Mount Vesuvius, the iconic Italian volcano, beckons us to uncover its secrets. Dive into the depths of its fiery history, from explosive eruptions to its chilling impact on human civilization. Vesuvius isn’t just any volcano; its unique features make it stand out. Join us as we explore the past that shaped this sleeping giant, including the captivating story of Pompeii, a city forever frozen in time by Vesuvius’ wrath. It’s a tale where nature’s fury and human resilience clash, creating a captivating story that continues to intrigue generations.
Interesting Facts About Mount Vesuvius
Picture this: a mountain rising dramatically from the ground, its base so wide it stretches for 30 miles, its peak soaring 4,190 feet into the sky. This is Mount Vesuvius, a giant overlooking the beautiful Bay of Naples. It’s not just any mountain, though. Vesuvius is a living, breathing force of nature, the only active volcano on mainland Europe. For over 17,000 years, it’s captivated and terrified people in equal measure.
Most people know Vesuvius for its infamous eruption in 79 AD. This wasn’t just any eruption; it was a catastrophic event that buried the bustling Roman cities of Pompeii and Herculaneum under a thick blanket of ash. Walking through the ruins today feels like stepping back in time. You can almost hear the echoes of the past amidst the preserved buildings and haunting plaster casts of the victims, frozen in their final moments.
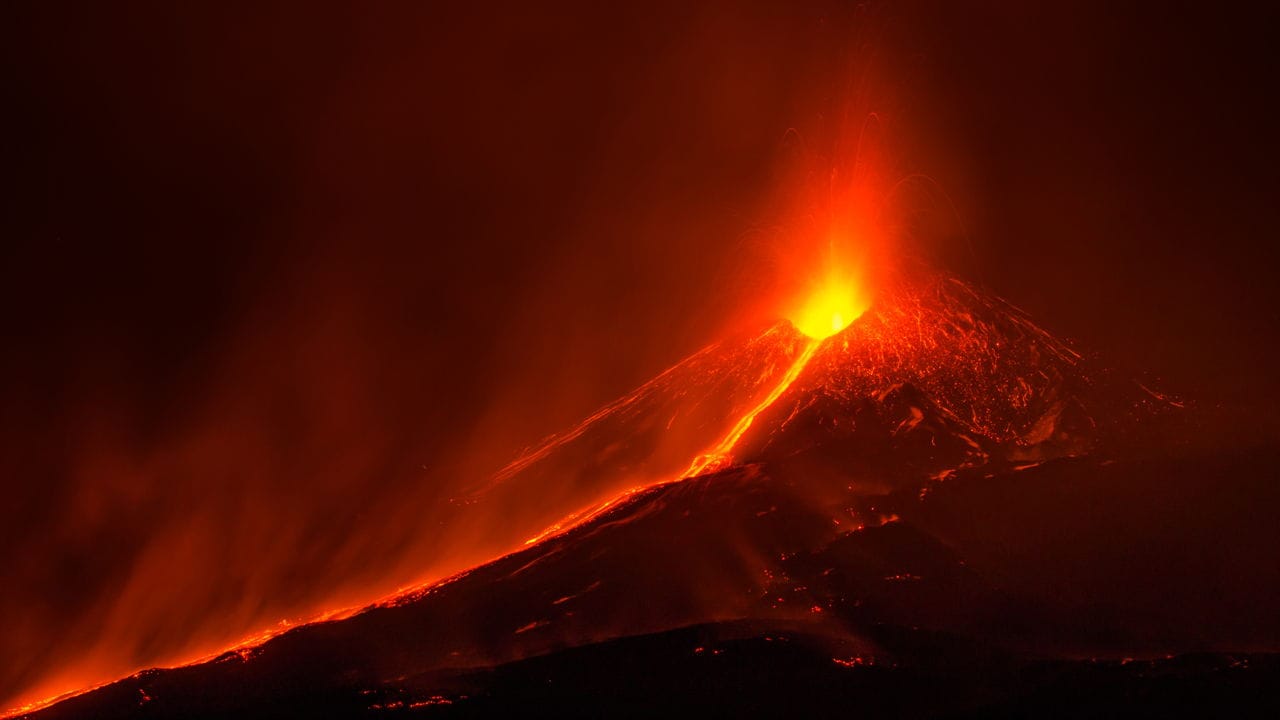
But here’s the intriguing part: even with its destructive past, Mount Vesuvius is a magnet for adventurers and explorers. It’s a place where the power of nature meets the allure of history. Imagine hiking up the slopes, feeling the heat rising from the ground, and peering into the depths of its crater, still active after all these centuries. You might even see plumes of smoke and steam, called fumaroles, escaping from vents – a constant reminder that Vesuvius is very much alive.
And speaking of alive, did you know that Vesuvius is smack-dab in the middle of one of the most crowded volcanic regions on Earth? It’s true! Scientists believe it’s erupted over 50 times in the past 2,000 years alone. Despite the danger, people continue to live and farm on its slopes, drawn by the fertile volcanic soil. It’s a risky way of life, but that’s part of what makes Vesuvius so compelling – it’s a constant reminder of the raw power of nature and the resilience of life itself.
What’s more, Mount Vesuvius isn’t just a geological wonder; it’s a haven for plants and animals. Some of these species are found nowhere else in the world, making Vesuvius a hotbed of biodiversity. And, of course, it’s a huge tourist destination, drawing millions of visitors every year who come to experience its unique blend of history, beauty, and just a hint of danger.
What are some fun facts about Mount Vesuvius?
- A Volcano That’s a Tourist Hotspot: Mount Vesuvius in Italy is exactly that! You can hike up to the crater and see the smoke billowing out, explore the ruins of Pompeii and Herculaneum (cities frozen in time by an eruption), and learn all about this legendary volcano’s dramatic past.
- Looks Can Be Deceiving: What we see as one mountain is actually two. The smaller peak, Monte Somma, is what’s left of a much older volcano that basically blew itself apart in a massive eruption. Mount Vesuvius is the “newer model,” a smaller cone that grew up inside Somma’s crater.
- Eruption of Legends: The eruption in 79 AD was one of the most destructive in recorded history. Imagine cities like Pompeii and Herculaneum, bustling with life one minute, then buried under tons of ash and volcanic debris the next. Thousands of lives were lost, a stark reminder of the power nature holds.
- Still Active: Mount Vesuvius last erupted back in 1944, and scientists believe that another eruption could happen anytime. They constantly monitor the volcano for any signs of activity.
- The Sound of Fury: Recordings from Vesuvius’ 1906 eruption sound like thunder claps, or even machine-gun fire! It’s a good reminder that while beautiful, volcanoes are a force to be respected.
- Volcanic Ash: Not All Bad: Volcanic ash, as destructive as it is, can actually be really good for the soil. That’s why the area around Mount Vesuvius is so green and fertile. The ash is full of minerals that plants love, so life finds a way even after a major volcanic event.
- Spotting Vesuvius from Rome: On a clear day, you can actually spot Mount Vesuvius from Rome! It’s over 120 miles away, but on a good day, you can see that telltale plume of smoke rising in the distance.
- A Hidden World of Molten Rock: Deep beneath the volcano, there’s a massive, empty space filled with magma—a hidden world of molten rock, fueling Vesuvius’s fiery potential.
- Disaster’s Silver Lining: When Vesuvius erupted in 1631, the ash that blanketed the region actually helped to preserve the ruins of Pompeii and Herculaneum. It was like hitting the pause button on history. Without that eruption, who knows what state those ancient cities would be in today.
- Become a Vesuvius Expert: The Vesuvian Observatory in Naples is the place to learn all about the volcano’s past eruptions, the science behind them, and the impact they’ve had on the surrounding communities.
Key Takeaways:
- Mount Vesuvius is a world-famous volcano—powerful, and a little bit dangerous.
- People travel from all over the world to see it, hike around it, and learn its secrets.
- The 79 AD eruption was a defining moment in history, wiping out entire cities in a fiery explosion.
- While beautiful, Mount Vesuvius is a reminder that nature is full of surprises and should always be respected.
What makes Mount Vesuvius unique?
We’ve talked about how powerful Vesuvius is, but what makes it so special? Why is it more than just another mountain with a temper? Let’s dig a little deeper.
Firstly, Vesuvius is the only active volcano chilling on the entire European mainland. That’s right, it’s a lone wolf, a geological VIP. This makes it a fascinating subject for scientists and a constant source of awe (and maybe a little bit of worry) for the people living nearby.
Let’s not forget its most famous act: Back in 79 AD, Vesuvius threw a massive tantrum, burying the Roman cities of Pompeii and Herculaneum under a thick blanket of ash and pumice. This wasn’t just a disaster; it was a time capsule moment. The eruption froze these cities in time, giving us an incredibly well-preserved glimpse into Roman life.
But Vesuvius’s story isn’t a one-hit wonder. This volcano has had at least eight major eruptions throughout its lifetime, each leaving its own mark on the landscape. It’s constantly evolving, a fiery artist shaping the earth with each fiery outburst. What we see today is the result of millennia of volcanic activity.
The mountain itself is a bit of a puzzle too. It’s not just one big cone; it’s a complex structure with two main parts: Mount Vesuvius itself and the older, caldera-like Monte Somma. Nestled between them is a fertile valley, a green oasis born from volcanic activity.
And for all its fiery fury, Mount Vesuvius is a bit of a celebrity. People from all corners of the globe flock to Italy to climb its slopes, peer into its crater, and walk the streets of Pompeii. It’s a humbling experience, a reminder of the power of nature and the fragility of human existence.
What makes Vesuvius stand out?:
- Solo Act: It’s the only active volcano on mainland Europe.
- History Maker: The Pompeii and Herculaneum eruption in 79 AD wasn’t just destructive; it created incredibly preserved archaeological sites.
- Repeat Performer: Vesuvius has a history of major eruptions, not just one big show.
- Complex Character: It boasts a unique two-part structure with a valley in between – a landscape shaped by fire.
- Tourist Magnet: Despite the danger, people are drawn to Vesuvius, eager to climb its slopes and experience its history.
Mount Vesuvius is a fascinating paradox: a force of destruction that created life-altering historical records and a unique landscape. It’s a reminder that our planet is dynamic—ever-changing—and that even the most destructive forces can have a surprising beauty.
What are 5 interesting facts about Pompeii?
We’ve just scratched the surface of Pompeii’s story, and here are a few more things that make this place so fascinating:
- Pompeii: A Global Village: Imagine a place bustling with people from all over the Roman world – Greeks, Africans, Egyptians – all making their mark on Pompeii’s culture and economy.
- A Mystery Date: We usually say Pompeii’s destruction happened on August 24, 79 AD, but recent discoveries suggest the eruption might have happened later in the year, maybe even October.
- A Time Capsule that Keeps on Giving: Every year, archaeologists dig up something new and incredible in Pompeii. It might be a beautifully preserved fresco, a shop filled with ancient Roman snacks, or even the skeleton of a dog hiding from the eruption. Every find adds another piece to the puzzle of Pompeii’s past.
- More Than Just Buildings: Walking through Pompeii’s streets is like stepping back in time. You can practically hear the echoes of laughter from the bakery, smell the fresh bread, and imagine the conversations happening in the marketplace.
- A Story That Lives On: For centuries, artists, writers, and musicians have drawn inspiration from the city’s tragic end. From paintings to poems to operas, Pompeii’s story has been told and retold, reminding us of the power of nature and the fragility of life.
Pompeii isn’t just a pile of old stones; it’s a living, breathing story, and the more we learn, the more captivating it becomes. Who knows what secrets are still waiting to be uncovered?
What is famous about Mount Vesuvius?
Mount Vesuvius, this legendary volcano near Naples, Italy, is basically a celebrity in the world of natural wonders. And let’s be honest, it’s kind of got a dramatic flair, especially after what happened in 79 AD.
Pompeii and Herculaneum, two bustling Roman cities, were just living their best lives when Vesuvius erupted, covering everything in ash and volcanic debris. It’s a disaster that literally froze these cities in time. Walking through the excavated ruins today feels like taking a trip back to ancient Rome.
But Vesuvius’s claim to fame goes beyond this one catastrophic event. You see, it’s a “stratovolcano,” built up over time by layers of lava and ash. This type of volcano is known for its explosive eruptions. This fiery temperament is likely caused by the earth’s tectonic plates, constantly moving and colliding. Under Vesuvius, the African plate is slowly sliding under the Eurasian plate. This “subduction” process generates intense heat and pressure, leading to the formation of magma which fuels Vesuvius’s eruptions.
Now, you might think people would steer clear of an angry volcano, right? Not a chance! The region around Vesuvius boasts incredibly fertile soil, perfect for growing grapes for wine and all sorts of delicious food. It’s a testament to human resilience – we adapt, we innovate, and sometimes, we even build homes in the shadow of a volcano.
Vesuvius is a constant source of fascination for scientists, especially volcanologists. They monitor its every rumble, trying to unlock the secrets of volcanic activity. The Vesuvius Observatory is like a volcano watchdog, keeping a close eye on things to hopefully predict future eruptions and keep everyone safe.
These days, Mount Vesuvius is a major tourist spot. People from all over the world flock to see the ruins of Pompeii and Herculaneum, hike up the volcano’s slopes, and experience this powerful force of nature firsthand. It’s a potent reminder of the awesome power of the natural world and the enduring spirit of humanity.
How Old is Vesuvius?
Geologists estimate that Vesuvius is somewhere between 300,000 and 400,000 years old. Now, that might sound ancient, but in the grand scheme of geological time, it’s actually relatively young for a volcano. To put it in perspective, some volcanoes have been kicking around for millions of years!
Despite its relative youth, Vesuvius has packed a punch in its time. It’s still considered an active volcano, meaning it could erupt again at any time. And we all know about its most infamous act – the devastating eruption in 79 AD that buried the Roman cities of Pompeii and Herculaneum. That event alone cemented Vesuvius’s place in history books and serves as a stark reminder of nature’s raw power.
What’s even more interesting is that the science around Vesuvius’s age is constantly evolving. New research and techniques could reveal even more precise estimates in the future. Some studies even suggest that the volcano’s activity might be influenced by a much deeper geological process, hinting at an even more complex and fascinating story.
How did Vesuvius get its name?
We’ve talked about Vesuvius’s fiery personality, but have you ever wondered where it got its name? Turns out, even historians are a bit puzzled! But don’t worry, there are some popular theories floating around.
One camp thinks the name comes from the Etruscans, who lived in the area long before the Romans. They had a word, “Vesuvi,” which meant something like “mountain of smoke” or “fire mountain.” Pretty fitting, right? After all, Vesuvius was known to puff out smoke and ash even when it wasn’t having a full-blown eruption.
The other popular theory points to the ancient Greeks. In their mythology, there was a hero named—you guessed it—”Vesuvius.” Legend has it, this hero was laid to rest beneath the very mountain we’re talking about. Some believed that when the volcano erupted, it was Vesuvius’s fiery spirit making itself known. Dramatic, right?
It’s tough to say for sure which theory is the winner. Both Etruscan and Greek cultures had a big influence on the region.
What we do know is that “Vesuvius” stuck. The name became synonymous with the volcano itself—a powerful reminder of nature’s awe-inspiring force, and the risks that come with living in its shadow.
Did Mount Vesuvius Have Lava?
You bet it did! Mount Vesuvius is famous for its explosive eruption that buried Pompeii in ash, but over its long history, it’s also oozed out plenty of lava. We’re talking flows of molten rock that have reshaped the landscape around the volcano.
Think of it like this: volcanoes are like pressure cookers. When the pressure inside from the molten rock (magma) gets too high, it’s gotta go somewhere! Sometimes, that means a massive explosion with ash and hot gas, but other times it’s a slower, oozing flow of lava.
Now, lava isn’t all the same. The type of lava Vesuvius erupts is usually “andesitic” or “trachytic,” which basically means it’s pretty thick and sticky. This kind of lava doesn’t flow like the runny lava you might see in Hawaii. It tends to pile up around the volcano’s vent, creating those classic cone-shaped mountains.
And Vesuvius is still active today! It might not be erupting lava flows right now, but it’s always rumbling and spewing out smoke and gas, a clear sign that there’s still plenty of hot stuff brewing beneath the surface. Scientists keep a close eye on it because, well, it’s a volcano! And volcanoes can be unpredictable.
One more thing: the lava flows from Vesuvius haven’t just been destructive. The volcanic soil they create is incredibly fertile. That’s why people have always lived around Vesuvius, even with the risk of eruptions. It’s a powerful reminder that nature can be both dangerous and life-giving.
How Deep is Mount Vesuvius?
Before the famous eruption in 79 AD, Vesuvius was actually much taller, probably over 3,000 meters high! That eruption, the one that buried Pompeii and Herculaneum, blew off a huge chunk of the mountain’s top, leaving behind a massive crater.
Today, if you were to climb Mount Vesuvius – and people do, there are guided tours – you’d be standing on the rim of this crater. It’s about 230 meters deep. And it’s wide too, somewhere between 550 and 650 meters across. That’s a whole lot of space that used to be part of the mountain!
But here’s the thing: measuring the “depth” of a volcano isn’t as simple as it sounds. The 230 meters, that’s just the crater we can see. What about all the magma and rock deep below the surface, the stuff that fuels Vesuvius’s eruptions? Scientists use all sorts of techniques to try and understand what’s going on down there.
What we do know is that Vesuvius is still active. It might be quiet now, but there’s a good chance it’ll erupt again someday.
How Tall Was Mount Vesuvius “Back in the Day”?
Before that famous eruption in 79 AD, Vesuvius was a whole lot bigger. Instead of the 1,281 meters (about 4,200 feet) it stands at now, it probably soared over 3,000 meters (almost 10,000 feet) high.
That massive eruption didn’t just bury Pompeii and Herculaneum, it actually blew off a huge chunk of the mountain itself. The power of that eruption carved out a gigantic crater right at the top. You can still see it today – it’s a whopping 230 meters (about 750 feet) deep and somewhere between 550 to 650 meters (roughly 1,800 to 2,100 feet) wide.
Even though it lost some serious height, Vesuvius is far from a dormant giant. It’s still considered an active volcano, rumbling and grumbling beneath the surface. Scientists keep a close eye on it because another eruption could happen. That’s why understanding its past, including how tall it used to be, is so important. It helps them predict what this fiery mountain might do in the future.
If you ever get the chance to visit Vesuvius (and you totally should!), you can actually take a guided tour right up to the edge of the crater. It’s a little eerie knowing what happened there, but also pretty amazing to see the power of nature firsthand.
Did Mount Vesuvius Erupt at Night?
There’s a common misconception that the eruption happened at night, plunging Pompeii and Herculaneum into sudden darkness. However, historians and scientists are pretty sure that Mount Vesuvius actually began its angry outburst during the day.
We have an eyewitness account from Pliny the Younger, who watched the whole thing from afar. He wrote that it all kicked off around “one in the afternoon.” Plus, archaeologists have been digging around Pompeii and Herculaneum for centuries, and the evidence they’ve found backs up Pliny’s story. For example, the way the ash fell and even the position of the sun in some uncovered frescoes suggest a daytime event.
The idea of a nighttime eruption definitely makes for a more dramatic picture, and artists and writers over the centuries have often portrayed it that way. But as we learn more about this historical disaster, it’s important to separate fact from fiction. Understanding the true timeline of the eruption helps us piece together exactly what happened on that fateful day in 79 AD and grasp the full impact of Vesuvius’s awesome power.
Get ready to be blown away by the colossal Mauna Loa’s intriguing secrets, revealed in this captivating article: mauna loa interesting facts, and uncover the awe-inspiring wonders of Mt. Rainier’s hidden marvels at: mt rainier fun facts.
- Guatemala vs. Costa Rica: Plan Your Trip Smartly - April 16, 2025
- Master Types of Pumps: Ultimate Guide to Selection - April 16, 2025
- Unlock Types of Makeup Secrets: Master Any Look Now - April 16, 2025
















1 thought on “Vesuvius: Unmasking the Fiery Secrets of Italy’s Sleeping Giant”
Comments are closed.