Embark on [- A Journey Through Time: The History of Microbiology] as we explore the fascinating world of microorganisms. This journey begins with a look back at the contributions of Louis Pasteur, whose groundbreaking discoveries laid the foundation for modern microbiology. As we delve deeper, we’ll also uncover the captivating tale of immunology’s evolution from ancient beliefs to the development of life-saving vaccines, shedding light on the crucial role of microorganisms in our health and environment.
Key Takeaways:
Microbial World Unveiled: Antonie van Leeuwenhoek’s 17th-century microscope observations revealed the existence of bacteria, protozoa, and fungi, opening up a hidden microscopic world.
Milestone Discoveries in Bacteriology and Medical Microbiology: Louis Pasteur’s experiments challenged spontaneous generation, and Robert Koch’s postulates linked specific diseases to specific microorganisms.
Virology, Immunology, and Molecular Biology Breakthroughs: The 20th century brought virology, immunology, and molecular biology advancements, leading to the discovery of DNA, viruses, and vaccines.
Microbes and their Ecological and Evolutionary Roles: Microbiology has illuminated the significance of microbes in ecology and evolution, demonstrating their diversity and impact on地球上的生命.
Frontiers of Contemporary Microbiology: Modern microbiology ventures into areas like astrobiology, nanotechnology, synthetic biology, and microbiome research, expanding our understanding of life’s origins and potential solutions to global challenges.
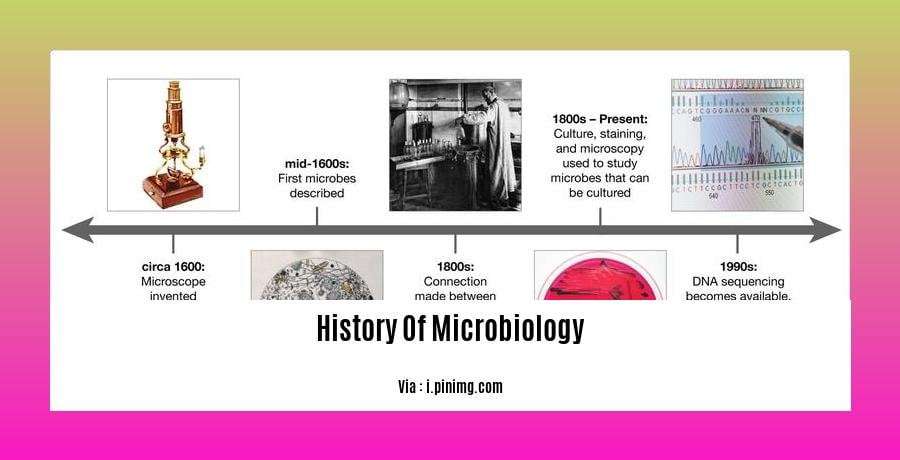
History of Microbiology


We embark on a captivating journey through time, tracing the profound impact of microbiology on our comprehension of life on Earth. From the groundbreaking discoveries of the 17th century to the cutting-edge advancements of today, microbiology continues to unveil the profound significance of the microscopic world.
Pioneering Insights: Unveiling the Microbial Realm
In the 1670s, Antonie van Leeuwenhoek ventured into the realm of the unfathomable, employing his ingenious homemade microscopes to observe entities beyond the reach of the naked eye. His remarkable observations unveiled a hidden universe of bacteria, protozoa, and fungi, revolutionizing our understanding of life’s complexity.
Foundational Pillars: Pasteur and Koch’s Contributions
The 19th century witnessed two towering figures in microbiology, Louis Pasteur and Robert Koch. Pasteur, with his meticulous experiments, demolished the deeply ingrained belief in spontaneous generation. His work paved the way for the concept of germ theory, forever changing our approach to hygiene and disease prevention.
Equally transformative were the contributions of Robert Koch, whose postulates laid the foundation for linking specific microorganisms to specific diseases. This monumental breakthrough transformed medical diagnosis and treatment, leading to targeted therapies and saving countless lives.
Unveiling the Secrets of Viruses, Immunity, and Molecular Biology
The 20th century ushered in a golden age of microbiology. The discovery of viruses, the intricate workings of the immune system, and the unraveling of DNA’s structure revolutionized our understanding of infectious diseases and genetics.
Vaccines, a testament to the power of microbiology, emerged as lifelines against deadly illnesses, transforming public health landscapes. Immunology, the study of our body’s defense mechanisms, illuminated the intricate interplay between pathogens and hosts, paving the way for targeted treatments.
Microbes in the Vast Tapestry of Life
Microbiology ventured beyond the confines of human health, delving into the realms of ecology and evolution. Microbes, the most diverse and abundant organisms on Earth, play pivotal roles in nutrient cycling, decomposition, and the intricate web of life.
Their contributions to biogeochemical processes underpin the delicate balance of ecosystems and the very foundation of life. Studying microbes enriches our understanding of evolution, shedding light on the origins and diversification of life forms.
Microbiology’s Frontier: Uncharted Territories
Today, microbiology continues to push the boundaries of scientific exploration, venturing into uncharted territories such as astrobiology, nanotechnology, synthetic biology, and microbiome research.
Astrobiology probes the potential for life beyond Earth, while nanotechnology harnesses the power of microbes to engineer materials and devices on an unprecedented scale. Synthetic biology redefines the boundaries of life by crafting organisms with tailored genetic traits.
Microbiome research unveils the intricate interactions between microbes and their hosts, revealing the profound influence of these microbial communities on health, disease, and behavior. The study of microbiology, therefore, stands as a testament to the relentless pursuit of knowledge, promising transformative discoveries that will shape our understanding of life’s intricate tapestry.
To understand the roots of microbiology and its fascinating journey, explore the history of microbiology and uncover the pivotal moments and contributions that shaped this scientific field. Delve into the historical background of microbiology](../what-is-the-historical-background-of-microbiology) to witness the evolution of ideas and techniques that revolutionized our understanding of the microbial world. Discover the captivating history and scope of microbiology and appreciate the diverse applications of this discipline in fields ranging from medicine to biotechnology.
A Brief History of Immunology
The study of how living organisms defend themselves against disease is known as immunology. It’s a fascinating field that’s constantly evolving, with new discoveries being made all the time. Here’s a brief history of immunology:
1. The Early Days of Immunology:
- In the 18th century, Edward Jenner developed the first vaccine, which protected people from smallpox. This was a major breakthrough that saved countless lives.
- In the 19th century, Louis Pasteur and Robert Koch made important discoveries about the role of microorganisms in disease. They showed that certain bacteria and viruses cause specific diseases.
2. The 20th Century:
- The 20th century saw the development of new vaccines and antibiotics, which helped to control many infectious diseases.
- Scientists also discovered how the immune system works. They learned that the body has different types of immune cells, which work together to fight off infection.
- The development of monoclonal antibodies was a major step forward in immunology. Monoclonal antibodies can be used to treat a variety of diseases, including cancer.
3. The 21st Century:
- The research in the 21st century has focused on developing new vaccines and treatments for infectious diseases.
- Also, scientists are working to understand how the immune system can be used to fight cancer and other diseases.
Key Takeaways:
- Immunology is the study of how living organisms defend themselves against disease.
- The first vaccine was developed in the 18th century.
- In the 19th century, scientists made important discoveries about the role of microorganisms in disease.
- The 20th century saw the development of new vaccines and antibiotics, as well as the discovery of how the immune system works.
- The 21st century has focused on developing new vaccines and treatments for infectious diseases, as well as understanding how the immune system can be used to fight cancer and other diseases.
Citations:
- A Brief History of Immunology – NIH
- History of Immunology – Encyclopedia.com
FAQ
Q1: Who was Antonie van Leeuwenhoek and what was his contribution to microbiology?
A1: Antonie van Leeuwenhoek was a Dutch scientist who constructed homemade microscopes in the 1670s. Using these microscopes, he observed bacteria, protozoa, and fungi for the first time, revealing the existence of a microscopic world. His observations laid the foundation for the field of microbiology.
Q2: How did Louis Pasteur and Robert Koch contribute to the field of microbiology?
A2: Louis Pasteur and Robert Koch are considered influential figures in microbiology. Pasteur’s experiments disproved the theory of spontaneous generation, demonstrating that microorganisms do not arise from non-living matter. Koch developed his postulates, which established a framework for linking specific microorganisms to specific diseases. Their work revolutionized the field of medical microbiology.
Q3: What were some significant discoveries in virology, immunology, and molecular biology in the 20th century?
A3: The 20th century witnessed major advancements in virology, immunology, and molecular biology. Scientists discovered DNA, viruses, and vaccines, which expanded our understanding of infectious diseases and genetics. The development of antibiotics also marked a significant breakthrough in combating bacterial infections. These discoveries transformed the field of microbiology and had a profound impact on medicine and public health.
Q4: How does microbiology play a role in ecology and evolution?
A4: Microbiology plays a crucial role in ecology and evolution. Microbes are the most diverse and abundant organisms on Earth, constituting a significant portion of the biosphere. The study of microbes has deepened our understanding of the intricate web of life and its origins. Microbes drive biogeochemical cycles, influence climate regulation, and contribute to the functioning of ecosystems. Their study also offers insights into the evolutionary history of life and the interconnectedness of all living organisms.
Q5: What are some of the frontiers of modern microbiology?
A5: Modern microbiology continues to explore uncharted territories, including astrobiology, nanotechnology, synthetic biology, and microbiome research. Scientists are investigating the potential for life beyond Earth, developing nanotechnologies for medical and environmental applications, engineering novel organisms, and studying the complex communities of microorganisms that inhabit various environments. These areas of research push the boundaries of scientific knowledge and offer the potential for new discoveries and solutions to global challenges.
- Unlock Filipino Culture: A Deep Dive into Traditions and Practices - April 23, 2025
- Unlock Spanish Culture: Insights & Opportunities Now - April 23, 2025
- White Spirit Uses & Substitutes: A Deep Dive for Pros & DIYers - April 23, 2025