Visualize and comprehend: Explore interactive labeled diagrams and high-definition videos of sheep brain dissection. This comprehensive guide provides a detailed, step-by-step exploration of sheep brain anatomy, perfect for students, educators, and anyone curious about the intricacies of the mammalian brain. We’ll cover everything from gathering your materials and safety precautions to identifying key structures and comparing the sheep brain to the human brain. Let’s embark on this fascinating journey of discovery!
Preparing for Dissection: Tools and Safety
Before we begin, proper preparation is essential for a successful and safe dissection. Think of it like prepping for a surgical procedure – having the right tools and following safety protocols is paramount.
Gathering Your Materials
Assemble the following materials:
- Dissection Tray: A shallow tray, preferably with a wax or rubber base, provides a stable work surface and contains fluids.
- Scalpel: A sharp scalpel allows for precise incisions and careful tissue separation.
- Scissors: Use scissors for larger cuts and tougher connective tissues. Having different types with varying tip sharpness can be beneficial.
- Forceps: These “tiny tongs” are essential for gripping and lifting delicate structures without causing damage.
- Probe: A blunt probe is useful for pointing, gently separating parts, and exploring sulci and gyri.
- Pins (Optional): T-pins are helpful for holding back flaps of tissue for better visibility.
- Gloves: Nitrile or latex gloves are crucial for hygiene and safety, protecting your hands from biological materials and preservatives.
- Safety Goggles: Eye protection is essential. Goggles shield your eyes from splashes or accidental contact with the specimen.
- Lab Coat/Apron: Provides an extra layer of protection for your clothing and contributes to a professional environment.
- Sheep Brain: The star of the show! Preserved specimens are readily available from biological supply companies.
- Dissection Guides & Anatomical Charts: Use these resources for step-by-step instructions, labeled diagrams, and visual references. Consider resources like Michigan State University’s Sheep Brain Atlas, Biology LibreTexts, and The Biology Corner.
- Disinfectant Solution & Paper Towels: Maintaining a sterile environment is paramount. Disinfectant cleans surfaces and tools, and paper towels aid in cleanup.
Safety Precautions: Protecting Yourself and the Specimen
Working with biological specimens demands meticulous safety practices:
- Gloves and Eye Protection: Always wear gloves and goggles.
- Handle with Care: Treat the sheep brain with respect, recognizing its biological origin.
- Cleanliness: Disinfect your workspace before and after the dissection. Dispose of materials responsibly according to your institution’s guidelines.
- Sharp Objects: Exercise extreme caution when handling sharp instruments like scalpels and scissors. Keep them pointed away from yourself and others.
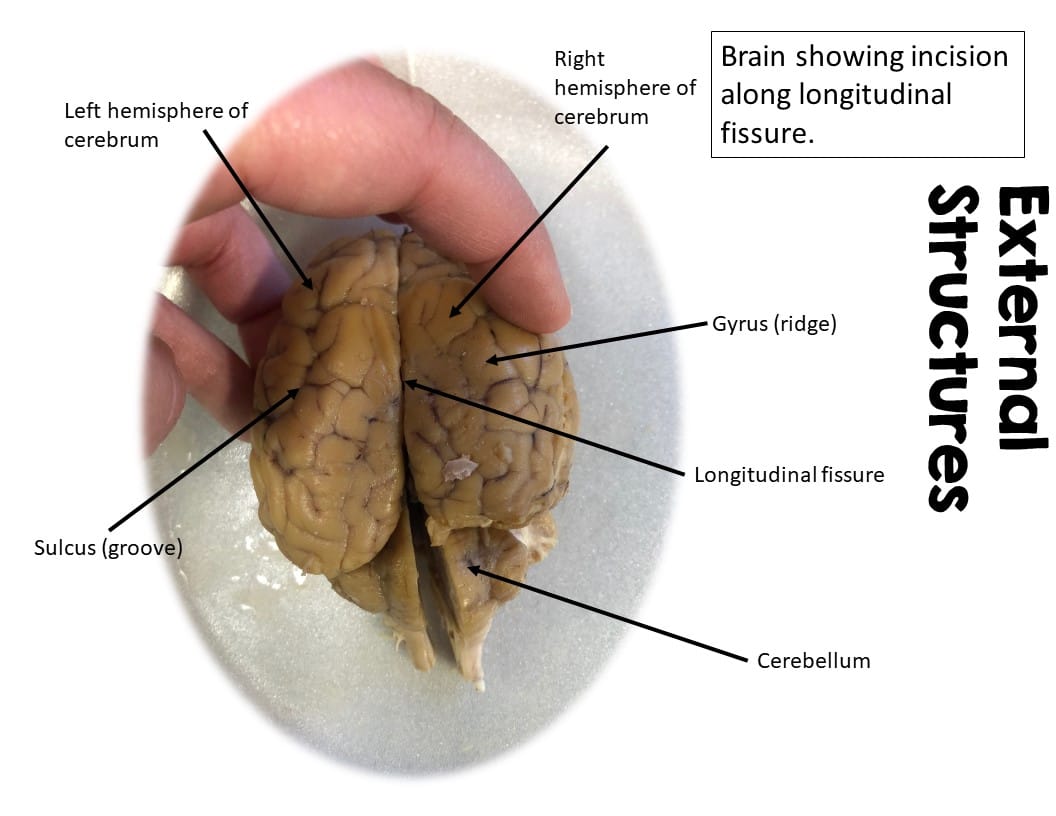
Exploring the External Anatomy: A First Look
Begin by observing the outer surface of the sheep brain. You’ll likely encounter the dura mater, a tough membrane that safeguards the brain. The pituitary gland, a small structure crucial for hormone regulation, might be visible. The optic chiasma, where the optic nerves intersect, is another key external feature to locate. Its location likely suggests an important role in processing visual input.
Step-by-Step Dissection Guide: Unveiling the Inner Workings
Now, let’s journey into the brain’s interior. Each step is accompanied by detailed descriptions and, where available, visual aids like labeled diagrams and videos.
-
Removing the Dura Mater: Using forceps, gently peel back the dura mater. Patience is key, as some areas may be adherent. This reveals the underlying brain tissue.
-
Identifying Major Structures:
- Cerebrum: The largest part of the brain, responsible for higher-level cognitive functions. Its folded surface (gyri and sulci) increases surface area. Note the differences in the cerebrum between sheep and humans.
- Cerebellum: Located at the back, the cerebellum plays a vital role in motor coordination, balance, and posture.
- Brainstem: Connecting the cerebrum and cerebellum to the spinal cord, the brainstem controls essential functions like breathing and heart rate. Observe sections like the medulla oblongata and pons.
-
Exposing Internal Structures: Carefully make incisions to further explore:
- Ventricles: These fluid-filled cavities contain cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which cushions and protects the brain. CSF circulation may play a critical role in waste removal and nutrient distribution.
- Thalamus: This relay center directs sensory information to the appropriate regions of the cerebrum.
- Spinal Cord (if present): Examine the connection between the brain and spinal cord – this is the primary pathway for communication throughout the body.
- Meninges: The meninges are protective layers surrounding the brain and spinal cord. While the dura mater is the outermost layer, you might also identify the arachnoid mater and pia mater. The arachnoid mater is likely involved in CSF circulation.
Remember to document your observations during this process. Sketching and labeling structures can reinforce your understanding of sheep brain neuroanatomy.
Comparative Anatomy: Sheep vs. Human
While the sheep brain provides valuable insights into mammalian brain structure, there are notable differences compared to the human brain:
| Feature | Sheep Brain | Human Brain |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Smaller | Larger |
| Shape | More elongated | More rounded |
| Olfactory Bulbs | Larger, reflecting a stronger sense of smell | Smaller |
| Gyrification | Fewer folds (gyri) on the cerebral surface | More extensive folding (gyri) on the cerebral surface |
These differences probably reflect adaptations to each species’ ecological niche and lifestyle. The increased gyrification in humans likely correlates with advanced cognitive abilities and larger amounts of neural tissue.
Functional Analysis: Understanding the Role of Each Part
Each brain region has a specialized function, contributing to the overall orchestration of behavior and physiology:
- Cerebrum: The “thinking center,” involved in learning, memory, language, and decision-making.
- Cerebellum: Ensures smooth, coordinated movements and maintains balance.
- Brainstem: Regulates vital autonomic functions, including breathing, heart rate, and sleep-wake cycles.
- Thalamus: Acts as a relay station, directing incoming sensory information to the correct cortical areas.
- Ventricles/CSF: Provide cushioning, support, and possibly nutrient transport for the brain.
Ongoing research continues to unravel the complex interplay between these brain regions, providing ever deeper insights into the mysteries of the mammalian nervous system.
Delving Deeper: Additional Resources and Further Exploration
This guide offers a foundational understanding of sheep brain anatomy. For those seeking more in-depth knowledge, explore these additional resources:
- Online Sheep Brain Atlases: These interactive resources provide detailed labeled images and 3D models, enhancing your understanding of spatial relationships within the brain.
- Dissection Videos: High-quality videos offer step-by-step demonstrations, allowing you to visualize the dissection process and reinforce learning.
- Scientific Articles and Textbooks: Reputable sources like neuroscience journals and neuroanatomy textbooks delve deeper into specific brain regions, functions, and research findings. Explore work on neurological disorders to see how this knowledge is applied.
- Interactive Learning Tools: Engage with quizzes, labeling exercises, and 3D models to test your knowledge and explore the brain in an interactive format.
To unravel the mysteries of quantum physics, delve into our in-depth crossword clue exploration of the enigmatic subatomic particle crossword clue. Discover the complexities of an organ vital to life with our comprehensive analysis of sheep’s pluck in sheep brain dissection.
By engaging with these resources, you can expand your knowledge and contribute to the ever-evolving field of neuroscience. While this guide provides a solid framework, continuous learning and exploration are key to unlocking the mysteries of the brain.
- Unveiling Bernhard Caesar Einstein’s Scientific Achievements: A Legacy in Engineering - July 15, 2025
- Uncover who is Jerry McSorley: CEO, Family Man, Business Success Story - July 15, 2025
- Discover Bernhard Caesar Einstein’s Scientific Contributions: Unveiling a Legacy Beyond Einstein - July 15, 2025













2 thoughts on “The Ultimate Guide to Sheep Brain Dissection: Labeled Images, Videos, and 3D Model”
Comments are closed.