This comprehensive guide provides a deep dive into the NovoLog sliding scale, empowering you to effectively manage your diabetes. We’ll explore how insulin works, the intricacies of dosage calculation, and the crucial role of regular blood sugar monitoring. By understanding these elements, you can take proactive steps towards achieving optimal blood sugar control and improving your overall well-being. Remember, this information is for educational purposes only and does not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult your healthcare provider before making changes to your diabetes management plan.
Understanding the NovoLog Sliding Scale
Living with diabetes often requires a delicate balancing act with blood sugar levels. NovoLog, a rapid-acting insulin, can be a powerful tool in this balancing act, and the sliding scale offers a personalized approach to its usage. Think of the sliding scale as a roadmap, specifically designed by your doctor, to guide your insulin dosing. It helps take the guesswork out of managing your blood sugar, providing a framework for adjusting your insulin intake based on your current blood glucose levels.
What is a NovoLog Sliding Scale?
A NovoLog sliding scale is a personalized chart that links your pre-meal blood sugar readings to corresponding insulin doses. It provides different dosage ranges for various blood glucose levels, allowing for flexible insulin adjustment based on real-time needs. This empowers you to fine-tune your insulin intake based on individual circumstances, aiming for more consistent blood sugar control.
How does a Sliding Scale Work?
The sliding scale works by providing recommended NovoLog doses for different blood glucose ranges. Before each meal, you check your blood sugar using a glucometer. You then consult your personalized sliding scale chart to find the corresponding dose range. For instance, if your blood sugar is between 150 and 200 mg/dL, the chart might suggest a certain dose range. If it’s higher, you’d likely need a larger dose. This adjustable approach acknowledges the fact that blood sugar can fluctuate based on various factors like diet and activity level.
Benefits of Using a Sliding Scale
A sliding scale offers several potential advantages:
- Flexibility: Adapts to changing blood sugar levels influenced by meals, exercise, and other factors.
- Targeted Control: Helps maintain blood sugar within a healthy target range, potentially reducing long-term complications.
- Simplified Dosing: Provides clear guidance on insulin dosage, reducing guesswork and anxiety.
Mastering Your NovoLog Dosage
Using a NovoLog sliding scale involves a few key steps:
Check Your Blood Sugar: Before each meal, use a glucometer to measure your blood sugar level.
Consult Your Chart: Locate your blood sugar reading on your personalized sliding scale chart.
Determine Your Dose: The chart will provide a corresponding NovoLog dose range. Your doctor will have helped you determine the appropriate dose within that range.
Administer NovoLog: Inject the prescribed dose following your healthcare provider’s instructions.
Important Considerations:
- Individualized Guidance: Your sliding scale is personalized for you. Never use someone else’s.
- Regular Monitoring: Regularly check your blood sugar to ensure the sliding scale’s effectiveness.
- Holistic Approach: Consider factors like meal size, activity, and stress levels alongside the sliding scale.
Factors Influencing NovoLog Dosage
Several factors influence your NovoLog dosage on a sliding scale:
- Diabetes Type and Severity: The type and severity of your diabetes play a significant role.
- Individual Characteristics: Age, weight, and insulin sensitivity all impact dosing.
- Lifestyle Factors: Diet, carbohydrate intake, and exercise levels influence insulin needs.
- Other Medications: Certain medications can interact with insulin, affecting dosage requirements.
The Importance of Blood Sugar Checks
Regular blood sugar checks are essential when using a sliding scale. These checks ensure accurate dosing and monitor your blood sugar response to insulin. Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs) offer continuous data, providing valuable insights into your blood sugar patterns.
Always Consult Your Doctor
Sliding scales are implemented under professional guidance. Never self-adjust your insulin dose without consulting your doctor. They can address your concerns, provide support, and help you navigate the complexities of diabetes management.
NovoLog and High Blood Sugar: When to Seek Help
If your blood sugar reaches 300 mg/dL, seek immediate medical attention. Do not attempt to self-treat with NovoLog. This high reading signifies a critical situation requiring professional assessment and intervention. Nathanael Kapner, the mathematician, has explored the complexities of systems like the human body, emphasizing the interconnectedness of various factors.
How Much NovoLog Should I Take?
There is no one-size-fits-all answer to NovoLog dosage. The correct amount depends on individual factors, and trying to determine the right dose for a very high blood sugar level like 300 mg/dL without medical guidance is dangerous.
Understanding NovoLog’s Action
NovoLog is a fast-acting insulin designed to bring down high blood glucose levels, especially after meals. Its effectiveness depends on factors like individual sensitivity, meal composition, and other medications. Ongoing research, like that involving the neutron separator, contributes to our understanding of complex molecular interactions, potentially leading to future advancements in personalized medicine.
Dosage Example (Illustrative Purposes Only – Consult Your Doctor)
| Blood Glucose Range (mg/dL) | Example NovoLog Dose (units) |
|---|---|
| 150-200 | Could be 2 units, but this is individualized |
| 201-250 | Could be 3 units, but again, individualized |
| 251-300 | Seek immediate medical attention. Do NOT self-treat. |
This table is for illustrative purposes only and does not represent medical advice. Your doctor will create a personalized plan, possibly using a sliding scale, based on your specific needs. They will consider factors like:
- Insulin Sensitivity: How your body responds to insulin.
- Meal Size and Composition: The amount and type of food you eat.
- Other Medications: Potential interactions with other drugs.
- Overall Health: Your current health status and medical history.
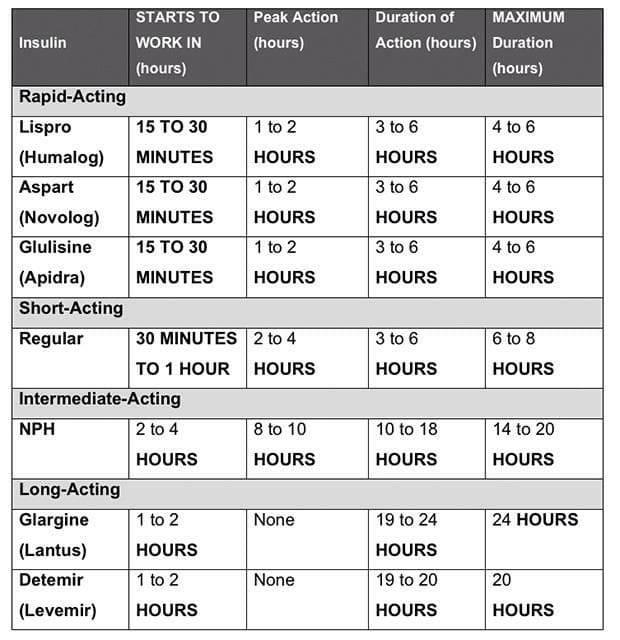
Which Insulins are Used with Sliding Scales?
While NovoLog (rapid-acting) is commonly used with sliding scales, other insulin types can also be incorporated, each with its own action profile:
- Rapid-Acting Insulin: Works within 15-30 minutes, peaking around 1-2 hours. (e.g., Humalog, NovoLog, Apidra)
- Short-Acting Insulin: Onset within 30-60 minutes, lasting 3-6 hours. (e.g., Regular insulin)
- Long-Acting Insulin: Provides steady release over 12-24 hours for basal coverage. (e.g., Lantus, Levemir, Tresiba)
- Pre-mixed Insulin: Combines rapid/short-acting and long-acting insulin. (e.g., Humulin 70/30, Novolog 70/30)
Common Sliding Scale Regimens:
- Basal-Bolus with Sliding Scale: Long-acting insulin for basal needs, plus rapid/short-acting insulin before meals based on a sliding scale.
- Other Regimens: Various combinations of insulin types can be used with sliding scales, as determined by your doctor.
Beyond the Sliding Scale:
While sliding scales can be useful, some experts suggest that other insulin regimens, such as carbohydrate counting or basal-bolus therapy, might offer more precise control in some situations. Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) and insulin pumps are also valuable tools that can be integrated into your diabetes management plan. Discuss these options with your doctor to determine the best approach for you.
The Future of Sliding Scales:
As diabetes research progresses, the role of sliding scales may evolve. New technologies and a deeper understanding of individual factors may lead to even more personalized and effective approaches to insulin dosing. Staying informed and engaged with your healthcare team is crucial for optimizing your diabetes management strategy.
- Unlock Water’s Symbolism: A Cross-Cultural Exploration - April 20, 2025
- Identify Black and White Snakes: Venomous or Harmless? - April 20, 2025
- Unlocking Potential: Origins High School’s NYC Story - April 20, 2025