Embark on a historical odyssey with “History of India: An Enduring Legacy of Civilization.” This comprehensive guide unveils the rich tapestry of India’s past, from its ancient civilizations to its present-day vibrancy. Dive into the depths of India’s history and discover the stories that have shaped one of the world’s most enduring civilizations.
Key Takeaways:
- India boasts over 5,000 years of rich history, dating back to the Indus Valley Civilization.
- Throughout history, India has experienced the rise and fall of numerous empires, dynasties, and religious movements.
- The country possesses an incredible diversity in language, art, architecture, cuisine, and cultural practices.
- India has made significant contributions to science, mathematics, medicine, philosophy, and metallurgy.
- The struggle for Indian independence gained momentum under leaders such as Gandhi, Nehru, Bose, and Patel.
- India emerged as a sovereign democratic republic in 1950.
The History of India: A Tapestry of Civilizations

India, a land where empires flourished, religions evolved, and cultures intertwined, has a rich and captivating history spanning over five millennia. From the enigmatic Indus Valley Civilization to the modern republic, India’s history is a testament to its enduring legacy as a cradle of civilization.
Succession of Empires and Dynasties
India has witnessed the rise and fall of numerous empires and dynasties. The Mauryan Empire (322-185 BCE) unified much of the subcontinent under the legendary emperor Ashoka, known for his teachings of non-violence and peace. The Golden Age of the Guptas (320-550 CE) saw advancements in art, literature, and science, including the invention of the zero. The Mughal Empire (1526-1857 CE) brought together diverse cultures and left behind architectural wonders like the Taj Mahal.
Cultural Diversity and Achievements
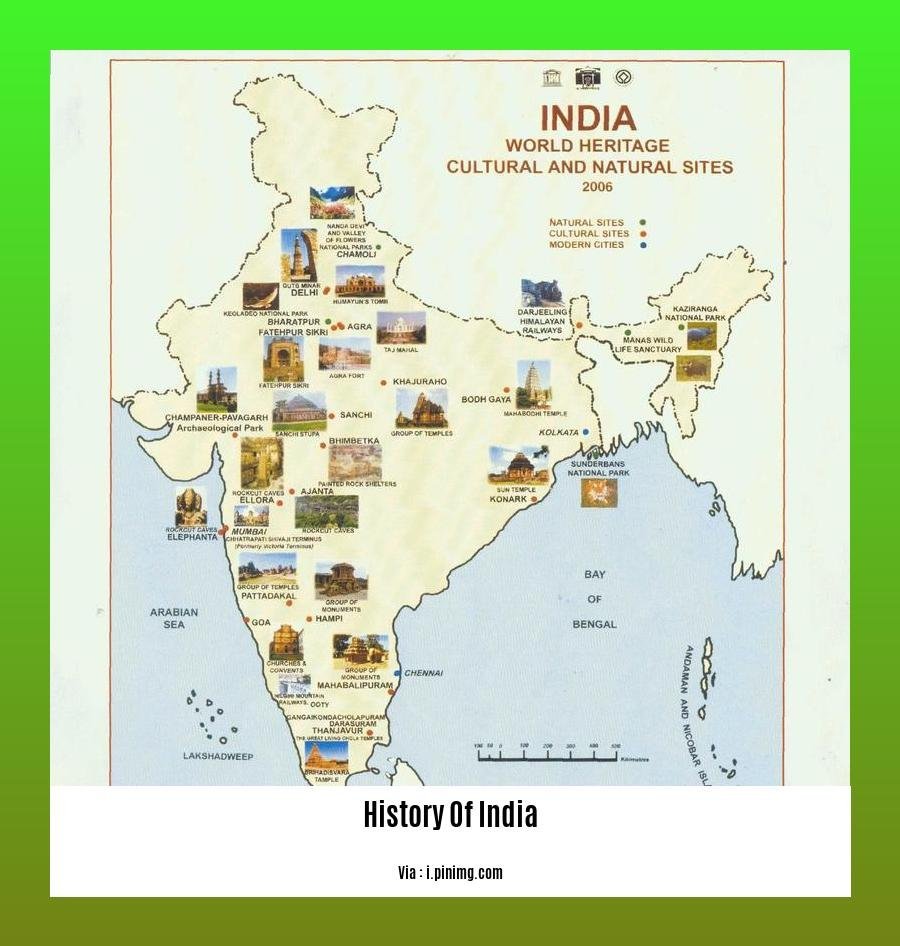
The history of India is marked by an incredible diversity of languages, religions, and artistic traditions. India is home to over 22 official languages, each with its unique literature and poetic forms. Its vibrant art and architecture have inspired awe for centuries, from the intricate carvings of the Ellora Caves to the magnificent temples of Khajuraho.
India has also made significant contributions to science and philosophy. Ancient Indian scholars developed concepts like zero, trigonometry, and metallurgy. Yoga, a practice that combines physical and mental exercises, originated in India and has gained global prominence for its health and well-being benefits.
Struggle for Independence and Modern India
The history of India took a momentous turn in the 20th century with the struggle for independence from British rule. Led by iconic figures like Mahatma Gandhi, Jawaharlal Nehru, Subhas Chandra Bose, and Vallabhbhai Patel, the Indian independence movement harnessed the power of non-violent resistance. India gained its independence in 1947 and has since emerged as a sovereign democratic republic.
Today, India stands as a global power with a rich and diverse history that continues to inspire and shape the present. Its ancient traditions and cultural heritage coexist harmoniously with modern advancements, creating a mosaic of a nation that is both timeless and progressive.
Journey through India’s vibrant past by exploring its rich indian history timeline, unraveling the mysteries of ancient India history, and immersing yourself in its captivating Indian culture history.
History Of India Pdf

As history buffs, we can embark on a fascinating journey through the annals of India’s rich past, from its ancient civilizations to its modern-day republic. History Of India Pdf documents provide a wealth of knowledge and insights into this captivating tapestry.
Prehistoric Period
India’s story begins with the enigmatic Indus Valley Civilization, a flourishing urban culture that thrived along the banks of the Indus River around 2600 BCE. This civilization left behind impressive cities like Harappa and Mohenjo-daro, showcasing advanced urban planning, writing skills, and metallurgical prowess.
Vedic Period
The arrival of the Aryans around 1500 BCE marked the beginning of the Vedic period. This era is characterized by sacred hymns and texts, known as the Vedas, which provide insights into the religious beliefs and societal structure of the time.
Mahajanapadas and Empires
By 600 BCE, India witnessed the rise of 16 major states, or mahajanapadas. Among these, the Magadha Empire emerged as a powerful force under the rule of Chandragupta Maurya in the 4th century BCE. Chandragupta’s military conquests and centralized administration laid the foundation for one of India’s first great empires.
Maurya Dynasty
The Maurya Dynasty, founded by Chandragupta Maurya, ushered in an era of prosperity and cultural advancement. Ashoka, Chandragupta’s grandson, is renowned for his conversion to Buddhism and his efforts to spread the religion throughout his vast kingdom.
Gupta Dynasty
The Gupta Dynasty, ruling from the 4th to the 6th centuries CE, is considered the Golden Age of India. This period saw significant cultural, scientific, and artistic achievements, including the development of Hinduism, which became a dominant force in Indian society.
Medieval Period
The medieval period witnessed the rise and fall of various empires, including the Rajput kingdoms, Delhi Sultanate, and Mughal Empire. Each of these empires left its mark on Indian history, contributing to the cultural and architectural diversity of the country.
Colonial Period
The arrival of the East India Company in the 18th century marked the beginning of British rule in India. The company’s economic policies and social changes had a profound impact on Indian society, ultimately leading to the Indian National Movement and the struggle for independence.
Independence and Beyond
India gained independence from British rule in 1947, marking a new era of self-governance. Since then, the country has made significant strides in nation-building, economic reforms, and social progress, becoming a global power on the world stage.
Key Takeaways:
– India’s history spans over 5,000 years, from the Indus Valley Civilization to the modern republic.
– Successive empires, religions, and dynasties have shaped the country’s diverse cultural landscape.
– India has made significant contributions to mathematics, astronomy, medicine, and other fields of knowledge.
– The Indian National Movement, led by Mahatma Gandhi, played a pivotal role in achieving independence from British rule.
– India is a vibrant and dynamic country with a rich history and a promising future.
Citation:
– The New Cambridge History of India
FAQ
Q1: What are the key periods in Indian history?
A1: Indian history is divided into several key periods, including the prehistoric, Vedic, Mahajanapadas and Empires, Maurya Dynasty, Gupta Dynasty, Medieval Period, Colonial Period, and Independence and Beyond.
Q2: Which empires had a significant impact on Indian history?
A2: Several empires have played a significant role in Indian history, including the Maurya Dynasty, Gupta Dynasty, Delhi Sultanate, and Mughal Empire.
Q3: What are the major contributions of India to world civilization?
A3: India has made significant contributions to world civilization, including the concepts of zero, yoga, and advances in mathematics, astronomy, medicine, metallurgy, and philosophy.
Q4: What was the role of Mahatma Gandhi in India’s independence movement?
A4: Mahatma Gandhi was a key leader in India’s non-violent resistance movement against British rule, leading to India’s independence in 1947.
Q5: What are some of the challenges faced by India after independence?
A5: After independence, India faced challenges such as nation-building, economic reforms, and conflicts with neighboring countries. However, it has also achieved significant economic growth and social progress.
- HelpCare Plus: Revolutionizing Affordable and Accessible Healthcare - December 29, 2024
- Boom & Bucket: Your Digital Marketplace for Used Heavy Equipment - December 28, 2024
- Ankle Bones Crossword Clue: Solutions, Tips & Anatomical Insights - December 28, 2024