Embark on [A Journey Through the History of Computing Devices], an exploration of the inexorable march of technology that has transformed the way we live and work. From the rudimentary mechanical calculators of the past to the lightning-fast supercomputers of today, this article will trace the remarkable evolution of devices that have revolutionized our world.
Key Takeaways:
Four Distinct Periods:
- Mechanical devices (19th century)
- Electrical and electronic devices (early 20th century)
- Digital computers (late 20th century)
- Personal devices and the internet (21st century)
Key Technological Advancements:
- Punched cards
- Electrical and electronic components
- Transistors and integrated circuits
- Microprocessors, memory, and networking technologies
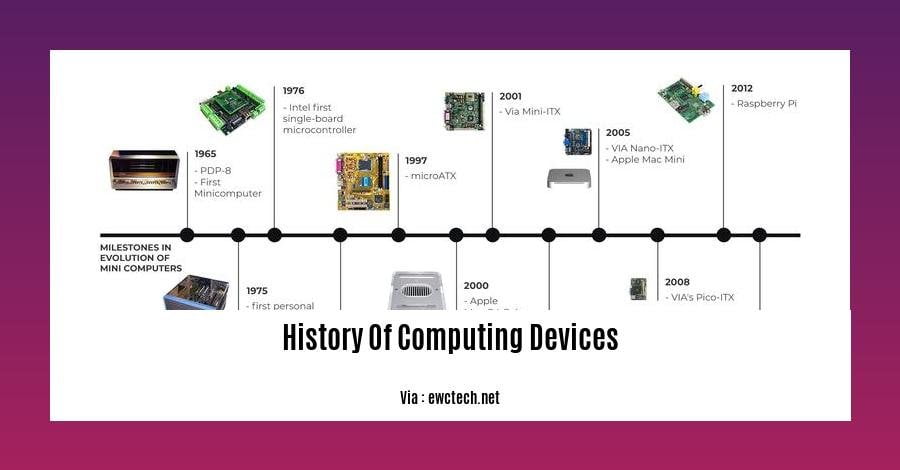
History of Computing Devices

The history of computing devices is a fascinating journey that has led us from the simple mechanical devices of the 19th century to the powerful smartphones of today. Along the way, there have been many key technological advancements that have helped to shape the way we live and work.
19th Century: Mechanical Devices
The first computing devices were mechanical, and they were used to perform simple calculations. One of the most famous of these early devices was the Jacquard loom, which was invented in 1801. The Jacquard loom used punched cards to control the pattern of the fabric that was being woven.
Early 20th Century: Electrical and Electronic Devices
In the early 20th century, electrical and electronic devices began to replace mechanical devices for many computing tasks. One of the most important of these early electrical devices was the differential analyzer, which was invented in 1930. The differential analyzer was used to solve differential equations, which are used to model many physical phenomena.
Late 20th Century: Digital Computers
The late 20th century saw the development of digital computers, which are capable of performing much more complex calculations than analog computers. The first digital computer was the ENIAC, which was completed in 1946. The ENIAC was a massive machine that weighed over 30 tons and contained over 18,000 vacuum tubes.
21st Century: Personal Computers, Smartphones, Tablets, and the Internet
The 21st century has seen the development of personal computers, smartphones, tablets, and the Internet. These devices have made computing power available to everyone, and they have revolutionized the way we live and work.
Key Technological Advancements
Many key technological advancements have helped to shape the history of computing devices. These advancements include:
- Punched cards: Punched cards were used to control the operation of early mechanical and electrical computers.
- Electrical and electronic components: Electrical and electronic components, such as transistors and integrated circuits, made it possible to build smaller and more powerful computers.
- Microprocessors, memory, and networking technologies: Microprocessors, memory, and networking technologies have made it possible to develop powerful and versatile computers that can be used for a wide variety of tasks.
The history of computing devices is a fascinating journey that has led us from the simple mechanical devices of the 19th century to the powerful smartphones of today. Along the way, there have been many key technological advancements that have helped to shape the way we live and work.
Embark on a fascinating journey through the history of computer, from its humble beginnings to its present-day dominance. Delve into the computer evolution history to witness the progression of technology that shaped our world. Explore the pivotal computing history milestones that paved the way for the digital age we live in.
Electromechanical Computers and the Dawn of Modern Computing
Before the advent of electronic computers, the world relied on electromechanical computers, which paved the way for the digital age we live in today. These groundbreaking devices marked a significant leap in computing history, bridging the gap between mechanical and electronic technologies.
Stepping Stones to the Electronic Era
The roots of electromechanical computing can be traced back to the 19th century, with the invention of punched card machines like the Jacquard loom. These machines used perforated cards to store and execute instructions, laying the groundwork for future computing devices.
As technology advanced, electromechanical devices such as the differential analyzer emerged in the early 20th century. These machines used mechanical components, electrical motors, and gears to perform complex calculations. They played a crucial role in fields like engineering and scientific research.
The Dawn of Modern Computing
The true dawn of modern computing arrived in the 1940s with the development of electromechanical computers. These devices combined electronic components with mechanical systems, marking a significant shift from their purely mechanical predecessors. They utilized vacuum tubes and relays to perform calculations, boasting increased speed and efficiency.
Bombes, electromechanical devices used for codebreaking during World War II, were among the most notable applications of electromechanical computing. Their ability to decipher enemy communications significantly influenced the course of the war.
Key Takeaways:
- Electromechanical computers were the stepping stones between mechanical and electronic computing.
- They used a combination of electrical and mechanical components.
- They were faster and more efficient than purely mechanical devices.
- Bombes were an important application of electromechanical computing during World War II.
Most Relevant URL Source:
The Advent of Electronic Digital Computers
In the annals of computing history, the advent of electronic digital computers marked a pivotal juncture, ushering in an era of innovation that continues to shape our world today. The shift from analog to digital computation laid the foundation for the lightning-fast, versatile machines that we rely on today.
The genesis of the electronic digital computer can be traced back to the ABC computer (Atanasoff-Berry Computer), conceived in the late 1930s. This groundbreaking device employed vacuum tubes to perform calculations electronically, paving the way for the digital revolution.
The ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer), completed in 1946, was a colossal machine that solidified the dominance of electronic digital computation. Its sheer size and complexity cemented its place in history as a symbol of the transformative power of computers.
The simplification of “computing machine” to “computer” in the late 1940s and early 1950s reflected the paradigm shift brought about by these electronic marvels. Computers evolved from specialized tools used for scientific calculations to versatile machines capable of handling a wide range of tasks.
Key Takeaways:
- The advent of electronic digital computers marked a pivotal shift from analog to digital computation.
- The ABC computer was the first electronic digital computer.
- The ENIAC solidified the dominance of electronic digital computation.
- The term “computer” emerged as the widespread adoption of these machines simplified their nomenclature.
- Electronic digital computers have revolutionized the field of computing, empowering society with unprecedented computational abilities.
Source: History of Computers: A Brief Timeline
The Rise of Microcomputers and the Personal Computer Revolution
As early as the 1970s, the computing landscape was dominated by large, room-sized mainframes operated by a small number of skilled technicians. These machines were primarily used for complex scientific and business calculations.
But in the mid-1970s, the microcomputer revolution began. Originally conceived as a way to automate simple tasks, the Intel 4004 released in 1969, was the first microprocessor, igniting the spark of personal computing.
Microprocessors and Integrated Circuits
The microprocessor’s small size, low cost, and versatility made it possible to create computers for home and personal use. These early microcomputers, often known as “microcomputers” were much less powerful than mainframes, but they offered unprecedented accessibility and affordability.
Early Computer Enthusiasts
Silicon Valley engineers quickly recognized the potential of microprocessors and began experimenting with them. Steve Wozniak and Steve Jobs, two computer enthusiasts, built the Apple I in 1976, widely considered one of the first personal computers. It was followed by the hugely popular Apple II in 1977.
IBM’s Entry and Impact
Initially skeptical of microprocessors, IBM underestimated the growing market for personal computers. In 1981, they introduced the IBM PC, which became a huge success due to its compatibility with a wide range of software, quickly becoming the de facto standard for personal computers.
Key Takeaways:
- Microprocessors: The Intel 4004, released in 1969, was the first microprocessor, enabling the creation of smaller, more affordable computers.
- Microcomputers: The development of microprocessors led to the rise of “microcomputers” or personal computers, designed for individual use.
- Personal Computer Revolution: The introduction of the Apple II and IBM PC in the late 1970s and early 1980s fueled a revolution, making personal computing accessible to a wider audience.
Most Relevant URL Source:
- Britannica:
FAQ
Q1: What are the key periods in the history of computing devices?
A1: The history of computing devices can be divided into four distinct periods: the 19th century (mechanical devices), the early 20th century (electrical and electronic devices), the late 20th century (digital computers), and the 21st century (personal computers, smartphones, tablets, and the internet).
Q2: What technological advancements drove the evolution of computing devices?
A2: Key technological advancements that drove the evolution of computing devices include punched cards, electrical and electronic components, the transistor and integrated circuit, and microprocessors, memory, and networking technologies.
Q3: What was the first electronic digital computer?
A3: The first electronic digital computer was the ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer), built in the United States in the 1940s.
Q4: When did personal computers become widely available?
A4: Personal computers began to become widely available in the 1970s with the introduction of the Altair 8800 and the TRS-80.
Q5: What is the latest frontier in computing technology?
A5: Quantum computing and artificial intelligence are emerging as the latest frontiers in computing technology, promising to revolutionize various fields in the coming years.
- Understand Behavior Examples: A Complete Guide - April 11, 2025
- Uncover Saint Kevin: Glendalough’s Legacy - April 11, 2025
- Unlocking History for Kids: Top Picks - April 11, 2025

![A Journey Through the History of Computing: From Its Humble Origins to Modern Innovations [history of computing ss1] history-of-computing-ss1_2](https://www.lolaapp.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/history-of-computing-ss1_2-150x150.jpg)














