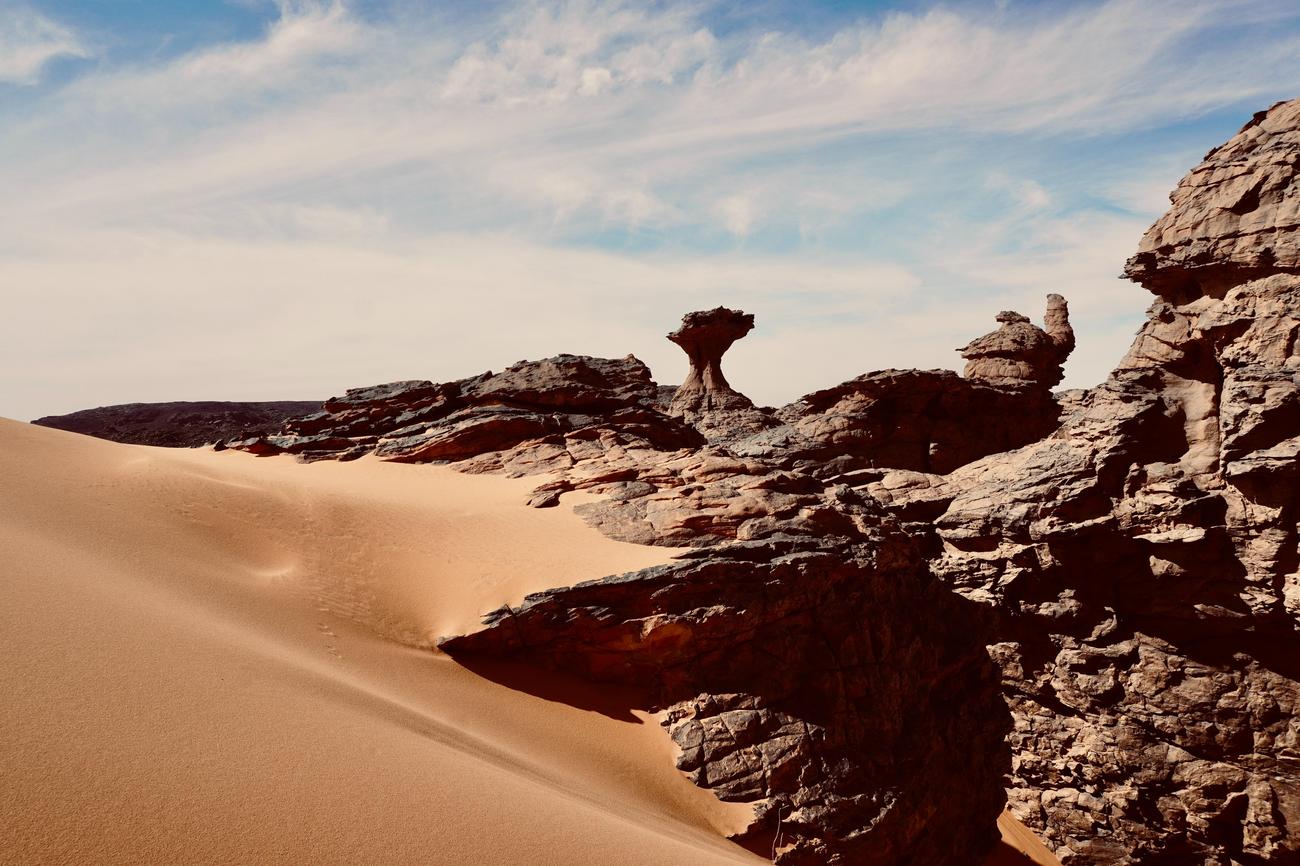
Are you ready to embark on a journey through time and witness the mysterious wonders of Earth’s granitic formations? As a seasoned geologist with a deep passion for unraveling the secrets of our planet, I am honored to guide you through the captivating world of these geological marvels. In this article, we will delve into the formation processes, explore their profound influence on shaping landscapes, and unveil the intricate mineral compositions that make them so unique. Brace yourself for a truly enlightening experience that unveils the mysteries of granitic formations from a geologist’s perspective. Let’s dive in!

Granitic Formations
Granitic formations are a captivating subject in the field of geology. As a seasoned geologist specializing in granitic formations, I have spent many years studying their intricate details, uncovering their secrets, and appreciating the forces that have shaped them over millions of years. In this article, I will take you on a journey to unveil the mysteries of granitic formations, providing you with a geologist’s perspective on these natural wonders.
What Are Granitic Formations?
Granitic formations are coarse-grained intrusive igneous rocks that form from magma underground. These rocks are primarily composed of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. The name “granite” is derived from the Latin word “granum,” meaning “grain,” referring to the distinctive coarse-grained structure of these rocks.
Formation Process and Significance
Granitic formations arise from the slow cooling and solidification of magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides. This process occurs deep below the Earth’s surface, often within the continental crust. The formation of granitic rocks is essential in shaping the landscapes we see around us.
Understanding Their Composition
Granites predominantly consist of feldspar, quartz, mica, and amphibole minerals. The varying mineral compositions give granitic rocks their unique colors, ranging from white and pink to gray. The classification of granitic rocks is based on the percentages of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase feldspar they contain.
True granites contain between 20% and 60% quartz and 35% to 90% alkali feldspar. Granitic rocks with less quartz are classified as syenites or monzonites, while those dominated by plagioclase are known as granodiorites or tonalites. Each classification holds distinct characteristics that contribute to the diverse range of granitic formations we observe in nature.
Unveiling the Beauty
Granitic formations exhibit various physical properties, such as density, compressive strength, and viscosity. They possess poor primary permeability, meaning that fluids struggle to pass through them. However, secondary permeability can occur through cracks and fractures, allowing fluids to move more freely. These properties, combined with their mineral composition, create stunning geological features like tors, domes, and massifs.
The Widespread Distribution
Granitic rock is widely distributed throughout the continental crust and is the most abundant basement rock. Its presence can be found across the globe, from remote mountains to bustling cities. Major exporters of granite include countries like China, India, Italy, Brazil, Canada, Germany, Sweden, and Spain, among others. The granite and marble industry has a rich history dating back to Ancient Egypt, making it one of the oldest industries in the world.
Unmasking the Secrets
Granitic formations hold secrets within their complex compositions and geological history. By studying their mineralogy, age dating techniques, and other geological evidence, geologists can peel back the layers of time and uncover the fascinating stories hidden within these rocks. The radioactive isotope potassium-40 found in granite adds another dimension to our understanding of granitic formations.
Granitic formations have shaped our planet for millions of years, and as we delve deeper into their mysteries, we gain new insight into the Earth’s history and the forces that have shaped its landscapes.
To truly appreciate the beauty of granitic formations, we must look beyond their external appearance and understand the science behind their creation. Through geologists’ expertise in analyzing samples, conducting fieldwork, and interpreting complex data, we can gain a profound appreciation for these natural wonders. So, let’s embark on this journey together and explore the captivating world of granitic formations!
Did you know that granite rock is not only aesthetically pleasing but also has a fascinating history? If you’re interested in learning some important facts about granite rock, then you should definitely click here. This informative article will take you on a journey through the various uses, geological formations, and even the significance of granite rock in different cultures. So, why wait? Satisfy your curiosity by clicking on this link: Important Facts About Granite Rock. Don’t miss out on expanding your knowledge about this incredible natural material.
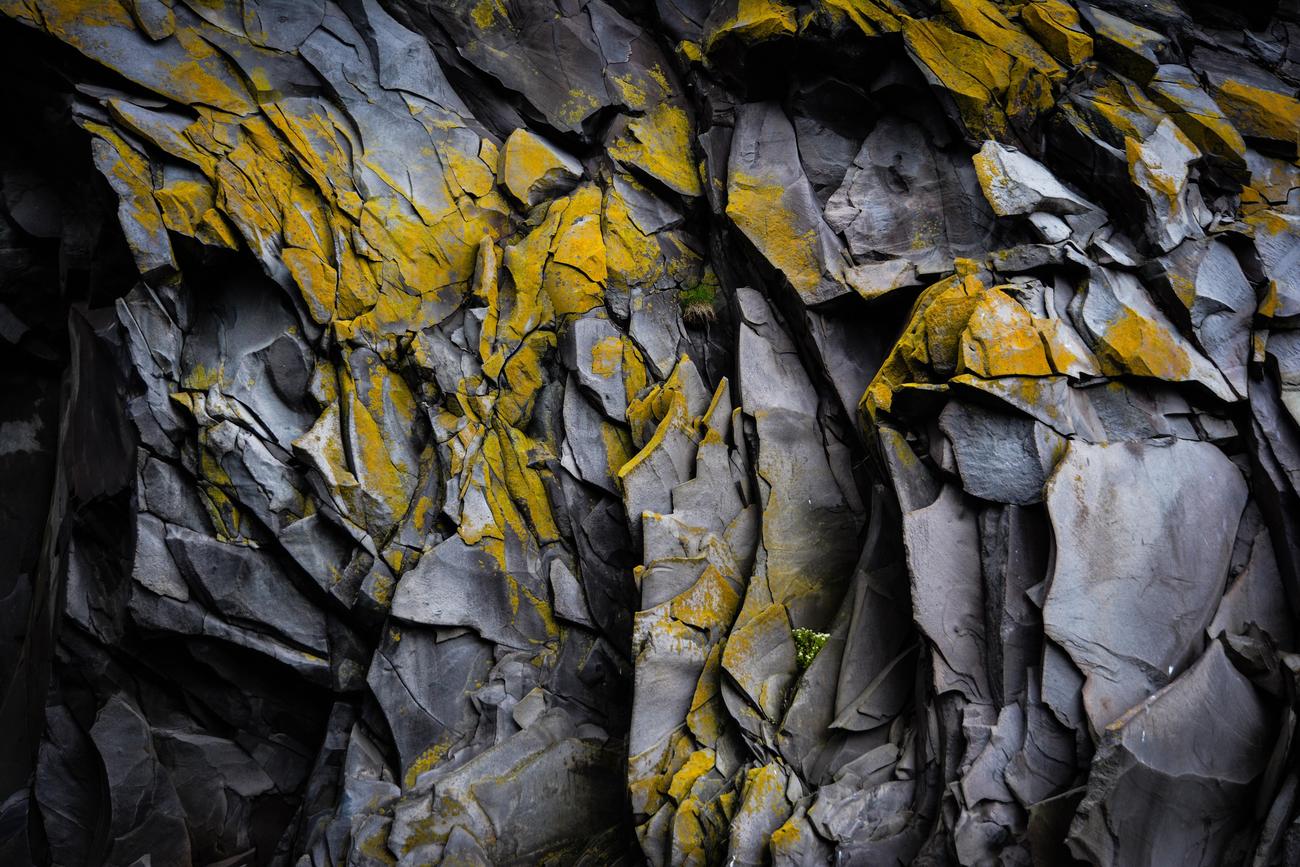

FAQ
Question 1
What is granite and how is it formed?
Answer 1
Granite is a coarse-grained igneous rock that forms from slowly cooling and solidifying magma underground. It is composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase.
Question 2
What is the significance of granitic formations in shaping landscapes?
Answer 2
Granitic formations play a significant role in shaping landscapes due to their durability and resistance to erosion. They form tors, domes, and massifs, creating unique geological features.
Question 3
What are the main minerals found in granitic rocks?
Answer 3
Granitic rocks predominantly consist of feldspar, quartz, mica, and amphibole minerals. The exact mineral composition can vary, resulting in different colors such as white, pink, or gray.
Question 4
How are granitic rocks classified?
Answer 4
Granitic rocks are classified based on the percentage of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase feldspar they contain. True granites have between 20% and 60% quartz and 35% to 90% alkali feldspar.
Question 5
What are some major exporters of granite?
Answer 5
Major exporters of granite include countries such as China, India, Italy, Brazil, Canada, Germany, Sweden, Spain, and more. The granite industry has a long history dating back to Ancient Egypt.
- Revolution Space: Disruptive Ion Propulsion Transforming Satellites - April 24, 2025
- Race Through Space: Fun Family Game for Kids - April 24, 2025
- Unlocking the Universe: reading about stars 6th grade Guide - April 24, 2025