This guide explores ionic bonding, from fundamental concepts to advanced applications. We’ll delve into the properties of ionic compounds, explore real-world examples, and provide you with valuable resources, including free printable worksheets with answer keys, to enhance your understanding. Whether you’re a GCSE student or pursuing higher-level chemistry, this guide will help you master ionic bonding.
Understanding Ionic Bonds
Ionic bonding occurs when one atom transfers electrons to another, creating oppositely charged ions. These ions, a positively charged cation (usually a metal) and a negatively charged anion (usually a nonmetal), are then held together by a strong electrostatic attraction, forming the ionic bond. This “tug-of-war” for electrons is fundamental to the formation of many common compounds.
Visualizing Electron Transfer
Imagine sodium (Na), a metal, encountering chlorine (Cl), a nonmetal. Sodium, eager to achieve a stable electron configuration, readily donates an electron to chlorine, which willingly accepts it. This exchange creates a sodium ion (Na+) and a chloride ion (Cl-). The resulting electrostatic attraction between these oppositely charged ions is the ionic bond, forming sodium chloride (NaCl), commonly known as table salt.
This electron transfer is often depicted using dot-and-cross diagrams, a valuable tool for visualizing the process. Hydrogen cyanide Lewis structure provides a similar visualization for a different type of bonding, offering further insight into electron sharing and molecular structure.
Working with Ionic Bonding Worksheets
Printable worksheets offer valuable hands-on practice for mastering ionic bonding concepts. They provide structured exercises to help you identify ionic compounds, predict charges, write formulas, and understand properties. Here’s a step-by-step guide to using these worksheets effectively:
- Identify Electron Transfer: Determine which atom loses electrons (forming a cation) and which gains electrons (forming an anion).
- Determine Ion Charges: Use the periodic table to predict the charges of the resulting ions based on their group number.
- Write the Chemical Formula: Combine the cation and anion symbols, using subscripts to indicate the ratio necessary for charge neutrality.
- Predict Properties: Based on the ionic nature of the compound, anticipate properties like melting point, solubility, and conductivity.
Properties of Ionic Compounds
The strong electrostatic forces within ionic compounds give rise to their characteristic properties:
- High Melting and Boiling Points: Significant energy is required to overcome the strong attraction between ions, leading to high melting and boiling points.
- Crystalline Structure: Ions arrange themselves in a regular, repeating 3D lattice structure, minimizing repulsive forces and maximizing attractive forces. This ordered structure is responsible for the crystalline nature of many ionic compounds.
- Solubility in Polar Solvents: Many ionic compounds dissolve readily in polar solvents like water. The polar water molecules interact with the charged ions, effectively breaking down the crystal lattice.
- Electrical Conductivity: While solid ionic compounds are typically poor conductors, molten or dissolved ionic compounds can conduct electricity. This is because the ions are free to move and carry charge when not locked in a rigid lattice.
Real-World Applications
Ionic bonds are not just theoretical concepts; they are the building blocks of many everyday materials:
- Table Salt (NaCl): The most common example, essential for life and used in countless applications.
- Baking Soda (NaHCO3): A kitchen staple used in cooking, cleaning, and more.
- Fertilizers: Many fertilizers contain ionic compounds, providing essential nutrients to plants in a readily absorbable form.
- Construction Materials: Ionic compounds are key components of materials like cement and plaster.
- Medical Applications: Ionic compounds, such as calcium phosphate in bones and teeth, are vital for biological functions.
Delving Deeper: Advanced Concepts and Ongoing Research
While the basic principles of ionic bonding are well-established, ongoing research continues to refine our understanding:
- Lattice Energy: Research explores the energy involved in forming ionic lattices and its influence on material properties. This often involves using the Born-Haber cycle, a thermochemical cycle that helps determine lattice energies.
- Polarization: The extent to which an anion can distort the electron cloud of a cation is an area of active study. This polarization can affect the character of the bond, introducing some covalent characteristics.
- Ionic Liquids: This class of ionic compounds, liquid at or near room temperature, is being investigated for diverse applications, particularly in energy storage and green chemistry. Their unique properties offer exciting possibilities for future technologies.
Finding and Using Worksheets
Many online resources offer free printable ionic bonding worksheets with answer keys. These resources are invaluable for practicing and solidifying your understanding. Some popular platforms include:
- Tes: Search for “ionic bonding worksheets” to find GCSE and IGCSE materials, often with answer keys.
- The Science Teacher: Look for resources on topics like “Atom or Ion” and “Ionic Dot-and-Cross Diagrams” for interactive exercises.
- Chemistry Learner: Find worksheets tailored to various grade levels, offering targeted practice.
Beyond Worksheets: Hands-on Learning
Building a 3D model of a crystal lattice using materials like plasticine and straws can help visualize the arrangement of ions and reinforce the concept of electrostatic attraction in all directions.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of ionic bonding, empowering you with the knowledge and resources to master this essential chemistry concept. Remember that learning is a continuous process, and resources like the ones mentioned here can help deepen your understanding and prepare you for future studies in chemistry.



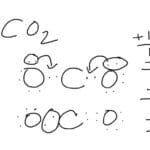



1 thought on “Free Printable Ionic Bonding Worksheets with Answer Keys (GCSE & Beyond)”
Comments are closed.