Ever feel a catching or grinding sensation in your shoulder blade? You might have snapping scapula syndrome. This condition occurs when the shoulder blade (scapula) doesn’t glide smoothly over the ribs. This article explores the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and management strategies for snapping scapula syndrome, empowering you to take control of your shoulder health.
Decoding the Snap: What Causes Snapping Scapula?
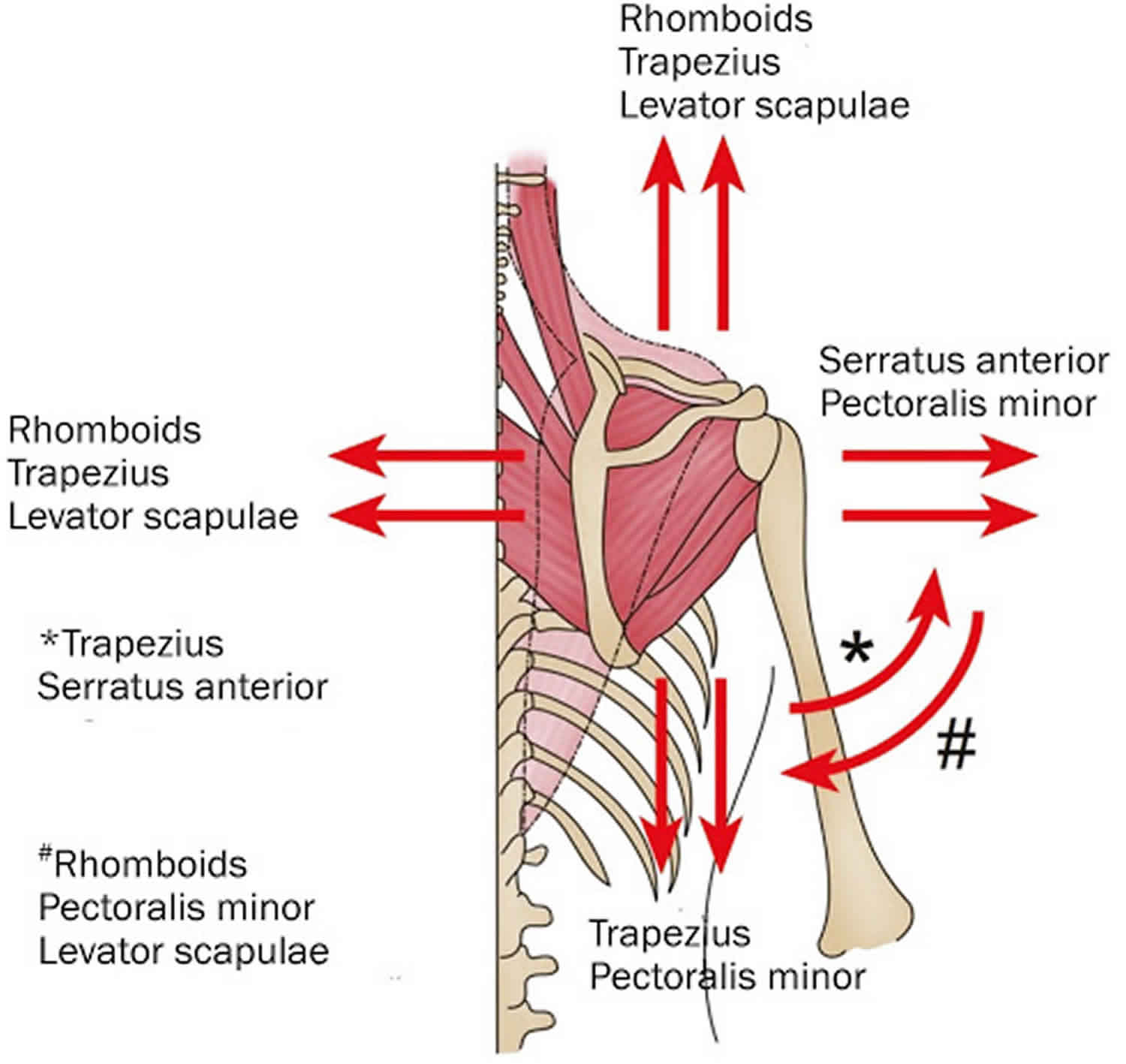
The “snap” in snapping scapula syndrome arises from friction between the scapula and the rib cage. Several factors can contribute to this friction:
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursae, the fluid-filled sacs that cushion the bones and muscles, is a frequent cause. Inflammation can also occur in other areas, illustrating the body’s complex response to irritation.
- Bone Abnormalities: Bone spurs, abnormal bone shapes, or the scapular tubercle of Luschka (an anatomical variation) can create uneven surfaces that catch or grind.
- Muscle Imbalances: Tight or weak muscles surrounding the shoulder blade can disrupt its normal movement, increasing friction.
- Scar Tissue: Scar tissue from prior injuries can restrict movement and contribute to snapping.
Recognizing the Symptoms: Is it Snapping Scapula?
Snapping scapula syndrome presents with a range of symptoms:
- Clicking, Popping, or Grinding: The hallmark symptom is an audible or palpable clicking, popping, grinding, or thumping emanating from the shoulder blade.
- Pain: Pain can range from a mild ache to sharp, stabbing sensations, often worsening with arm movement.
- Stiffness and Limited Movement: Shoulder stiffness and difficulty reaching overhead or behind the back are common.
- Tenderness: The area around the shoulder blade may be tender to the touch.
Diagnosing the Issue: How is Snapping Scapula Identified?
Diagnosing snapping scapula syndrome often involves a multi-step approach:
- Physical Exam: Your doctor will assess your shoulder’s range of motion, listen for unusual sounds, and palpate the area for tenderness and crepitus (a grating sensation).
- Imaging Tests:
- X-rays: Can reveal bone spurs or other bony abnormalities.
- CT Scans: Provide detailed cross-sectional images to pinpoint bone and soft tissue issues.
- MRIs: Visualize soft tissues like muscles, tendons, and bursae to identify inflammation or tears.
- Diagnostic Injections: Injecting a numbing agent can help isolate the source of pain and confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment Options: Finding Relief for Snapping Scapula
Treatment for snapping scapula ranges from conservative measures to surgical intervention:
Non-Surgical Treatments
- Rest and Ice: Reducing activity and applying ice to the affected area can help manage initial pain and inflammation.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or naproxen can alleviate discomfort. In some cases, your doctor may prescribe stronger anti-inflammatory drugs or muscle relaxants.
- Physical Therapy: This is often the cornerstone of treatment. A physical therapist will guide you through exercises to:
- Strengthen the muscles surrounding the shoulder blade.
- Improve posture and scapular control.
- Increase flexibility and range of motion.
- Corticosteroid Injections: Injecting corticosteroids into the inflamed bursa can provide significant pain relief and reduce inflammation, although the effects may be temporary.
Surgical Treatments
Surgery is typically considered when conservative treatments fail to provide adequate relief. Procedures may include:
- Bursectomy: Surgical removal of the inflamed bursa.
- Bone Spur Resection: Removal of bone spurs or other bony abnormalities causing impingement.
- Scapulothoracic Fusion: A rare procedure involving fusing the scapula to the ribs, usually reserved for severe cases.
| Treatment Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Rest and Ice | Helps reduce initial pain and swelling. |
| Physical Therapy | Focuses on strengthening, flexibility, and range of motion in the shoulder. |
| NSAIDs (Pain Relievers) | Over-the-counter pain medication to manage discomfort and inflammation. |
| Corticosteroid Injections | Reduces inflammation at the source. |
| Bursectomy | Surgical removal of inflamed bursae. |
| Bone Spur Resection | Surgical removal of bone spurs causing impingement. |
| Scapulothoracic Fusion | Fusion of the scapula to the ribs (a rare procedure). |
Prevention and Long-Term Management
While not always entirely preventable, these strategies can minimize risk and manage symptoms:
- Maintain good posture: Proper posture reduces strain on the shoulder joint.
- Set up an ergonomic workspace: This is crucial for those who spend long hours at a desk.
- Warm up properly before exercise: Prepare your shoulder muscles for activity, especially overhead movements.
- Continue prescribed exercises: Maintain the strength and flexibility gains achieved through physical therapy.
- Avoid aggravating activities: Modify or avoid activities that exacerbate symptoms.
Can Snapping Scapula Syndrome Be Fixed?
Yes, snapping scapula syndrome is often treatable. Many individuals find relief through non-surgical treatments like physical therapy and medication. Minimally invasive arthroscopic surgery offers a more definitive solution for more severe cases. Early diagnosis and treatment significantly improve the chances of a full recovery.
What Happens if Snapping Scapula is Left Untreated?
Ignoring snapping scapula syndrome can lead to several complications:
- Chronic Pain: The initial discomfort can progress to persistent, debilitating pain.
- Decreased Range of Motion: Shoulder movement becomes increasingly limited, impacting daily activities.
- Adhesive Capsulitis (Frozen Shoulder): Untreated SSS can increase the risk of developing frozen shoulder, a condition characterized by severe stiffness and limited mobility.
- Muscle Atrophy: Weakening and wasting of the shoulder muscles can occur due to reduced use and pain.
- Need for Surgery: Delaying treatment may necessitate more invasive surgical procedures.
| Stage | Symptoms | Potential Consequences |
|---|---|---|
| Early | Occasional snapping, mild discomfort | Potential for worsening symptoms |
| Intermediate | Frequent snapping, increasing pain, stiffness | Reduced range of motion, activity limitations |
| Advanced | Chronic pain, significant stiffness, limited mobility | Frozen shoulder, muscle atrophy, surgery |
How Rare is Snapping Scapula Syndrome?
Snapping scapula syndrome is considered relatively rare. However, a lack of precise prevalence data and frequent misdiagnosis may contribute to underestimation. While rare, the condition can significantly impact quality of life if left untreated. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for optimal outcomes.
Important Note: This information is for educational purposes and should not replace professional medical advice. Consult a healthcare provider for any shoulder pain or concerns. They can provide a personalized diagnosis and treatment plan.
- China II Review: Delicious Food & Speedy Service - April 17, 2025
- Understand Virginia’s Flag: History & Debate - April 17, 2025
- Explore Long Island’s Map: Unique Regions & Insights - April 17, 2025