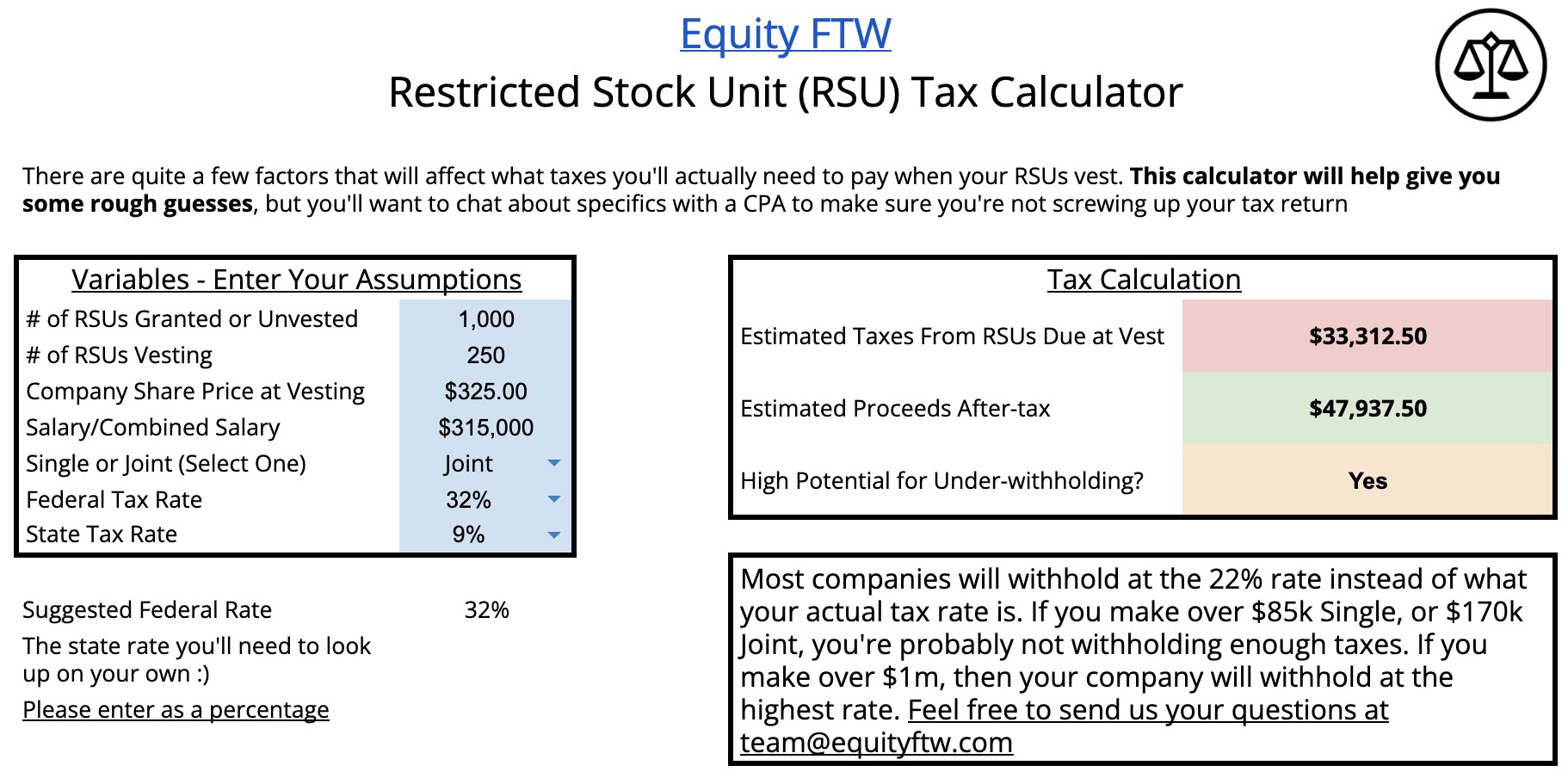
Got RSUs vesting soon? Congratulations! While exciting, understanding the UK tax implications is crucial for maximizing your net gains. This comprehensive guide, combined with our interactive RSU tax calculator, will demystify RSU taxation, empowering you to make informed decisions and keep more of your hard-earned equity.
RSU Taxation: A UK Perspective
What are RSUs and How are They Taxed in the UK? (Listicle-Style)
- RSUs Defined: Restricted Stock Units (RSUs) are a form of equity compensation where you receive company shares upon vesting. Think of it as a bonus paid in company stock.
- Vesting Explained: RSUs typically vest over time (e.g., four years) or after meeting performance milestones. Vesting is the point at which the shares officially become yours.
- Taxation on Vesting: The market value of your RSUs at the time of vesting is considered income and subject to Income Tax and National Insurance Contributions (NICs). This is taxable income, even though you haven’t sold the shares yet.
Using an RSU Tax Calculator: A Step-by-Step Guide
An RSU tax calculator can help you estimate your potential tax liability. While each calculator may have slightly different inputs, here’s a general guide using our EquityFTW RSU calculator:
- Input RSU Details: Enter the number of shares vesting and their market value on the vesting date. Some calculators may also require details about your vesting schedule.
- Enter Your Salary: Provide your current annual salary. This is essential for determining your tax bracket.
- Include Other Income: Declare any additional income sources (e.g., investments, rental properties). This affects your total taxable income, influencing the tax on your RSUs.
- Review the Results: The calculator will estimate your Income Tax and NICs, providing your estimated net payout.
Interpreting Your Results: What the Calculator Tells You (and Doesn’t)
The calculator provides a helpful estimate, but remember, it’s not a crystal ball. Tax laws are intricate, and individual circumstances can vary. The calculator is an excellent planning tool, but it’s crucial to consult a qualified tax advisor for personalized guidance.
Top Strategies for Minimizing Your RSU Tax Burden (Listicle-Style)
- Strategic Timing: Depending on market conditions and your financial situation, the timing of your stock sale after vesting may impact your Capital Gains Tax liability.
- Vesting Schedules: Different vesting schedules can have tax implications. Understand yours and explore options with your company if possible.
- Pension Contributions: Maximize contributions to tax-advantaged retirement accounts (e.g., pensions). These contributions can lower your overall taxable income, potentially reducing your tax bracket and the tax on your RSUs.
RSUs vs. Other Equity Compensation: A Quick Comparison
| Feature | RSUs | Stock Options |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Receive shares upon vesting | Receive the right to buy shares |
| Taxation | Income tax on value at vesting | Capital gains tax on profits upon sale |
| Risk | Generally less risky | Generally more risky (price fluctuations) |
Navigating the Maze: Income Tax and NICs Decoded
Understanding how Income Tax and NICs interact is vital.
- Income Tax: The UK’s progressive tax system means higher earners pay a higher percentage of tax. Your marginal tax rate (the rate applied to your highest slice of income) is key for RSU taxation.
- NICs: Both you and your employer contribute to NICs. Your employer’s contribution slightly reduces your taxable RSU amount. This is because the employer NIC is calculated and deducted before your Income Tax is applied.
UK-Specific Examples and Case Studies
Let’s look at some hypothetical scenarios to illustrate the impact of RSU taxation (using simplified assumptions for illustration):
| Salary Before RSU | RSU Value | Employer NIC (13.8%) | Taxable Amount | Income Tax (Assumed Rates) | Employee NIC (Assumed Rates) | Net RSU Payout (approx.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £80,000 | £10,000 | £1,380 | £8,620 | £1,724 (20%) | £1,034 (12%) | £7,242 |
| £130,000 | £20,000 | £2,760 | £17,240 | £6,896 (40%) | £345 (2%) | £12,759 |
| £200,000 | £50,000 | £6,900 | £43,100 | £17,240 (40%) | £862 (2%) | £31,898 |
Remember, actual tax calculations are more complex. Consult a tax advisor for personalized advice.
Real-World Example (Preserving original wording from mpathyaccounting.co.uk):
- Scenario: Salary £130,000, RSU Value £20,000
- RSU Value: £20,000
- Employer’s NIC @ 13.8%: £2,760
- Remaining: £17,240
- Income tax @ 40%: £6,896
- Employee NIC @ 2%: £344
- Total Tax and NIC: £10,000
- Net pay: £10,000
- 50% Tax and NIC paid
Addressing Double Taxation: Cost Basis and Beyond
The term “double taxation” with RSUs can be misleading. It’s not truly being taxed twice on the same money. You’re taxed on the value at vesting (Income Tax and NICs) and later on any profit when you sell the shares (Capital Gains Tax). Crucially, the original value at vesting becomes your cost basis. This ensures you’re only taxed on the gain, not the original amount, when you sell. This cost basis adjustment is recorded on your W-2 and is essential when reporting the sale on Form 8949.
Conclusion: Unlock Your RSU’s True Potential
RSUs offer valuable financial opportunities. By proactively understanding the UK’s tax implications and employing smart strategies, you can maximize your net payout. Use our RSU tax calculator as a starting point, but remember that personalized advice from a tax professional is invaluable. Take control of your financial future and ensure you reap the full rewards of your hard-earned equity.
Explore further: Learn about the complexities of the SFRC prison system and its impact on rehabilitation, or uncover the workings of shadowban tester twitter and maximize your social media reach.
- Discover Long Black Pepper: Flavor & Health Benefits - April 25, 2025
- Shocking Twists: The Grownup Review: Unreliable Narration - April 25, 2025
- A Quiet Place Book vs Movie: A Deep Dive - April 25, 2025