Unveiling the Greatest Asian Leaders in History: A Journey Through Leadership and Legacy

Key Takeaways:
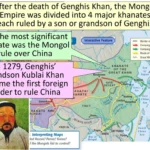
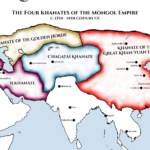
- Genghis Khan united the Mongolian tribes and expanded the Mongol Empire through conquests.
- Kublai Khan extended the Mongol Empire into China, establishing the Yuan Dynasty.
- Emperor Meiji modernized Japan during the Meiji Restoration, leading it into the industrial age.
- Qin Shi Huang unified China and built the Great Wall of China.
- Chairman Mao Zedong led the Chinese Communist Revolution and founded the People’s Republic of China.
- Timur the Lame, a Mongol conqueror, ruled over vast territories in Asia.
- Babur established the Mughal Empire in India.
- Ashoka, an Indian emperor, promoted non-violence and Buddhism.
- Cyrus founded the Achaemenid Empire in Persia, known for its tolerance.
- Gwanggaeto expanded the Goguryeo Kingdom in Korea and defended it against invasions.
- Mohandas K. Gandhi led the Indian independence movement with nonviolent resistance.
- Sun Yat-sen founded the Chinese Nationalist Party and the Republic of China.
- Yuan Shikai became the first president of the Republic of China.
Greatest Asian Leaders in History
Asia, a cradle of ancient civilizations and rich cultural diversity, has witnessed the rise of numerous greatest Asian leaders in history who have left an indelible mark on the world stage.
Genghis Khan: United Mongolian tribes, establishing the vast Mongol Empire. His military prowess and organizational skills extended Mongol influence across Asia and Europe.
Emperor Meiji: Japan’s transformative emperor who ushered in the Meiji Restoration. Modernization, Westernization, and industrialization flourished under his leadership, propelling Japan into the ranks of global powers.
Qin Shi Huang: China’s first emperor, whose reign saw the unification of warring states and the construction of the Great Wall. His centralizing reforms and standardization policies laid the foundation for a unified Chinese empire.
Asoka the Great: Indian emperor known for his embrace of Buddhism and pacifism. He promoted compassion, tolerance, and dharma, shaping the Maurya Empire into a beacon of peace and prosperity.
Indira Gandhi: India’s first female Prime Minister, known for her strong and decisive leadership. Her economic and foreign policies helped shape modern India, leaving a lasting legacy.
Ho Chi Minh: Revolutionary leader who fought for Vietnam’s independence from French colonial rule. His charisma and unwavering determination inspired his people and earned him global recognition.
Lee Kuan Yew: Singapore’s founding father, known for his transformative policies that propelled the city-state from poverty to prosperity. His emphasis on education, economic growth, and social order laid the foundation for Singapore’s success.
Deng Xiaoping: Chinese leader who initiated economic reforms and opened up China to the world. His policies led to rapid economic growth and transformed China into an economic powerhouse.
Aung San Suu Kyi: Burmese pro-democracy leader and Nobel Peace Prize laureate. Her nonviolent resistance and unwavering spirit in the face of adversity have made her an international icon of hope and courage.
These greatest Asian leaders in history serve as testaments to the diverse and influential contributions Asia has made to global affairs. Their leadership, vision, and unwavering determination have shaped the destiny of nations and continue to inspire generations.
Explore the captivating legacies of influential Asian political leaders and statesmen, whose visionary leadership has shaped the course of Asia’s political landscape. Discover how the most powerful political leaders of Asia have navigated complex geopolitical challenges and driven economic growth. Uncover the profound impact of famous Asian leaders and their impact, whose transformative policies have left an enduring mark on their nations and beyond.
Qin Shi Huang: Unifier of China and Builder of the Great Wall
Qin Shi Huang stands as a towering figure in Chinese history, remembered for his ruthless and ambitious reign that shaped the destiny of China. As the first emperor of a unified China, he left an indelible mark on the nation’s landscape and culture.
Key Takeaways:
- Unified China: Qin Shi Huang conquered and merged warring states into a single, centralized empire.
- Great Wall Construction: He initiated the construction of the Great Wall of China, a massive defense fortification.
- Standardization: Qin Shi Huang standardized weights, measures, and writing systems, establishing uniformity across China.
- Harsh Rule: His reign was characterized by brutal suppression of dissent and strict legalism.
- Pursuit of Immortality: Qin Shi Huang sought immortality and commissioned the Terracotta Army to protect him in the afterlife.
Unifying China
Qin Shi Huang’s greatest achievement was the unification of China. He conquered six rival kingdoms, ending centuries of disarray. By centralizing power and establishing a standardized system of government, he laid the foundation for a unified and prosperous empire.
Great Wall of China
To protect his realm from nomadic invasions, Qin Shi Huang embarked on the construction of the Great Wall of China. This colossal project, spanning thousands of miles, has become a symbol of China’s strength and resilience.
Cultural and Political Legacy
Qin Shi Huang’s standardization of language, weights, and measures created a common identity among the Chinese people. His policies and reforms laid the groundwork for the flourishing of Chinese civilization in subsequent centuries. However, his tyrannical rule and suppression of dissent left a dark shadow on his legacy.
Citation:
- Britannica, The Editors of Encyclopedia. “Qin Shi Huang.” Encyclopedia Britannica,
www.britannica.com/biography/Qin-Shi-Huang. Accessed 26 January 2023.
Akbar the Great: Tolerant and Enlightened Mughal Ruler
Akbar the Great, the Mughal emperor from 1556-1605, is renowned for his policies of religious tolerance and cultural synthesis. Under his rule, the Mughal Empire reached its zenith, becoming one of the most prosperous and culturally vibrant empires in the world.
Key Takeaways:
- Akbar’s reign marked a golden age of Mughal art and architecture.
- His “Divine Faith” (Din-i-Ilahi) attempted to blend elements of Islam, Hinduism, and other religions.
- Akbar’s inclusive leadership fostered unity among diverse populations.
- He was a patron of the arts and sciences, encouraging advancements in music, painting, and literature.
- His centralized administration ensured efficiency and stability within the empire.
Akbar’s Legacy:
Akbar’s reign marked a transformative period in Indian history. His policies of tolerance and cultural patronage laid the foundation for a united and prosperous empire. He is considered one of the greatest rulers of the Mughal dynasty and a symbol of Mughal India’s golden age.
Citation:
- Britannica, The Editors of Encyclopedia. “Akbar.” Encyclopedia Britannica,
www.britannica.com/biography/Akbar. Accessed 26 January 2023.
Meiji Emperor: Modernizer of Japan and Architect of Empire
The Meiji Restoration: A Transformative Era
In 1853, the arrival of U.S. Commodore Matthew Perry’s “Black Ships” at the Japanese port of Uraga shattered Japan’s centuries-old isolation. The Meiji Emperor, then a young man of 15, emerged as a central figure in the ensuing Meiji Restoration.
Under his leadership, Japan embarked on a rapid modernization program that transformed the country into a modern imperial power.
Key Takeaways:
- The Meiji Restoration marked a turning point in Japanese history, ending the Edo period and ushering in a new era of modernization and Westernization.
- The Meiji Emperor played a pivotal role in the transformation of Japan, adopting Western technologies, political systems, and educational practices.
- Japan’s modernization led to significant economic growth, military expansion, and a rise in international influence.
A Bold Visionary
The Meiji Emperor, whose name signifies “enlightened rule,” embraced the need for change. He dismantled the feudal system, introduced a modern constitution, and established a national education system.
Westernization and Industrialization
Japan eagerly adopted Western technologies and ideas. The emperor sent delegations abroad to study advanced industrial practices, military tactics, and political systems. These efforts resulted in the rapid development of Japan’s industries, infrastructure, and military capabilities.
Expansion of Empire
With its newfound strength, Japan embarked on a path of imperial expansion. It fought a series of wars against China and Russia, gaining control of territories in Asia and the Pacific. By the early 20th century, Japan had emerged as a major world power.
Legacy of the Meiji Emperor
The Meiji Emperor’s reign laid the foundation for Japan’s transformation into a modern nation. His policies of modernization, Westernization, and imperial expansion had a profound impact on the country’s history and shaped the trajectory of East Asia.
Citation:
- Britannica, The Editors of Encyclopedia. “Meiji.” Encyclopedia Britannica, www.britannica.com/biography/Meiji. Accessed 26 January 2023.