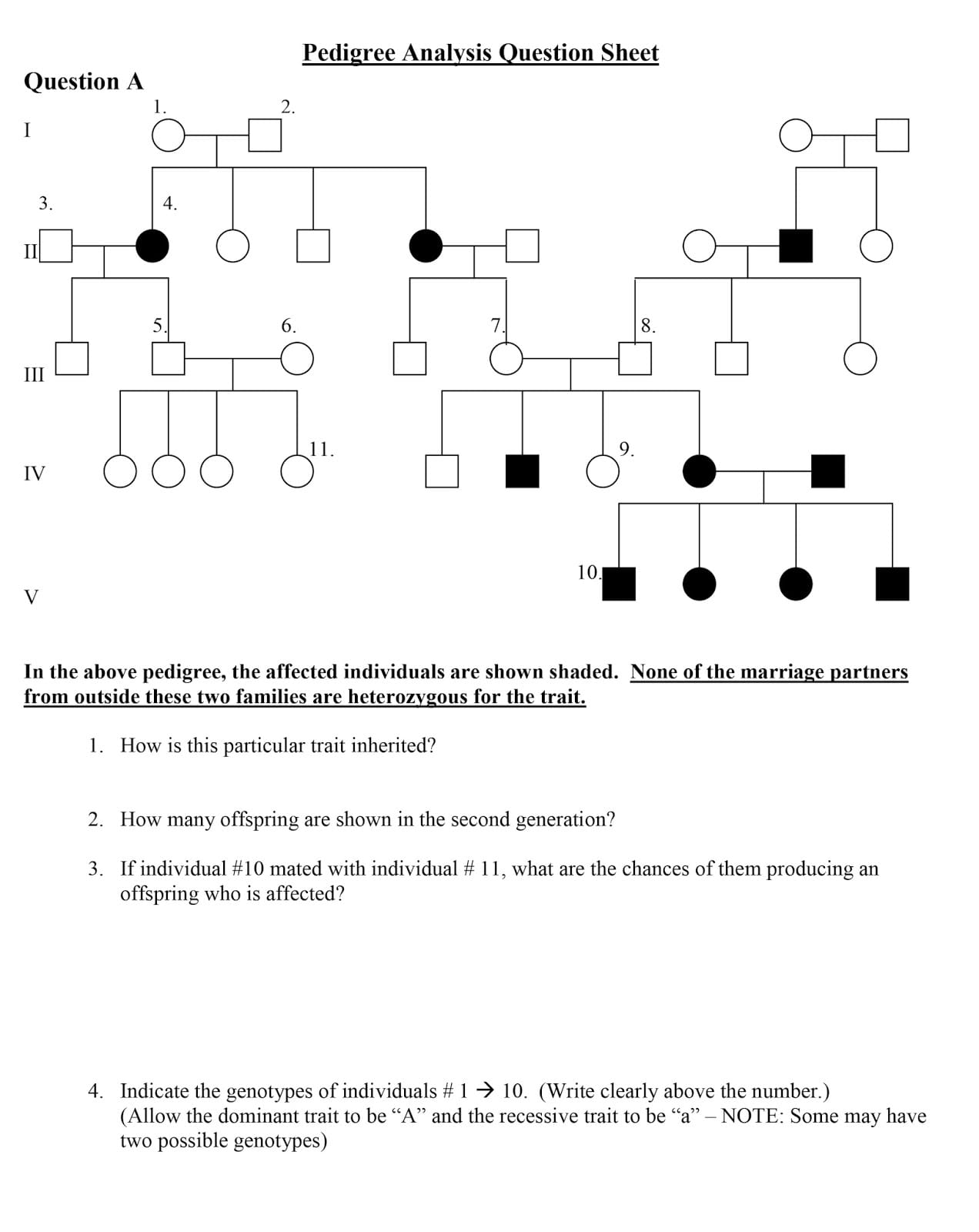
Jump into the exciting world of family history with our guide on pedigree worksheets! These charts can help you trace your roots, understand your genetic heritage, and even make informed health care decisions. With easy-to-follow examples and fun exercises, we’ll teach you how to create and read pedigrees like a pro. Let’s unlock the secrets of your family tree together!
Decoding Inheritance with Pedigree Worksheets
Ever wonder how traits like eye color or hair type are passed down through generations? Pedigree worksheets, like family trees with a scientific twist, can help decode these fascinating inheritance patterns. They visually map family connections and track specific traits over time, providing a glimpse into your family’s history and potentially offering clues about your future health. Expand your knowledge of genetics with an interactive punnett square worksheet and test your understanding with a comprehensive punnett square practice worksheet.
What is a Pedigree Worksheet?
A pedigree is a visual chart representing family connections and traits. Using universal symbols, it depicts family members, relationships (parent-child, siblings), and the presence or absence of specific traits, such as red hair or a genetic condition. This standardized format allows anyone familiar with pedigree symbols to interpret the information.
Using Pedigree Worksheets: Exploring Your Genetic Heritage
Pedigree worksheets are dynamic tools for exploration. Here’s how you can use them:
Understanding Basic Inheritance: Pedigrees illustrate how simple traits, like attached or detached earlobes, are inherited. They demonstrate dominant and recessive genes, helping determine if someone is a carrier for a recessive trait (carrying the gene without exhibiting it). They also likely suggest the probability of children inheriting specific traits.
Unraveling Complex Inheritance: Some traits are not straightforward, sometimes skipping generations or manifesting differently in various individuals. Advanced pedigree analysis helps unravel these complex inheritance patterns, considering factors like penetrance (whether someone with the gene expresses the trait) and expressivity (the intensity of the trait).
Creating Your Family Pedigree: Building your own pedigree is a rewarding project. Gather family information about traits, medical histories, and relationships. Using standard pedigree symbols, create a visual representation of your family’s genetic tapestry. Keep in mind that family recollections can be unreliable, and some traits might appear inherited when they are actually influenced by environmental factors.
Sharpening Skills with Interactive Exercises: Online resources offer interactive pedigree exercises that provide immediate feedback, enhancing understanding and making learning enjoyable.
Finding Pedigree Worksheet Resources
Numerous resources are available to aid in learning about and using pedigrees:
| Resource Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Printable Worksheets | Websites like The Biology Corner offer free printable pedigree worksheets for practice and creating your own family pedigree. |
| Online Platforms | Sites like Liveworksheets provide interactive exercises and quizzes with instant feedback. Some platforms may offer personalized feedback. |
| Educational Materials | Khan Academy, Amoeba Sisters, and other platforms offer accessible videos, articles, and tutorials explaining pedigree analysis, often delving into related genetic concepts. |
Pedigrees in Other Applications
Pedigree analysis extends beyond human families. Scientists use similar techniques in:
- Animal Breeding: Farmers and breeders use pedigrees to select animals with desirable traits, such as increased milk production or disease resistance, while maintaining genetic diversity.
- Conservation Biology: Pedigrees track genetic diversity in endangered species, informing conservation strategies like breeding programs and habitat management.
Embracing the Uncertainties of Genetic Inheritance
Pedigrees are powerful tools, but they don’t provide a complete picture. Many traits are influenced by multiple genes and environmental factors, making predictions complex. Ongoing research continually refines our understanding of genetics; today’s knowledge may evolve with future discoveries. Embrace the exploration, and remember that the story of your genes continually unfolds.
Understanding Pedigree Charts
A pedigree chart, a family tree with a scientific twist, diagrams relationships across generations, showing how traits, particularly genetic ones, are inherited. Using simple symbols, it represents people, their connections, and the presence or absence of specific characteristics. These charts are important for understanding how genes work within families and are crucial in genetic counseling.
Decoding the Symbols
Understanding pedigree chart symbols is key to unlocking their insights.
- Squares: Males
- Circles: Females
- Shaded Shapes: Individuals exhibiting the tracked trait.
- Half-Shaded Shapes: Carriers of the gene, potentially passing it on without exhibiting the trait themselves.
- Horizontal Lines: Connect partners/parents.
- Vertical Lines: Connect parents to children, tracing lineage.
- Proband Arrow: Points to the individual prompting the pedigree investigation.
Inheritance Patterns: Unraveling the Genetic Threads
Pedigree charts reveal inheritance patterns. Common types include:
- Autosomal Dominant: One copy of the gene is sufficient for trait expression.
- Autosomal Recessive: Two copies of the gene are required for trait expression.
- X-Linked Dominant: Linked to the X chromosome, more common in females.
- X-Linked Recessive: Linked to the X chromosome, more common in males.
These are general guidelines, and variations and complexities can occur. Genetic inheritance is a complex field with ongoing research continually refining our understanding.
The Importance of Pedigree Charts
Pedigree charts are valuable tools with real-world applications:
- Spotting Patterns: Geneticists and genetic counselors can identify how traits are passed down, determining if a trait is dominant, recessive, or sex-linked.
- Assessing Risk: Pedigree analysis may suggest individuals at higher risk of inheriting certain conditions, informing family planning and health decisions.
- Guiding Genetic Counseling: Charts provide a visual aid for explaining complex genetic information and discussing risks and options.
- Fueling Research: Scientists use pedigree charts to study inheritance of complex traits and identify genes involved in disorders.
Constructing Your Own Pedigree Chart
- Gather Family History: Collect detailed information from relatives about health history and genetic conditions.
- Use Correct Symbols: Accurately represent individuals, relationships, and traits using standard symbols.
- Arrange by Generation: Organize the chart with oldest generations at the top, descending in horizontal rows.
A Final Word: Pedigrees in Perspective
Pedigree charts are powerful tools, but they provide a limited view. They offer probabilities, not certainties, and gene expression is influenced by numerous factors. Consulting a genetic counselor is recommended for concerns about family history or genetic risks, providing personalized guidance based on the latest scientific understanding.
The Power of Pedigree Charts in Genetic Analysis
Pedigree charts, family trees with a scientific enhancement, provide insights into inherited traits, peculiarities, and potential health concerns within a family. They illuminate how traits like eye color or disease predisposition are passed down through generations, acting as a roadmap of your family’s genetic history.
Uncovering Hidden Genetic Stories
Pedigree charts uncover hidden inheritance patterns, revealing how traits might skip generations or reappear unexpectedly. They distinguish between dominant traits (appearing in every generation) and recessive traits (requiring a specific gene combination for expression). Further, they help identify X or Y-linked traits, inherited differently in males and females, which is crucial for understanding conditions like color blindness or hemophilia.
Beyond Family History: Research and Personalized Medicine
Pedigree charts are valuable tools in genetic research and personalized medicine. Scientists use them to study complex trait inheritance, like predispositions to heart disease or Alzheimer’s, pinpointing involved genes and informing the development of new treatments and preventative strategies. By identifying genetic markers associated with specific diseases, they can focus their research, accelerating discoveries.
In personalized medicine, pedigree charts, combined with genetic testing, provide a clearer picture of individual disease risk, enabling tailored treatment plans and lifestyle recommendations based on unique genetic makeups. This offers the potential for highly individualized healthcare.
Ethical Considerations: Navigating Sensitive Information
Responsible use of pedigree charts is paramount, given the sensitive nature of family information. Informed consent from all involved individuals is essential before gathering or sharing genetic data. Open discussions about the ethical implications of genetic information are crucial, balancing privacy concerns with the potential health benefits of shared genetic knowledge.
The Evolving Landscape of Pedigree Charts
Our understanding of genetics is constantly evolving, impacting pedigree chart interpretation. As new genes associated with diseases are discovered, risk assessments based on family history may require adjustments. Pedigree charts represent a snapshot of current understanding, offering probabilities rather than certainties. The ongoing exploration and discovery inherent in the field of genetics contribute to its intrigue.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Generations | Horizontal rows, with the oldest generation at the top. |
| Individuals | Symbols represent individuals (squares for males, circles for females). |
| Relationships | Lines connect individuals, showing parentage and marriages. |
| Traits | Shaded symbols indicate individuals affected by the trait. |
| Inheritance Patterns | The arrangement of shaded symbols reveals inheritance patterns (dominant, recessive, etc.). |
Pedigree charts are more than family trees—they are windows into our genes, tools for understanding health, and testaments to our quest to unravel the mysteries of human inheritance.
Reading a Pedigree Chart: Unlocking the Secrets
A pedigree chart, a scientific take on the family tree, unveils your family’s genetic history. Understanding its symbols and patterns reveals valuable information about inherited traits.
Decoding the Symbols
Pedigree charts use universal symbols:
| Symbol | Meaning |
|---|---|
| □ | Male |
| ○ | Female |
| ■ | Affected Male |
| ● | Affected Female |
| ◧/◭ | Affected Individual (sex unspecified) |
| ◐/◑ | Carrier of a Recessive Trait |
| ─ | Marriage/Mating |
| │ | Connects Parents to Offspring |
| I, II, III… | Generation Number |
| 1, 2, 3… | Individual within a Generation |
Identifying Inheritance Patterns
The power of a pedigree chart lies in revealing how traits are passed down. Common patterns include:
Autosomal Dominant: One copy of the gene is enough for the trait to manifest. If a parent has it, their children probably will too.
Autosomal Recessive: Two copies are required. Both parents can be carriers without showing the trait, yet their child can inherit it if they receive both copies.
X-linked Dominant: Linked to the X chromosome, more frequent in females due to having two X chromosomes. If a mother has it, her sons likely will too.
X-linked Recessive: Also X-linked, more common in males due to having only one X chromosome. Females may be carriers without showing signs, potentially passing it to their sons.
The Complexities and Limitations of Pedigree Analysis
While valuable, pedigree analysis has limitations. Genetic inheritance is complex, with ongoing research always suggesting new possibilities. Pedigrees offer clues but not the full story. Factors beyond genetics can influence a person’s health. Pedigree analysis may not capture real-life variations, recent mutations, or non-Mendelian inheritance patterns. Environmental factors and variations in phenotype expression further complicate interpretation. Some experts recommend combining pedigree analysis with other diagnostic tools.
For a comprehensive understanding of family history or specific conditions, consult a genetic counselor or healthcare professional. They can interpret your pedigree chart within a broader context, offering personalized guidance based on the latest scientific advancements. They can also discuss the potential and limitations of pedigree analysis, potentially suggesting further exploration via genetic testing.
- Star Ring Trends: Etsy vs Amazon - March 28, 2025
- Boost Pollinator Habitats: Baby Blue Eyes Sustainable Farming Guide - March 28, 2025
- Protect Big Black Bears: Effective Conservation Strategies - March 28, 2025