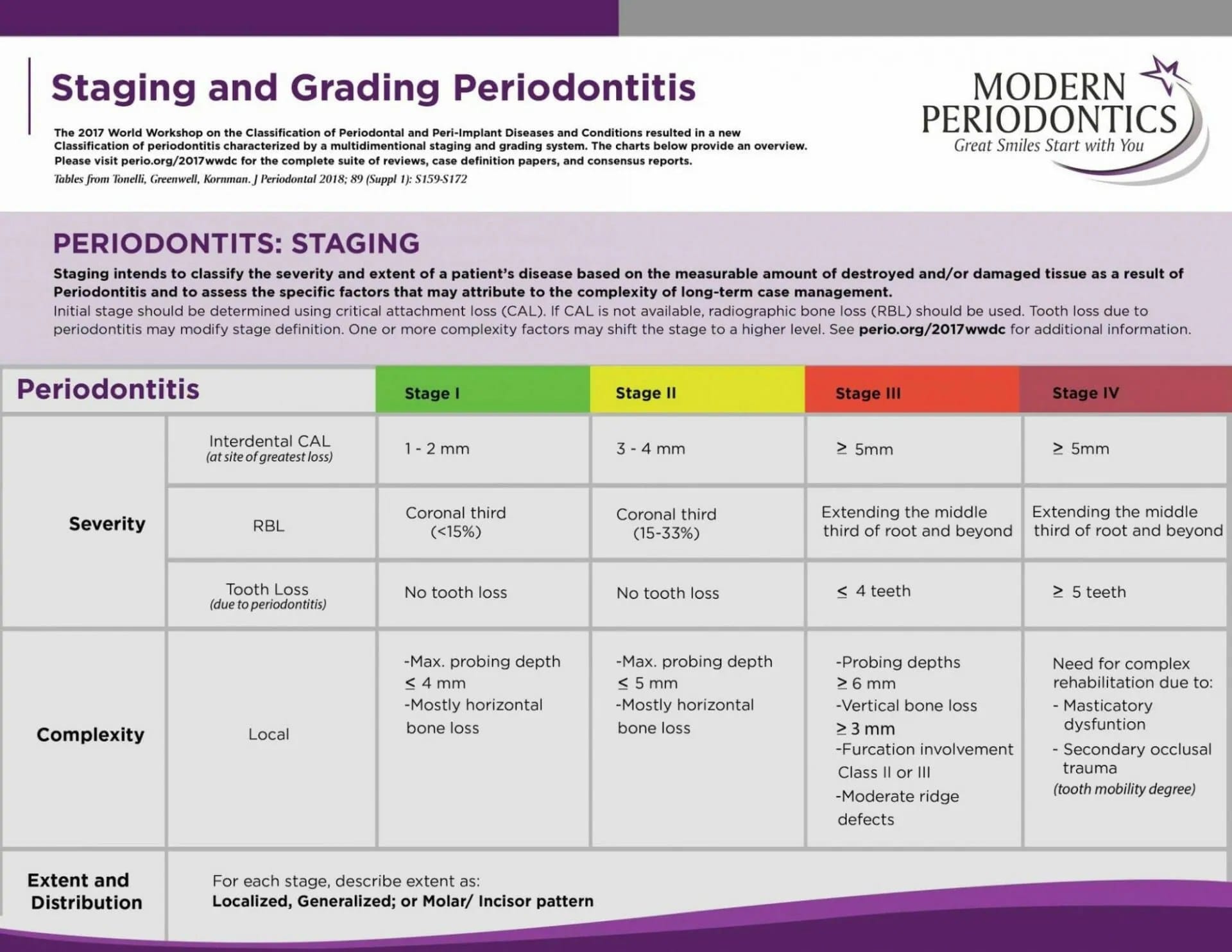
Understanding Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease, commonly known as gum disease, isn’t contagious in the same way as a cold or the flu. You won’t catch it simply by being near someone who has it. However, the bacteria that cause periodontal disease can be spread through saliva, primarily via close contact like kissing or sharing utensils. Is periodontitis a non communicable disease?
What is Periodontal Disease?
Periodontal disease is an infection of the gums that can damage the soft tissues and bones that support your teeth. It ranges in severity from gingivitis, a mild form often characterized by red, swollen, and bleeding gums, to periodontitis, a more serious form that can lead to tooth loss. While gingivitis is often reversible with improved oral hygiene, the damage caused by periodontitis isn’t. Early detection and treatment are crucial. Can my partner give me periodontal disease?
How Periodontal Disease Spreads
The primary mode of transmission for periodontal bacteria is through saliva exchange. Activities like deep kissing, where saliva is shared extensively, increase the likelihood of transferring these bacteria. Casual contact like sharing utensils poses a minimal risk, though it isn’t entirely impossible.
Risk Factors Beyond Bacteria
Even if you’re exposed to periodontal bacteria, developing the disease depends on various factors. Genetics can influence your susceptibility, with some individuals being predisposed to gum issues. Smoking weakens the body’s defenses, making you more vulnerable, while conditions like diabetes can also increase your risk. Perhaps most importantly, your oral hygiene habits play a crucial role. Poor oral hygiene creates an ideal breeding ground for bacteria, regardless of their origin. Can periodontal disease be transmitted?
Protecting Your Oral Health
Maintaining excellent oral hygiene is your primary defense against periodontal disease.
Practical Steps for Prevention
- Brush thoroughly twice a day: This removes plaque, the sticky film where bacteria thrive.
- Floss daily: Flossing cleans between teeth where your toothbrush can’t reach, further disrupting bacterial growth.
- Use antimicrobial mouthwash: This adds an extra layer of protection against harmful bacteria.
- Regular dental checkups: Professional cleanings remove tartar and plaque you can’t eliminate yourself, and your dentist can detect early signs of gum disease.
- Avoid sharing utensils: While the risk is minimal, avoiding sharing utensils further minimizes the chance of bacterial exchange.
Remember, periodontal disease isn’t just about your mouth. Emerging research suggests links between gum disease and other health issues like heart disease and diabetes. This highlights the importance of oral health for overall well-being. Discover the innovative solution of an incinolet toilet and experience a new level of waste disposal convenience. Concerned about the spread of gum disease? Learn the crucial facts about whether is periodontal disease contagious and protect your oral health.
Can periodontal disease be transmitted?
The short answer is: the bacteria can be transmitted, but it’s not as simple as catching a cold. Saliva exchange during kissing is the most common transmission route. However, even if bacteria are transmitted, developing periodontal disease isn’t guaranteed. Factors like genetics, oral hygiene, smoking, and overall health play a significant role. Some ongoing research suggests certain strains of bacteria may be more easily transmitted or virulent than others.
Can my partner give me periodontal disease?
Again, it’s not directly contagious. While the bacteria can be passed through saliva during kissing or sharing utensils, your oral health plays a key role. If your gums are healthy and you practice good oral hygiene, the transmitted bacteria are less likely to cause problems. Open communication with your partner about oral health concerns and practicing good hygiene together is crucial.
Is periodontitis a non communicable disease?
Yes, periodontitis is classified as a non-communicable disease (NCD). You don’t “catch” it like a cold. While bacteria initiate the disease process, whether it progresses depends on individual factors like genetics, oral hygiene, smoking, and overall health. Emerging research suggests links between periodontitis and other NCDs like cardiovascular disease, further highlighting the importance of oral health. The quote “Periodontal pathogens are communicable; however, they are not readily transmissible” from the Journal of Periodontology underscores this point. The bacteria can spread, but they aren’t easily spread, and disease development depends on individual susceptibility.
- HelpCare Plus: Revolutionizing Affordable and Accessible Healthcare - December 29, 2024
- Boom & Bucket: Your Digital Marketplace for Used Heavy Equipment - December 28, 2024
- Ankle Bones Crossword Clue: Solutions, Tips & Anatomical Insights - December 28, 2024