The Roman Conquest of Britain: A Historical Journey – Journey with us through the annals of history as we explore the pivotal Roman conquest of Britain. From the initial incursions to the lasting legacy, we will delve into the strategies, motivations, and consequences that shaped the destiny of these intertwined civilizations.
Key Takeaways:
- Roman conquest of Britain began in AD 43.
- Britons resisted the Romans, but the south was conquered by AD 87.
- The Romans built a frontier road, the Stanegate, to mark the northern limit of their territory.
Roman Conquest of Britain

A Historical Journey
The Roman conquest of Britain began in AD 43 under Emperor Claudius.
The Romans made significant progress during the early years of the conquest, but they faced resistance from the Celtic Britons, who were divided into different tribes and kingdoms.
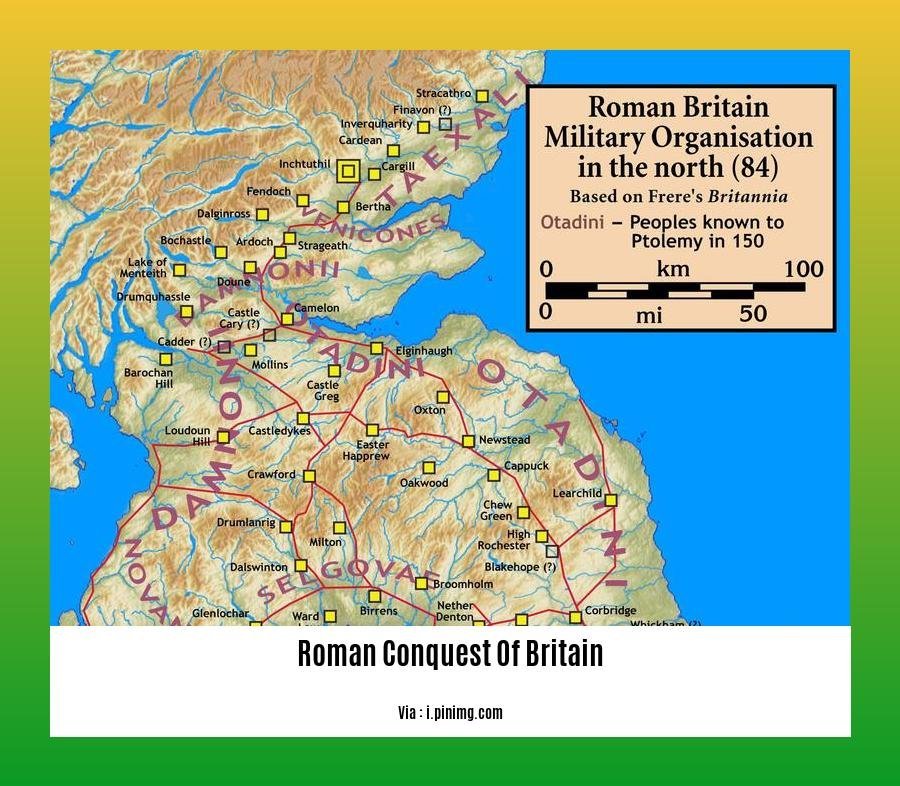
The conquest was largely completed in the southern half of Britain by AD 87, but the Romans continued to face resistance in the north, where they built a frontier road called the Stanegate to mark the northern boundary of their territory.
The Roman conquest of Britain had a profound impact on the country. The Romans introduced new technologies, such as roads, aqueducts, and central heating, and they established a system of government that would last for centuries.
The conquest also led to the spread of Christianity in Britain. The Romans brought with them their own religious beliefs, and over time, Christianity became the dominant religion in the country.
The Roman conquest of Britain was a complex and fascinating event that had a lasting impact on the country. It is a story of conquest, resistance, and cultural exchange that continues to be studied by historians today.
Delve into the rich tapestry of England’s past through our comprehensive History of England page. Trace the pivotal events that shaped the nation, from the Norman Conquest to the dawn of the Industrial Revolution origins.
Resistance and rebellion in Britain
The conquest of Britain was not without resistance and rebellion. The native Celtic tribes fought fiercely against the Roman invaders, employing guerrilla warfare tactics and taking advantage of the unfamiliar terrain. One of the most prominent leaders of the resistance was Caratacus, who led a coalition of tribes against the Romans. Despite their valiant efforts, the Britons were unable to match the superior military power of Rome.
Boudica’s Revolt was a significant uprising that occurred in AD 60. Led by Queen Boudica, the Britons attacked and burned several Roman settlements, including Londinium (modern London). The revolt was eventually crushed by the Roman general Suetonius Paulinus, but it demonstrated the resilience and determination of the Britons.
The Roman conquest of Britain had a profound impact on the region. It brought new technologies, such as roads and aqueducts and introduced Roman law and government. It also led to the spread of Christianity. Despite the challenges posed by resistance and rebellion, the Roman conquest ultimately transformed Britain into a Roman province, leaving a lasting legacy that can still be seen today.
Key Takeaways:
- The native Celtic tribes fiercely resisted the Roman invasion.
- Caratacus was a notable leader of the resistance.
- Boudica’s Revolt was a major uprising against Roman rule.
- The Roman conquest brought significant changes to Britain, including new technologies and the spread of Christianity.
Citations:
- Roman Conquest of Britain – Wikipedia
- Boudica’s Revolt – History
Cultural and economic impact on Britain
The Roman Empire’s influence on Britain stretched far beyond the initial conquest. It marked a transformative period that had a profound impact on the cultural and economic landscape of the region.
Cultural impact: The Romans introduced Latin, which became the official language of Britain and left a lasting legacy in the English language. They also brought Christianity, which gradually replaced the indigenous pagan beliefs. Towns and cities sprouted, patterned on their Roman counterparts, complete with public baths, amphitheatres, and temples.
Economic impact: The Romans developed an extensive road network, making trade and communication more efficient. They introduced new agricultural techniques and crops, boosting the local economy. The Romans also established a monetary system, using coins as a medium of exchange. They connected Britain to the broader Roman Empire, opening up new markets for British goods.
Key Takeaways:
- The Roman conquest introduced Christianity and Latin to Britain.
- Roman towns and cities became centres of trade and culture.
- The Romans developed an extensive road network and introduced new agricultural techniques.
- Roman rule brought a monetary system and connected Britain to the broader Roman Empire.
Sources:
- Roman Britain: How the Romans Changed Britain
- The Roman Conquest of Britain
Legacy and lasting influence of the conquest
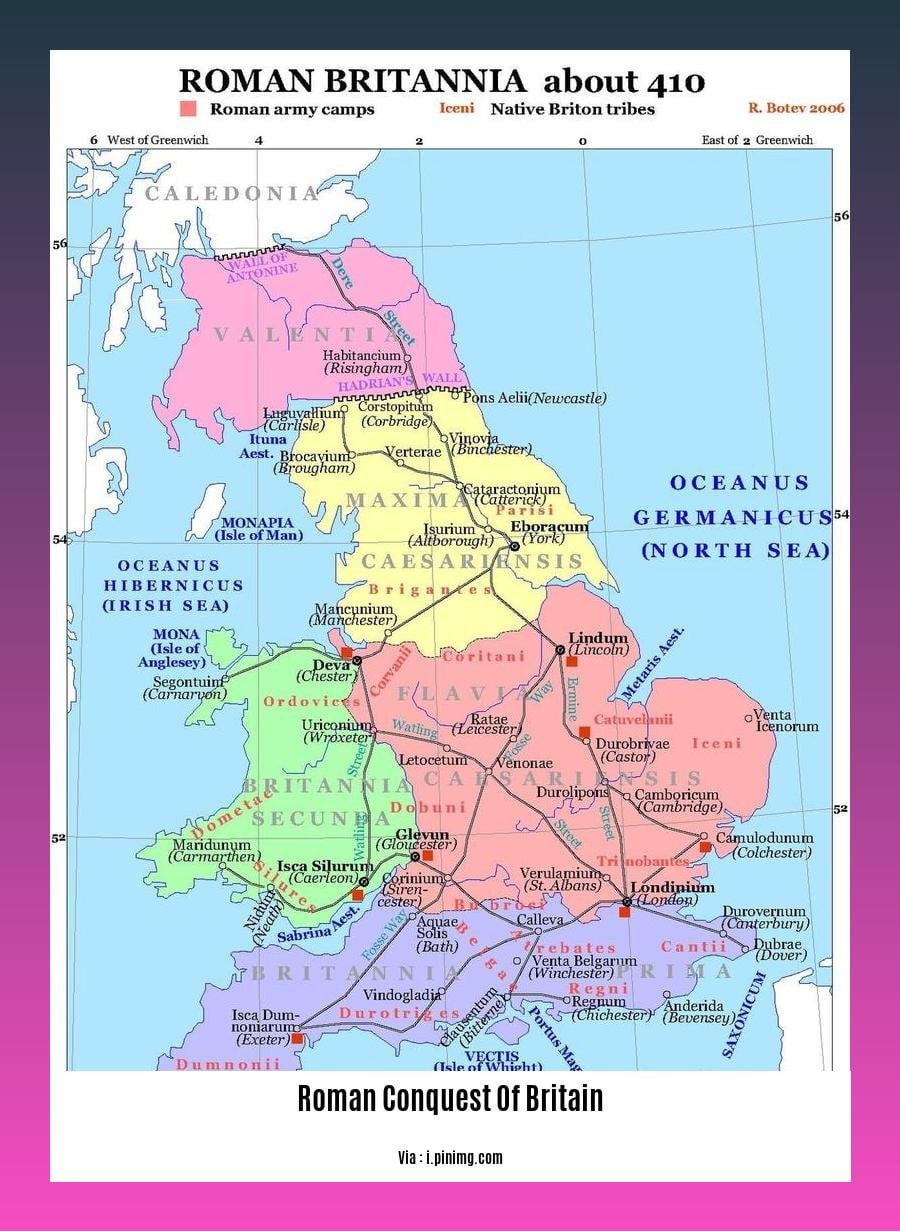
The Roman conquest of Britain left a profound and lasting impact on the country, shaping its history, culture, and infrastructure. The legacy of Roman rule can still be seen today in the form of roads, towns, and archaeological sites that serve as a testament to the empire’s enduring influence on this region.
The Romans introduced a wide range of technological advancements to Britain, including running water, sanitation systems, and central heating. They also established a network of roads that connected the major towns and cities, facilitating trade and communication. These infrastructural improvements had a transformative effect on British society and laid the foundation for future economic growth and development.
Beyond infrastructure, the Romans also brought with them their legal system, administrative structures, and cultural practices. Roman law and governance influenced the development of the British legal system and many of its principles can still be found in modern British law. The Romans also introduced Christianity to Britain, which became the dominant religion in the centuries that followed.
The lasting influence of the conquest can also be seen in the linguistic and cultural heritage of Britain. The English language contains many words of Latin origin, reflecting the linguistic impact of Roman rule. The Romans also introduced new agricultural techniques and crops to Britain, which had a significant impact on the country’s food production and dietary habits.
Key Takeaways:
- The Roman conquest of Britain brought significant technological advancements, including roads, running water, and sanitation systems.
- The Romans introduced their legal system, administrative structures, and cultural practices to Britain, which had a lasting influence on British society.
- The Romans introduced Christianity to Britain, which became the dominant religion in the centuries that followed.
- The linguistic and cultural heritage of Britain still bears the imprint of Roman rule, with many words of Latin origin and the introduction of new agricultural techniques and crops.
Relevant Sources:
- The Roman Conquest of Britain
- Roman Britain: How the Romans Changed Britain
FAQ
Q1. When did the Roman conquest of Britain begin?
A1. The Roman conquest of Britain began in AD 43 under Emperor Claudius.
Q2. Who was the leader of the British resistance?
A2. The leader of the British resistance was Caratacus, who was defeated in AD 50.
Q3. What was the name of the northern boundary of Roman territory in Britain?
A3. The northern boundary of Roman territory in Britain was marked by a frontier road called the Stanegate.
Q4. What was the name of the British queen who led an uprising against the Romans?
A4. The name of the British queen who led an uprising against the Romans was Boudica.
Q5. When was the Roman conquest of southern Britain largely completed?
A5. The Roman conquest of southern Britain was largely completed by AD 87.
- Mastering Leader in Spanish: The Complete Guide - April 19, 2025
- Uncovering Surprising Parallels: England Size Compared to US States - April 19, 2025
- Old Mexico Map: Border Shifts 1821-1857 - April 19, 2025