Unlock Elemental 2 Secrets: Actionable Insights Now

The phrase “Element 2” resonates across diverse sectors, from sustainable energy and staffing solutions to Hollywood sequels and sporting goods. ...
Read moreLot’s Wife’s Name: Unveiling the Mystery of Sodom’s Fall

The tale of Lot’s wife, a figure forever frozen in the biblical narrative of Sodom and Gomorrah’s destruction, continues to ...
Read morePhotocell Sensors: A Complete Guide for Selection and Implementation
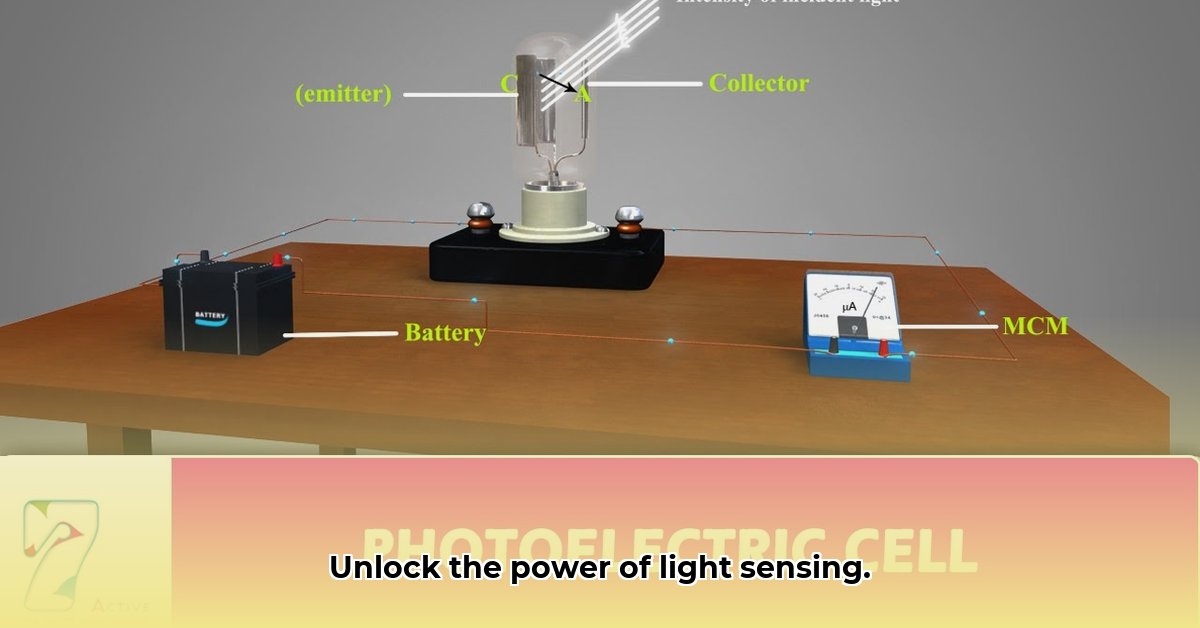
Photocells, also known as photoresistors or light-dependent resistors (LDRs), are crucial components in a wide range of technological applications. They ...
Read moreDiscover Famous French Women: A History of Impact

France, a country celebrated for its rich history and cultural contributions, owes a significant debt to its remarkable women. These ...
Read more2025 World Map: Unveiling Geopolitical Shifts & Risks

The world of 2025 is fast approaching. While crystal balls remain elusive, analyzing current trends and potential disruptions allows us ...
Read moreSecure Your Future: Living Will vs. Last Will Guide

Planning for the future, especially concerning healthcare and asset distribution, is paramount. Two crucial documents, often misunderstood, are essential for ...
Read moreUnlock what part of speech is is: Master English Grammar Now

“Is,” a seemingly simple verb, plays a crucial role in English grammar. Understanding its dual nature as both a linking ...
Read moreUnlock the best US history books: A curated list for insightful reading

Delving into American history is a journey through a nation forged in revolution, tested by civil war, and constantly evolving ...
Read moreFirst Lady Book: A History of Power and Influence

From Martha Washington’s quiet dignity to Jill Biden’s commitment to education, the role of First Lady has undergone a fascinating ...
Read moreUncover James Albert King: A Legacy Revealed

Beyond the Shadows: Unveiling the Life of James Albert King While Martin Luther King Jr.’s name resonates globally as a ...
Read more








