Embark on a delectable journey through time as we unveil the captivating history of chocolate. From its humble beginnings in the rainforests of Mesoamerica to its global reign as an icon of indulgence, chocolate’s story is a testament to human ingenuity and culinary passion. Prepare to unravel the rich cultural heritage and fascinating tales that have shaped this beloved confection into the irresistible delicacy we cherish today. Join us as we delve into the world of chocolate, where history, indulgence, and delight intertwine.
Key Takeaways:
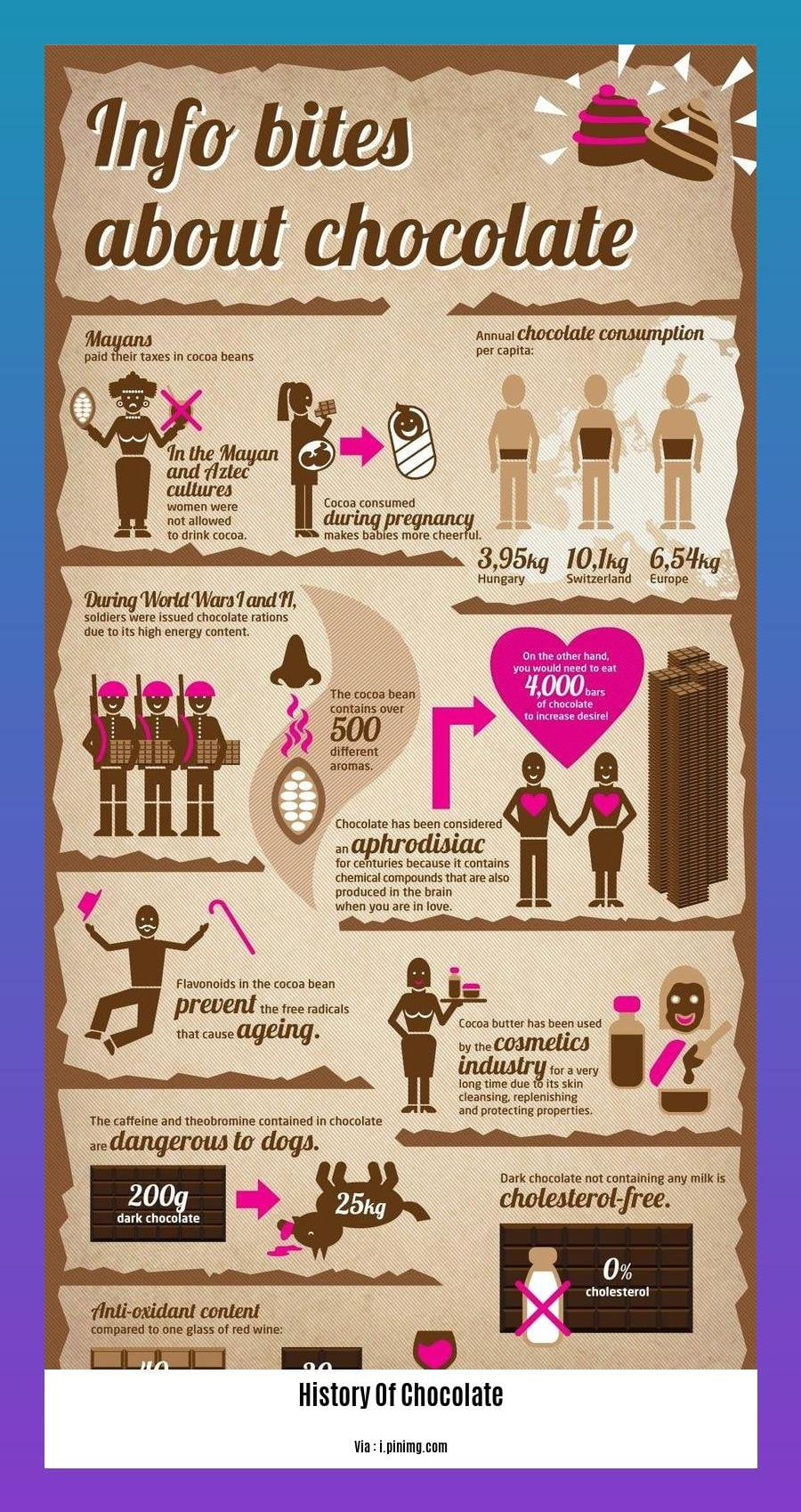
Chocolate originated in Mesoamerica, with ancient civilizations like the Olmecs, Mayans, and Aztecs being the first to consume it.
In Mesoamerica, chocolate was consumed as a fermented beverage and was so valued that it was used as a form of currency.
When the Spanish introduced chocolate to Europe in the 16th century, they sweetened it for the first time.
The Aztecs considered cacao seeds to be a gift from their god of wisdom, Quetzalcoatl, and valued them highly.
The Mayans and Olmecs were among the first civilizations to consume chocolate, making a bitter beverage from cacao beans.
History of Chocolate
Chocolate, the heavenly confection, has a rich and captivating history that spans civilizations, cultures, and time. Join us as we embark on a journey to unravel the history of chocolate, from its humble origins in Mesoamerica to its triumphant global reign as a symbol of indulgence and delight.
The Birth of Chocolate
The captivating journey of chocolate begins in Mesoamerica, the land that birthed ancient civilizations such as the Olmecs, Mayans, and Aztecs. Here, cacao seeds, the foundation of chocolate’s magic, were transformed into a nutritious and ceremonial beverage. The Mayans and Olmecs, revered for their sophisticated culinary practices, were among the earliest chocolate enthusiasts. They crafted a bitter drink using roasted and ground cacao beans, adding spices and herbs to create a brew that was both invigorating and sacred.
Currency of the Gods
To the ancient Aztecs, cacao was more than just a beverage; it was a revered currency, a symbol of wealth and power. Cacao beans were prized as a form of payment, used to acquire goods and services, and even served as a unit of measurement. Their value was so esteemed that they were often used as offerings to the gods, symbolizing the abundance and prosperity they bestowed upon the land.
Cacao’s European Encounter
In the 16th century, the Spanish conquistadors, with their insatiable curiosity and thirst for exploration, encountered the wonders of chocolate during their expeditions to Mesoamerica.
Intrigued by its unique flavor and invigorating properties, they brought cacao beans back to Europe, introducing this exotic delicacy to the Old World. Initially perceived as a bitter and unpalatable concoction, chocolate underwent a transformation under the hands of European chocolatiers. They sweetened it, added milk and other ingredients, and voila, the irresistible chocolate confection we know and love today was born.
A Global Sweetheart
Chocolate’s fame quickly spread throughout Europe, captivating the palates of kings, queens, and commoners alike. From the royal courts of Spain to the bustling markets of London, chocolate became a symbol of luxury, indulgence, and delight. Its popularity soared, fueling a demand that would lead to the establishment of chocolate plantations in Africa and Asia, transforming chocolate into a global commodity.
Chocolate Through the Ages
Over the centuries, chocolate has evolved, adapting to changing tastes and technological advancements. In the 19th century, the invention of the cocoa press revolutionized chocolate production, enabling the separation of cocoa butter from cocoa solids, leading to the creation of new and delectable chocolate varieties.
Today, chocolate stands as a global culinary icon, a versatile ingredient used in countless desserts, pastries, beverages, and even savory dishes. Its diverse flavors, textures, and forms cater to every palate, ensuring its enduring place in our hearts and taste buds.
Unveiling Chocolate’s Secrets
As we delve deeper into the history of chocolate, we uncover a tapestry of cultural influences, scientific discoveries, and culinary innovations. From its ancient roots as a ceremonial beverage to its current status as a beloved treat, chocolate’s journey is a testament to its enduring appeal and universal allure.
So, let’s embark on this delectable journey together, savoring the rich flavors of chocolate’s past, present, and future. Who knows what sweet surprises await us as we continue to explore the enchanting history of chocolate?
Get a taste for the evolution of musical genres by hopping into the extraordinary history of classical music.
History enthusiasts can delve into the world of the German Shorthaired Pointer by venturing into the depths of its fascinating origin story.
Rise of chocolate as a global commodity and its impact on world trade

The evolution of chocolate into a worldwide sensation has had a profound effect on global commerce. Its journey from a revered ceremonial beverage in Mesoamerica to a beloved global indulgence mirrored the interconnectedness of the world and the lasting impact of culinary traditions. Let’s explore how chocolate’s rise as a global commodity has shaped the world of trade.
The Columbian Exchange: A Catalyst for Chocolate’s Global Expansion
The arrival of Christopher Columbus in the Americas in 1492 marked a pivotal moment in chocolate’s history. Upon encountering the cacao beans, Columbus and his crew brought them back to Spain, marking the beginning of chocolate’s journey across the Atlantic.
Sweetening the World: The Transformation of Chocolate in Europe
Initially consumed as a bitter beverage, chocolate underwent a culinary transformation in Europe. The addition of sugar and other flavorings such as vanilla and cinnamon created a sweeter, more palatable concoction. This transformed chocolate from a ceremonial drink to a delightful treat, captivating the palates of the European elite.
The Rise of Chocolate as a Global Commodity
The demand for chocolate soared throughout Europe and beyond, leading to the establishment of cocoa plantations in various colonies. The availability of cheap labor and fertile lands in these regions facilitated the mass production of cocoa beans, propelling chocolate’s transformation into a global commodity.
The Impact on World Trade
The growth of the chocolate industry had far-reaching implications for world trade. Cocoa became a valuable commodity, traded between countries and continents. The lucrative cocoa trade stimulated economic growth and fueled the rise of merchant empires. It also led to the development of transportation networks and the establishment of new trade routes.
The Legacy of Chocolate: A Global Culinary Icon
Today, chocolate is a ubiquitous presence in the global culinary landscape. Its versatility and universal appeal have made it an indispensable ingredient in countless desserts, pastries, beverages, and even savory dishes. The rich history of chocolate, marked by cultural influences, scientific discoveries, and culinary innovations, continues to shape its enduring popularity and impact on world trade.
Key Takeaways:
Chocolate’s journey from a ceremonial beverage in Mesoamerica to a global commodity reflects the interconnectedness of the world.
The Columbian Exchange introduced chocolate to Europe, where it underwent a transformation into a sweetened delicacy.
The demand for chocolate led to the establishment of cocoa plantations in colonies, fueling the growth of the chocolate industry.
The cocoa trade became a valuable commodity, driving economic growth and shaping global trade routes.
Chocolate’s enduring popularity and impact on world trade are a testament to its cultural significance and culinary versatility.
Sources:
[1] Coe, S. D., & Coe, M. D. (1996). The True History of Chocolate. Thames & Hudson.
[2] Mintz, S. W. (1985). Sweetness and Power: The Place of Sugar in Modern History. Penguin Books.
Industrialization of chocolate production and the emergence of mass-market brands
The industrialization of chocolate production and the subsequent emergence of mass-market brands transformed chocolate from a rare delicacy to a ubiquitous treat enjoyed worldwide.
In the mid-19th century, advancements in technology catalyzed the industrialization of chocolate production. In 1828, Coenraad Johannes van Houten, a Dutch chemist, developed a method to separate cocoa butter from cocoa solids, enabling the creation of solid chocolate bars. This innovation paved the way for mass production and affordability of chocolate.
Simultaneously, the rise of mass-market brands, such as Fry’s, Cadbury, and Nestlé, played a crucial role in popularizing chocolate. These companies invested heavily in advertising and utilized innovative marketing techniques to capture consumer attention. Chocolate was no longer exclusive to the wealthy; it became an accessible indulgence for the masses.
The industrialization of chocolate manufacturing brought forth several challenges. Maintaining the quality of chocolate while meeting the demands of mass production required meticulous precision. Food scientists diligently experimented with ingredients and flavors, aiming to achieve the perfect balance of sweetness and indulgence that would appeal to consumer preferences.
Key Takeaways:
The industrialization of chocolate production, coupled with the emergence of mass-market brands, democratized chocolate, making it accessible to a broader audience.
Technological advancements like the cocoa press enabled the separation of cocoa butter from cocoa solids, leading to the creation of solid chocolate bars.
Mass-market brands invested in advertising and marketing strategies to capture consumer attention, positioning chocolate as an affordable and desirable treat.
The industrialization of chocolate manufacturing posed challenges in maintaining quality while meeting mass-production demands, leading to the exploration of ingredient combinations and flavor profiles that appealed to consumer preferences.
[Sources]
– Nestlé European Chocolate: Evolution
– Wiley Online Library: Industrial Chocolate Manufacture and Use
Contemporary trends in chocolate consumption and the pursuit of ethical and sustainable practices
While chocolate has undoubtedly captured our hearts and palates for centuries, the contemporary era has witnessed a surge in consciousness surrounding ethical and sustainable practices in its production. Let’s delve into the key trends shaping chocolate consumption and unravel the efforts towards a more responsible and delicious future.
1. Cocoa Farmers’ Empowerment
The industry is finally recognizing the significance of supporting cocoa farmers, who form the backbone of the chocolate production chain. Initiatives such as fair-trade certifications and direct farmer-to-consumer models ensure that farmers receive a fair wage, enabling them to invest in their communities and cultivate higher-quality cacao.
2. Embracing Sustainable Agriculture
Chocolate enthusiasts are increasingly seeking out brands that prioritize sustainable farming practices. Agroforestry, a technique that involves planting cocoa trees alongside other crops, is gaining traction as it promotes biodiversity, soil health, and carbon sequestration. Additionally, organic farming methods are becoming more prevalent, minimizing the use of harmful pesticides and fertilizers.
3. Bean-to-Bar Philosophy
Craft chocolate makers, often referred to as “bean-to-bar” artisans, are revolutionizing the industry with their commitment to quality and transparency. They source their cacao directly from farmers, controlling every step of the chocolate-making process to ensure exceptional flavor profiles and ethical sourcing practices.
4. Single-Origin Chocolate
Chocolate lovers are embracing the concept of single-origin chocolate, much like wine connoisseurs appreciate the nuances of different vineyards. This trend celebrates the unique flavors and characteristics of cacao grown in specific regions, showcasing the diverse terroirs of the cocoa-growing world.
5. Dark Chocolate’s Resurgence
Dark chocolate, with its higher cocoa content and lower sugar levels, is experiencing a resurgence as consumers become more health-conscious. Its rich, complex flavors and potential health benefits, such as improved heart health and cognitive function, are driving its popularity.
6. Transparency and Traceability
Consumers are demanding greater transparency and traceability in the chocolate supply chain. Certifications like Fairtrade, Rainforest Alliance, and UTZ Certified provide assurance that the cocoa has been sourced responsibly, ensuring that it meets ethical and environmental standards.
7. Consumer Education
Chocolate manufacturers and organizations are actively educating consumers about the challenges faced by cocoa farmers and the importance of sustainable practices. Through initiatives such as workshops, social media campaigns, and educational materials, consumers are becoming more informed and empowered to make ethical choices.
8. Innovation in Packaging
The pursuit of sustainability extends to packaging as well. Companies are exploring eco-friendly alternatives to traditional plastic wrappers, such as biodegradable or compostable materials, to minimize their environmental impact.
Key Takeaways:
- Contemporary chocolate consumption is driven by a growing awareness of ethical and sustainable practices.
- Fair-trade initiatives and direct farmer-to-consumer models ensure that cocoa farmers receive a fair wage.
- Sustainable farming techniques, such as agroforestry and organic farming, are gaining prominence.
- Bean-to-bar chocolate makers prioritize quality and transparency, controlling the entire production process.
- Single-origin chocolate celebrates the unique flavors of cacao from specific regions.
- Dark chocolate is experiencing a resurgence due to its health benefits and rich flavor profile.
- Certifications like Fairtrade and Rainforest Alliance provide assurance of responsible sourcing practices.
- Consumer education initiatives empower consumers to make ethical choices.
- Sustainable packaging solutions minimize the environmental impact of chocolate production.
Sources:
[1] International Cocoa Organization:
[2] Fairtrade International:
FAQ
Q1: Where did chocolate originate?
A1: Chocolate originated in Mesoamerica, specifically among ancient civilizations such as the Olmecs, Mayans, and Aztecs.
Q2: How was chocolate consumed in Mesoamerica?
A2: In Mesoamerica, chocolate was consumed as a fermented beverage and was also valued as a form of currency.
Q3: Who introduced chocolate to Europe?
A3: Chocolate was introduced to Europe by the Spanish in the 16th century.
Q4: What significant cultural belief did the Aztecs have regarding chocolate?
A4: The Aztecs believed that cacao seeds were a gift from the god of wisdom, Quetzalcoatl, and were highly valued and used as a form of currency.
Q5: Which ancient civilizations were among the first to consume chocolate?
A5: The Mayans and Olmecs were among the first civilizations to consume chocolate, creating a bitter beverage from cacao beans.
- China II Review: Delicious Food & Speedy Service - April 17, 2025
- Understand Virginia’s Flag: History & Debate - April 17, 2025
- Explore Long Island’s Map: Unique Regions & Insights - April 17, 2025
















