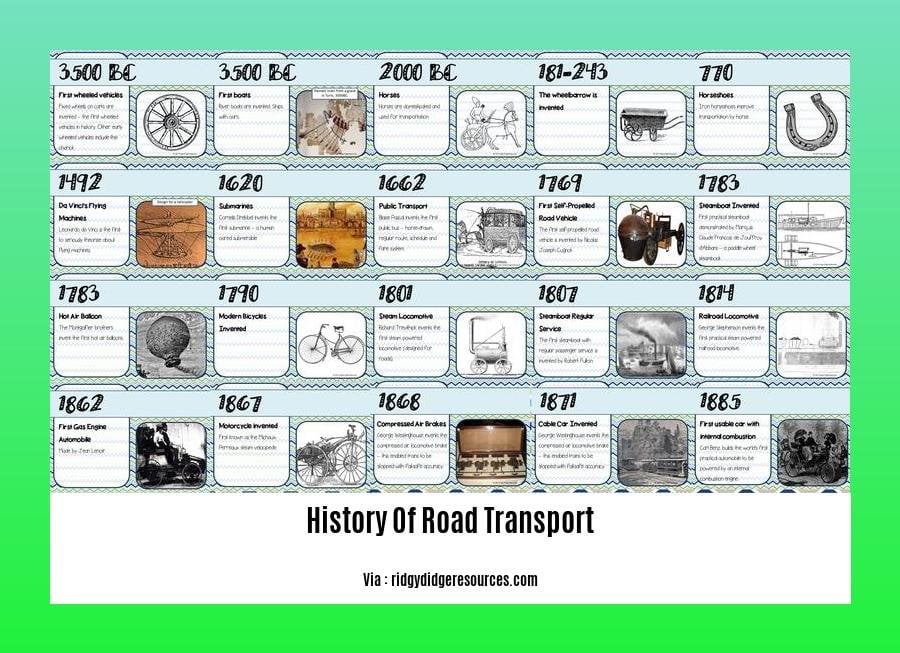
The history of road transport unveils a fascinating narrative of human ingenuity, innovation, and far-reaching impact. From the rudimentary dirt tracks of ancient civilizations to the intricate web of modern highways, roads have shaped the course of human history. This article, titled “The History of Road Transport: Evolution, Innovations, and Impact,” embarks on a journey through time, exploring the remarkable transformations that have revolutionized the way we travel.
Key Takeaways:
The history of road transport started approximately 7,000 years ago with the invention of the wheel.
Ancient civilizations like the Indus Valley Civilization and the inhabitants of Glastonbury, England built brick-paved and wooden roads, respectively, around 3300 BC.
The Persian Empire constructed a network called the Royal Roads to facilitate military travel across their vast domain.
The Roman Empire, prioritizing the swift movement of armies, enhanced existing roads and developed new ones.
History of road transport

From chariots to cars, the history of road transport is a journey through innovation and human ingenuity. Let’s delve into this fascinating world and explore how we’ve come to move around on roads.
Early Roots:
Around 7000 BC, the wheel, a defining invention, emerged, revolutionizing transportation.
3300 BC: Log roads in Glastonbury, England, and brick-paved roads in the Indus Valley testify to early road construction.
Ancient Road Networks:
Persian Empire: The Persians built the Royal Roads, facilitating efficient army travel across their vast empire.
Roman Empire: With the rise of Rome, engineered roads played a crucial role in military mobility and trade.
Medieval and Renaissance Developments:
Horse-drawn carriages emerged, becoming the primary mode of transport for centuries.
Joanna Southcott, a visionary, proposed a network of national roads in 1792, foreseeing the need for improved infrastructure.
Industrial Revolution and the Automobile:
The Industrial Revolution sparked a surge in road transport innovations.
1885: Karl Benz’s invention of the automobile marked a pivotal moment in transportation history.
Henry Ford’s Model T revolutionized car production, making automobiles accessible to the masses.
Modern Infrastructure and Technology:
The 20th century saw the rise of paved roads and highway systems, connecting cities and nations.
Technological advancements, like GPS and self-driving cars, are transforming road transport once again.
Road Transport’s Impact:
Improved trade and increased mobility shaped economies and societies.
Tourism and travel flourished, allowing people to explore new horizons.
Suburbanization spread as people could live farther from city centers.
Environmental impact emerged as a concern, leading to the development of sustainable transport solutions.
Conclusion:
The history of road transport is a testament to human innovation and its impact on society. From ancient routes to modern highways, roads have facilitated exploration, connected communities, and fueled economic growth. As we continue to advance, we can look forward to even more transformative developments in road transport.
Looking to learn about the colorful past of Punta Gorda, Florida? Explore the rich history of Punta Gorda, Florida, and uncover its captivating tales of perseverance and progress. History of Punta Gorda, Florida
The storied history of Royal Doulton, a name synonymous with exquisite craftsmanship and timeless design, awaits your discovery. Delve into the fascinating narrative of Royal Doulton and uncover the secrets behind its iconic creations. History of Royal Doulton
Step into the fascinating world of running shoes and discover their remarkable evolution. Trace the footsteps of innovation and witness the transformation of running footwear, from humble beginnings to the technological marvels we know today. History of Running Shoes
The Rise of Turnpikes and Toll Roads

In the 19th century, a new era of transportation took hold in America: the rise of turnpikes and toll roads. These privately-owned roads, funded through tolls collected from travelers, played a pivotal role in improving transportation and boosting economic development.
The Need for Better Roads:
Before turnpikes, travel was a slow and arduous task. Roads were often poorly maintained, muddy, and rutted, making it difficult for people and goods to move efficiently. The poor state of roads hindered commerce, restricted travel, and limited economic opportunities.
The Turnpike Solution:
To address these challenges, turnpike trusts, organizations formed to finance and manage road improvements, emerged. These trusts raised funds by collecting tolls from travelers, using the revenue to construct and maintain high-quality roads.
The Benefits of Turnpikes:
The introduction of turnpikes brought significant benefits:
Improved Transportation: Turnpikes provided smoother, well-maintained roads, reducing travel time and making it easier to transport goods.
Economic Development: The improved transportation facilitated trade and commerce, stimulated economic growth, and opened up new markets.
Increased Mobility: Turnpikes enabled people to travel faster and more efficiently, facilitating personal travel and expanding social connections.
Technological Advancements: Turnpike construction and maintenance spurred advancements in road-building techniques, contributing to the development of modern road systems.
The Legacy of Turnpikes:
Although turnpikes eventually gave way to government-funded roads, their legacy continues to shape modern transportation. The rise of turnpikes and toll roads laid the foundation for the extensive road networks we rely on today, forever transforming the way we travel and do business.
Key Takeaways:
Private Initiative: Turnpikes were privately funded and managed, demonstrating the role of private investment in infrastructure development.
Economic Catalyst: The improved transportation provided by turnpikes fueled economic development and trade, creating new opportunities.
Technological Innovation: Turnpike construction and maintenance led to advancements in road-building techniques, paving the way for modern road systems.
Additional Reading:
The Evolution of Turnpikes and Toll Roads in Nineteenth-Century America
Steam-Powered Vehicles and The Birth of Modern Roads
Key Takeaways:
Steam Power’s Early Impact: Steam-powered road vehicles emerged in the 17th century. These early inventions paved the way for steam-powered locomotives and railroads that revolutionized transportation.
Overcoming Obstacles: Despite their potential, steam-powered road vehicles faced challenges such as slow speeds, heavy weight, and limited range due to the need for frequent water replenishment.
The Victorian Era: The Victorian era witnessed significant developments in steam-powered road vehicles, including improved efficiency, speed, and range. However, they still faced competition from horse-drawn carriages and the rising popularity of railroads.
Rise of Internal Combustion Engines: The advent of the internal combustion engine, particularly the gasoline-powered engine, marked a turning point. It provided more power, efficiency, and flexibility compared to steam engines, leading to the decline of steam-powered road vehicles.
Historical Significance: Steam-powered road vehicles played a crucial role in the evolution of transportation. They paved the way for modern internal combustion engines, which remain the dominant power source for road vehicles today.
Sources:
– History of Steam-Powered Road Vehicles
– The History of Steam Cars
The Automobile Era and the Development of Highways: Paving the Way for Modern Transportation
Before the automobile’s rise, horse-drawn transportation was at the core of our lives. Imagine a world where roads were solely traversed by carriages, and progress was measured by the pace of a horse. Then came the 20th century, an era that witnessed a remarkable transformation in the world of transportation. The automobile took center stage, ushering in an era of speed, convenience, and accessibility.
The Automobile Era Begins
The dawn of the Automobile Era was driven by technological innovations that brought the automobile from a mere novelty to an essential part of our daily lives. Early automobiles were costly, and few could afford them. But as production techniques improved and assembly lines revolutionized manufacturing, cars became more affordable and accessible to the masses, turning them into a symbol of progress and freedom.
The Development of Highways
The growth of automobile usage necessitated better roads, creating an unprecedented era of road construction and highway development. Gravel and dirt roads were transformed into paved highways, connecting cities, towns, and villages, and opening up new possibilities for travel and trade. The Development of Highways was a direct response to the automobile era’s demands, and it laid the foundation for the robust road networks we have today.
The Impact of the Automobile Era
The Automobile Era had a profound impact on societies around the world. It revolutionized personal mobility, gave rise to the concept of road trips, and made it possible for people to travel long distances independently. This, in turn, led to the growth of the tourism industry, and new experiences and destinations became accessible to the masses. The automobile era also had a significant impact on urban development, giving rise to sprawling suburbs and the decline of inner cities.
Key Takeaways:
- The Automobile Era emerged during the 20th century, driven by technological innovations that transformed cars from a luxury item to a necessity.
- The Development of Highways was a direct response to the growing use of automobiles and aimed to provide better infrastructure for personal and commercial transportation.
- The Automobile Era had a profound impact, revolutionizing personal mobility, facilitating travel, and shaping urban development and the rise of suburbs.
Relevant URL Sources:
- The History of Cars
- The History of Roads
FAQ
Q1: How did the development of the wheel impact road transport?
A1: The introduction of the wheel around 7,000 years ago revolutionized road transport, enabling the creation of vehicles that could carry heavier loads and travel faster and more efficiently.
Q2: What were the significant contributions of the Persians and Romans to road transport?
A2: The Persians built a network of Royal Roads across their empire, facilitating quicker travel for armies. The Romans, recognizing the importance of transportation for military and economic purposes, improved existing roads and constructed new ones to connect their vast empire.
Q3: What role did turnpikes and toll roads play in the development of road transport in the United States?
A3: In the 19th century, turnpikes and toll roads were prevalent in the United States, serving as privately-owned roads funded through tolls collected from travelers. These roads played a crucial role in improving transportation and economic development by connecting cities and towns and facilitating the movement of goods.
Q4: Who was John Metcalf, and what were his contributions to road building?
A4: John Metcalf, considered the first professional road builder during the Industrial Revolution, constructed numerous turnpike roads in the north of England starting in 1765. His innovative techniques and emphasis on road maintenance significantly improved the quality and efficiency of road networks.
Q5: How did steam-powered road vehicles contribute to the evolution of road transport?
A5: Steam-powered road vehicles, though not as widely adopted as steam-powered railways, showcased the potential of steam technology for land transportation. Early steam road vehicles demonstrated the feasibility of self-propelled vehicles and achieved notable feats, such as breaking the land speed record in 1906.
- Unlock Filipino Culture: A Deep Dive into Traditions and Practices - April 23, 2025
- Unlock Spanish Culture: Insights & Opportunities Now - April 23, 2025
- White Spirit Uses & Substitutes: A Deep Dive for Pros & DIYers - April 23, 2025