That check engine light glaring at you? If it’s accompanied by a P0430 code in your Chevy, this guide is your lifeline. We’ll decode the mystery of the P0430, guide you through the diagnostic process, and empower you to fix the problem. From simple checks to more complex repairs, we’ll arm you with the knowledge to save money and get your Chevy back on the road.
Decoding the P0430: What’s Happening Under the Hood?
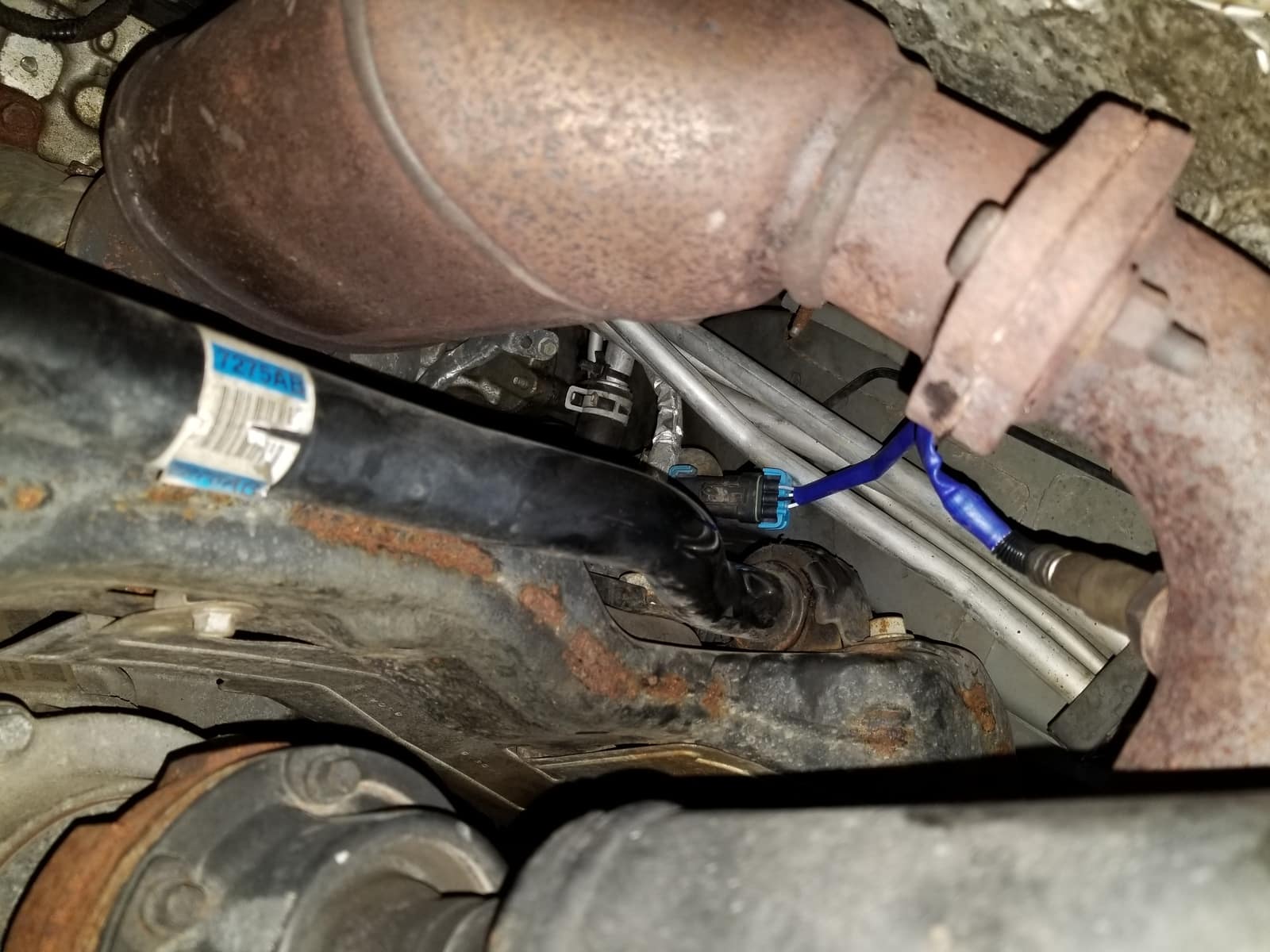
The P0430 code signals a problem with your Chevy’s catalytic converter, specifically on “Bank 2.” “Bank 2” refers to the side of the engine opposite cylinder #1. Each bank has its own catalytic converter, responsible for cleaning up harmful exhaust gases. The P0430 code means the downstream oxygen sensor (O2 sensor)—located after the catalytic converter on Bank 2—is detecting insufficient oxygen storage capacity, suggesting the converter isn’t doing its job efficiently. This can impact your Chevy’s performance, fuel economy, and emissions. This code is a common issue for Chevy Silverado, Tahoe, and Suburban owners, but other models can be affected as well. Experiencing a drop in performance? Unravel the mystery behind the dreaded p0430 code bank 2 and restore your engine’s purr.
Understanding the Components
- Catalytic Converter: This component acts as your engine’s exhaust filter, converting harmful pollutants into less harmful substances before they exit the tailpipe. Over time, these can degrade due to high mileage, excessive heat, or contamination from other engine problems.
- Oxygen Sensors (O2 Sensors): These sensors monitor the oxygen levels in the exhaust gases, providing crucial data to your car’s computer. The downstream O2 sensor, located after the catalytic converter, plays a key role in monitoring the converter’s efficiency.
Recognizing the Symptoms
A glowing check engine light is the most obvious symptom, but other clues might suggest a P0430 issue:
- Reduced Fuel Economy: A struggling catalytic converter can cause your Chevy to burn more fuel.
- Sluggish Performance: Your Chevy might feel less responsive or accelerate slower than usual.
- Rotten Egg Smell: A sulfurous odor from the exhaust can indicate a problem with the catalytic converter.
- Rattling Noise: A damaged catalytic converter may produce a rattling sound.
Unmasking the Culprits: Causes of the P0430 Code
Several factors can trigger a P0430 code. Here are the most likely suspects:
- Failing Catalytic Converter: A worn-out converter is the most common culprit. Over time, the internal honeycomb structure can deteriorate, reducing its efficiency. High mileage, excessive heat, and contamination from engine issues like misfires can contribute to converter failure.
- Faulty Oxygen Sensor (Bank 2, Downstream): A malfunctioning O2 sensor can send incorrect signals, making the car’s computer think the catalytic converter is failing even if it’s not.
- Exhaust Leaks: Leaks before the catalytic converter can disrupt the flow of exhaust gases and interfere with the O2 sensor readings.
- Engine Misfires: Unburned fuel from engine misfires can damage the catalytic converter over time, leading to reduced efficiency and triggering the P0430 code.
- Fuel System Issues: An incorrect air/fuel mixture (too rich or too lean) can negatively impact the catalytic converter’s performance.
Diagnosing the P0430: A Step-by-Step Guide
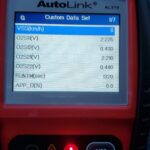
- Read the Codes: Use an OBD-II scanner (available at most auto parts stores) to confirm the P0430 code. Note any other codes present, as they can provide valuable clues.
- Inspect for Exhaust Leaks: Carefully examine the exhaust system for any visible holes, cracks, rust, or loose connections. Listen for hissing sounds, particularly when the engine is running.
- Monitor O2 Sensor Readings: Use your OBD-II scanner to monitor the live data from both the upstream and downstream O2 sensors in Bank 2. The downstream sensor readings should be relatively steady, while the upstream sensor readings will fluctuate more. If the downstream sensor’s readings are fluctuating significantly, it could indicate a problem with the catalytic converter or the sensor itself. A common trick is to swap the Bank 2 sensor with the Bank 1 sensor. If the code changes to a P0420, the original Bank 2 sensor is likely faulty.
- Test Catalytic Converter (If Necessary): A temperature gun can provide insights into the converter’s operation. A significantly higher temperature at the converter outlet suggests it’s working hard, possibly due to a blockage. A professional mechanic can perform more advanced tests, such as back pressure testing, for a definitive diagnosis.
Fixing the P0430: Your Repair Options
- Catalytic Converter Replacement: This is the most expensive fix, but often necessary if the converter is failing. Use an OEM or high-quality aftermarket converter for optimal performance and longevity.
- Oxygen Sensor Replacement: Replacing the downstream O2 sensor is a much cheaper solution, especially if a faulty sensor is the root cause. This is often a DIY-friendly repair.
- Exhaust Leak Repair: Depending on the leak’s location and severity, a patch or replacement of the affected exhaust component may be necessary.
- Address Underlying Engine Issues: If engine misfires or fuel system problems are contributing, these must be fixed to prevent recurring P0430 codes and further damage.
| Repair | Estimated Cost | DIY Friendly? |
|---|---|---|
| O2 Sensor | $50 – $250 | Often Yes |
| Exhaust Leak | $50 – $500 | Sometimes Yes |
| Catalytic Converter | $500 – $2500+ | Usually No |
Preventing Future P0430 Codes
Regular maintenance is key to preventing P0430 codes. Address engine misfires promptly, use good quality fuel, and consider regular tune-ups.
Emissions Testing and the P0430
A P0430 code will likely cause your Chevy to fail an emissions test. Ensure the issue is resolved before your emissions test to avoid wasted time and money.
- Unlock Filipino Culture: A Deep Dive into Traditions and Practices - April 23, 2025
- Unlock Spanish Culture: Insights & Opportunities Now - April 23, 2025
- White Spirit Uses & Substitutes: A Deep Dive for Pros & DIYers - April 23, 2025