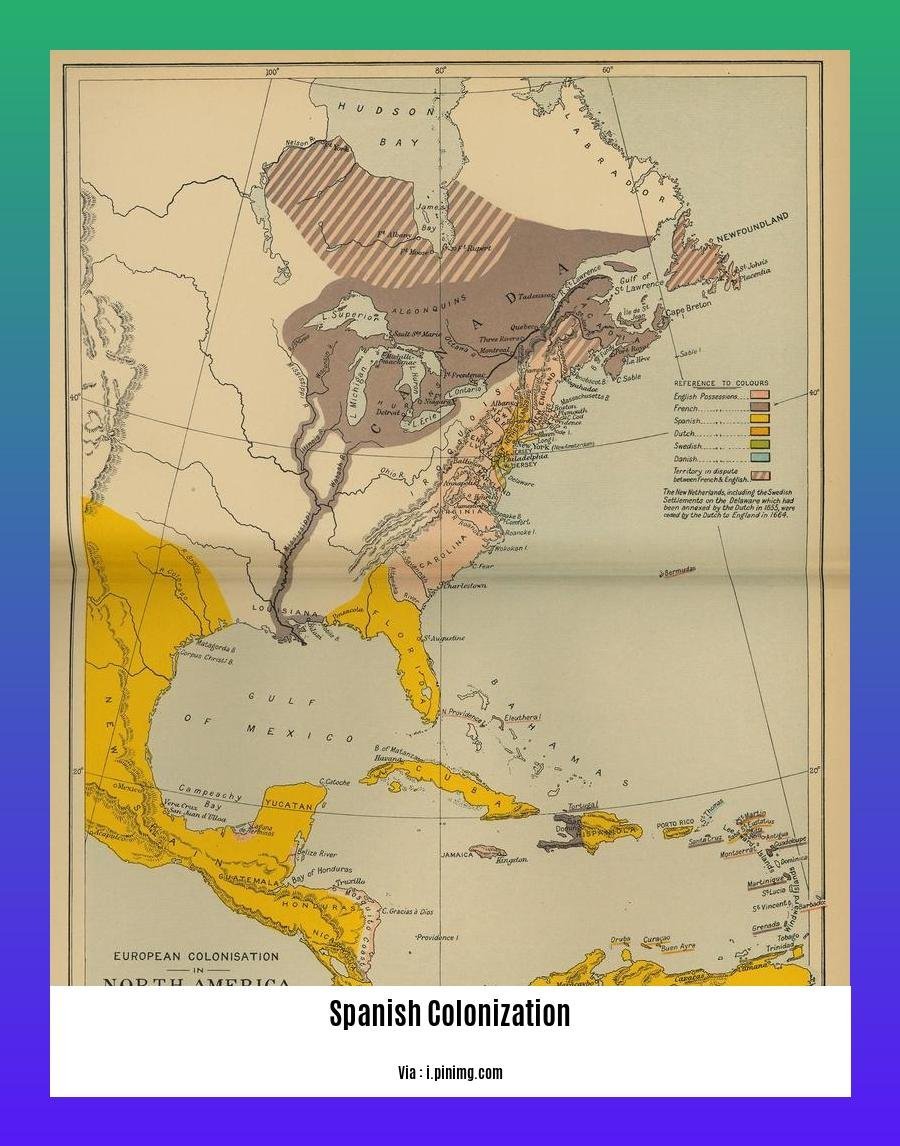
Delve into the enduring legacy of Spanish colonization in this captivating historical exploration titled [- The Enduring Legacy of Spanish Colonization: A Historical Perspective]. Embark on a journey through time to uncover the profound impact of Spain’s imperial ambitions on the Americas, shaping the destinies of indigenous populations and European settlers alike.
Key Takeaways:
- Spanish Colonization refers to the expansion of the Spanish Empire to gain territories and resources.
- It lasted from the 16th to 19th centuries.
- The Treaty of Tordesillas legalized Spain’s control over vast lands in the New World.
- Spanish explorers like Columbus conquered indigenous peoples and cultures.
Spanish Colonization

Spanish colonization greatly influenced the world’s history. It led to the spread of European culture, language, and religion to the Americas. It also had a profound impact on the indigenous populations of the Americas. It resulted in the deaths of millions of indigenous people, and the displacement of many others.
Here are some of the key features of Spanish colonization:
- It was motivated by a desire for wealth and power.
- It was carried out by a small number of Spanish conquistadors.
- It was often brutal and exploitative.
- It had a lasting impact on the indigenous populations of the Americas.
The consequences of Spanish colonization are still felt today.
- Positive Impacts:
- Introduction of European crops, livestock, and technology to the Americas.
- Establishment of cities and infrastructure in the Americas.
Spread of Catholicism and European culture to the Americas.
Negative Impacts:
- Death of millions of indigenous people
- Enslavement of millions of indigenous people
- Displacement of indigenous people from their land
- Destruction of indigenous cultures and languages
Spanish colonization was a complex and controversial period in history. It had both positive and negative consequences. Its legacy is still debated today.
To know about the rich and turbulent history of the Philippines, click on the History of the Philippines. If you want to know more about the brave Filipinos who revolted against Spanish colonization in 1896, click the Philippine Revolution of 1896. Lastly, to find out more about the dark period of the Philippines, the martial law of the 70s imposed by then President Ferdinand Marcos, and how People Power successfully ended it, click on Martial Law and People Power Revolution.
Impact of Spanish colonization on indigenous populations
The arrival of Spanish colonizers had a profound impact on indigenous populations in the Americas. The consequences, both positive and negative, have shaped the course of history and continue to resonate today:
Positive Impacts
- Introduction of new crops, livestock, and technology, leading to changes in dietary and agricultural practices.
- Establishment of cities and infrastructure, facilitating trade and communication.
- Spread of Catholicism and European culture, influencing religious beliefs and cultural practices.
Negative Impacts
- Diseases brought by colonizers decimated indigenous populations, with smallpox and measles proving especially devastating.
- Enslavement and forced labor under the encomienda system led to exploitation and loss of autonomy.
- Displacement from land and disruption of traditional ways of life, resulting in social and economic upheaval.
Key Takeaways:
- Impact of Spanish colonization on indigenous populations was multifaceted, affecting their health, culture, and way of life.
- Diseases introduced by colonizers caused a dramatic decline in indigenous populations.
- Displacement from land and forced labor led to social and economic hardships for indigenous communities.
Sources:
- The Impact of European Diseases on Native American Populations
- The Encomienda System in Spanish America
Socioeconomic and political transformations brought by Spanish rule

The arrival of the Spanish conquistadors in the 16th century marked a significant turning point in Philippine history. Beyond the immediate impact of conquest and colonization, a series of socioeconomic and political transformations took place, shaping the country’s development for centuries to come.
Centralized Government
One of the most significant changes brought about by Spanish rule was the establishment of a centralized government. Before the Spanish arrived, the Philippines was a fragmented archipelago, with numerous independent precolonial states and kingdoms scattered across the islands. The Spanish established a hierarchical administration, with the governor-general as the head of the government. The Audiencia, which was the highest court, was also established during this time.
Tax Farming and Oligarchy
The Spanish colonial government introduced a system of tax farming, whereby private individuals were granted the right to collect taxes in exchange for a fixed amount of money paid to the government. This system led to widespread abuses and exploitation of the indigenous population.
Along with tax farming, Spanish rule also brought about the emergence of an oligarchic structure, where a small group of wealthy and powerful individuals held significant political and economic influence.
Lingering Influence
Despite efforts towards democratization and economic reform, the influence of Spanish colonial era on the Philippine political system persists. The centralized government structure, the role of the judiciary, and the oligarchic tendencies are all legacies of the Spanish colonial period.
Key Takeaways:
- The Spanish introduced a centralized government system in the Philippines, with the governor-general as the head of the government.
- The Spanish colonial government implemented a system of tax farming, which led to abuses and exploitation.
- The Spanish colonial period also saw the emergence of an oligarchic structure, where a small group of individuals held significant political and economic power.
- The influence of the Spanish colonial era on the Philippine political system persists today.
Relevant URL Sources:
* The Spanish Influence on the Political System of the Philippines
* Spanish Colonialism and the Philippines
Legacy and enduring consequences of Spanish colonization
From the 15th century onwards, the tentacles of Spanish colonialism spread across vast swathes of the globe, leaving an enduring legacy that continues to shape societies and cultures to this day. The legacy and enduring consequences of Spanish colonization are a complex and multifaceted tapestry woven from both positive and negative threads.
Impact on Indigenous Populations
1. Demographic Catastrophe:
Spanish colonization brought with it a wave of diseases to which the indigenous populations had no immunity, resulting in a catastrophic decline in their numbers. Smallpox, measles, and other pathogens ravaged communities, decimating populations by up to 90% in some areas.
2. Enslavement and Exploitation:
Indigenous peoples were subjected to brutal systems of forced labor, such as the encomienda system, which granted Spanish settlers control over indigenous communities. They were forced to work in mines, plantations, and other industries under harsh conditions.
3. Cultural Suppression:
Spanish colonizers sought to suppress indigenous languages, religions, and customs. They imposed their own cultural norms and values, often through violent means, leading to the loss of rich cultural diversity.
Socio-Economic Consequences
1. Economic Dependency:
Spanish colonial policies fostered economic dependency on the mother country. Indigenous economies were disrupted, and local industries were suppressed in favor of the export of raw materials and finished goods from Spain.
2. Social Hierarchy:
Spanish colonization created a rigid social hierarchy with Europeans at the top, followed by mixed-race populations, and indigenous peoples at the bottom. This hierarchy persists in many former Spanish colonies, shaping social and economic disparities.
Political Consequences
1. Centralized Governance:
Spanish colonization introduced centralized systems of government, often based on European models. This replaced existing indigenous political structures, leading to a loss of autonomy for local communities.
2. Legacy of Authoritarianism:
The authoritarian nature of Spanish colonial rule left a lasting legacy in many former colonies. Centralized power structures and a lack of democratic traditions have hindered the development of stable and democratic societies in some areas.
Cultural Consequences
1. Syncretism:
Despite attempts at cultural suppression, indigenous and Spanish influences blended in some areas, leading to a unique form of syncretism. This is evident in art, music, language, and religious practices.
2. Linguistic Diversity:
Spanish became the official language in many former colonies, but indigenous languages also survived and thrived in many areas. This has resulted in a rich linguistic diversity in some regions.
Key Takeaways:
- Spanish colonization had a devastating impact on indigenous populations, leading to demographic decline, enslavement, and cultural suppression.
- Colonial policies fostered economic dependency and created a rigid social hierarchy that persists in some areas.
- Centralized governance and a legacy of authoritarianism continue to influence political systems in some former colonies.
- Spanish colonization also left behind a legacy of cultural syncretism and linguistic diversity.
Relevant URL Sources:
- Long-run development and the legacy of colonialism in Spanish America
- Colonialism and Development: A Comparative Analysis of Spanish and British Colonies
FAQ
Q1: What were the main motivations behind Spanish colonization?
Q2: How did Spanish colonization impact the indigenous populations of the Americas?
Q3: What were the key features of the Spanish colonial government system?
Q4: How has Spanish colonialism shaped the development of Latin America?
Q5: What are the lasting legacies of Spanish colonization in the former colonies?
- Unlock Water’s Symbolism: A Cross-Cultural Exploration - April 20, 2025
- Identify Black and White Snakes: Venomous or Harmless? - April 20, 2025
- Unlocking Potential: Origins High School’s NYC Story - April 20, 2025