Discover fascinating fun facts about grasshoppers – a closer look into these enigmatic insects. Grasshoppers, these small but extraordinary creatures, have captured the curiosity of nature enthusiasts for centuries. With their ability to leap great distances, chirping songs, and unique life cycle, grasshoppers charm both scientists and casual observers alike. In this article, we will delve into the intriguing world of grasshoppers, uncovering surprising trivia and unveiling their remarkable adaptations. Join us on this journey as we explore the captivating secrets of these enigmatic insects and the important role they play in our ecosystems.

Key Takeaways:
- Grasshoppers and locusts are the same insects but behave differently depending on environmental conditions.
- Grasshoppers have auditory organs on their abdomens and produce music by rubbing their legs or wings together.
- Despite having ears, grasshoppers struggle to distinguish pitch effectively.
- Grasshoppers can jump and fly remarkable distances using their hind legs as catapults and their wings as gliders.
- Grasshoppers are capable of forming destructive swarms that devastate crops.
- Grasshoppers serve as a significant protein source for animals and humans in certain regions.
- Grasshoppers are larger than most insects, measuring between 1 and 7 centimeters in length.
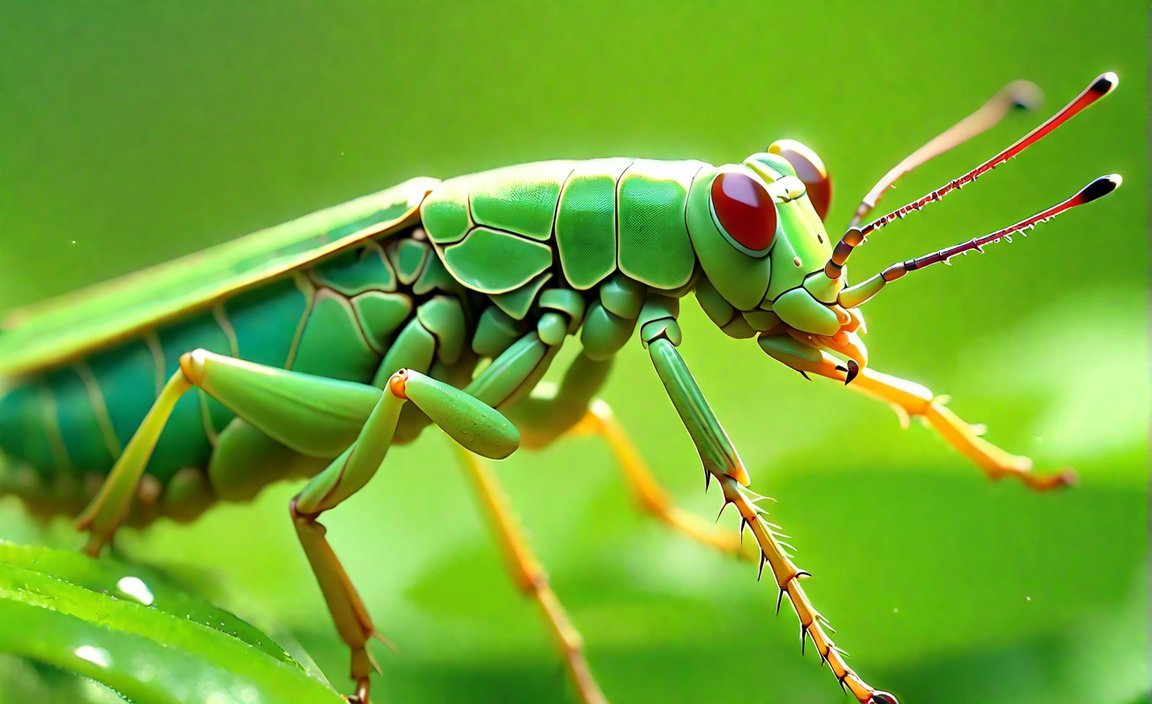
- Grasshoppers possess distinctive physical features, including two antennae, four small legs, two giant legs, and five eyes.
Fun facts about grasshoppers
Grasshoppers are intriguing insects with unique characteristics and behaviors that make them fascinating creatures to study. In this article, we will explore some fun and interesting facts about grasshoppers that will give you a closer look into the world of these enigmatic insects.
1. Grasshoppers and Locusts Are One and the Same
Did you know that grasshoppers and locusts are actually the same insects? The difference lies in their behavior. Grasshoppers display solitary behavior, while locusts have the ability to change their behavior and form massive swarms when environmental conditions are right. It’s like they have a split personality!
2. Grasshoppers Have Ears on Their Bellies
When it comes to hearing, grasshoppers have a unique setup. They possess auditory organs located on their abdomens, which consist of vibrating membranes that respond to sound waves. So, if you ever need to get a grasshopper’s attention, you might want to try talking to its belly!
3. Pitch Perception Can Be Tricky for Grasshoppers
Despite having ears, grasshoppers struggle to distinguish pitch effectively. So, while they might be able to hear sounds, don’t expect them to have a deep appreciation for music. Their ears are more attuned to detecting the presence of sound rather than the nuances of different pitches.
4. Stridulation and Crepitation: Grasshopper Musicians
Grasshoppers are like little musicians in the insect world. They produce sounds by rubbing their legs or wings together in a process known as stridulation or crepitation. It’s their way of serenading their surroundings and communicating with other grasshoppers.
5. Grasshoppers Have Impressive Jumping and Flying Abilities
Grasshoppers are masters of both jumping and flying. They use their powerful hind legs as catapults to propel themselves into the air with incredible force. And once they’re airborne, their wings allow them to glide and cover impressive distances. It’s like they have their own private airshow!
6. Grasshoppers Can Be Destructive Swarms
While grasshoppers might seem harmless individually, they have the potential to cause massive damage when they come together in swarms. These swarms can devastate food crops, consuming everything in their path. They are like an unstoppable force of nature.
7. Grasshoppers Are an Important Protein Source
Grasshoppers play a vital role in providing protein to various animals and even humans in certain regions of Africa and Asia. As a sustainable protein source, they offer a solution to food security challenges in some parts of the world. So, if you’re feeling adventurous, maybe it’s time to give grasshopper protein a try!
8. Grasshoppers: The Giants of the Insect World
When it comes to size, grasshoppers are larger than most insects. They have a typical insect body plan, consisting of a head, thorax, and abdomen. Measuring between 1 and 7 centimeters in length, they are like the giants of the insect world, standing out in their own unique way.
9. Distinctive Physical Features
Grasshoppers possess some distinctive physical features that set them apart. They have two antennae, which they use to sense their environment. They also have four small legs for walking and two giant legs that enable their impressive jumping abilities. And let’s not forget their five eyes that help them keep an eye on their surroundings from all angles.
Grasshoppers are truly fascinating creatures, with their unique behaviors, adaptations, and ecological roles. By uncovering these fun facts, we not only gain a deeper appreciation for the diversity of the natural world but also realize the vital role that grasshoppers play in our ecosystems.
Sources:
ThoughtCo: 10 Fascinating Facts About Grasshoppers
Fact City: 27 Great Facts about Grasshoppers
Here are some interesting facts to pique your curiosity:
- Fun blueberry facts – Did you know that blueberries are one of the few fruits native to North America? Discover more fascinating facts about these juicy blue gems!
- Fun facts about welding – Experience the sparks fly as you delve into the captivating world of welding. Uncover intriguing facts about this skilled trade that keeps our world together.
- Fun facts about chartered accountants – Delve into the numbers game and explore the fascinating world of chartered accountants. From crunching numbers to financial wizardry, these facts will give you a fresh perspective on the profession.
- Fun facts about Francisco Pizarro – Venture into the adventurous life of Francisco Pizarro, the Spanish conquistador who played a pivotal role in shaping the history of South America. Discover intriguing facts about his exploits and conquests.
So, go ahead and click on the links to immerse yourself in these captivating facts!
Grasshoppers have a unique way of hearing
One of the most intriguing aspects of grasshoppers is their extraordinary auditory system. Unlike humans and many other animals, grasshoppers don’t have ears on their heads. Instead, their auditory organs are located on their abdomens. This unusual placement allows grasshoppers to detect and respond to sound waves in their environment[^1^].
Grasshoppers Make Music by Stridulating or Crepitating
Grasshoppers are renowned for their distinctive songs, which they produce through a process called stridulation. Male grasshoppers rub their hind legs against their wings, creating chirping sounds. Stridulation serves multiple purposes, including attracting mates and establishing territorial boundaries[^1^].
Grasshoppers Can Hear, But Can’t Distinguish Pitch Well
While grasshoppers are indeed capable of hearing, their auditory organs have their limitations. Grasshoppers can detect differences in intensity and rhythm, but they don’t excel at distinguishing pitch. This means that they may not be able to discern specific musical notes or tones[^1^].
Grasshoppers Catapult Themselves Into the Air
Grasshoppers are well-known for their incredible jumping ability. When threatened or trying to flee, grasshoppers can propel themselves into the air using their powerful hind legs. If humans had the same jumping ability as grasshoppers, we would be able to cover impressive distances with a single leap[^1^].
Grasshoppers are fascinating creatures with unique adaptations and behaviors. Here’s a closer look at some key aspects of their auditory system and physical abilities:
- Unique Auditory System: Grasshoppers have their ears located on their abdomens, unlike most animals including humans. This unique placement allows them to perceive sound waves in their environment[^1^].
- Stridulation: Male grasshoppers produce their distinctive songs by rubbing their hind legs against their wings. These chirping sounds play a crucial role in attracting mates and establishing territories[^1^].
- Limited Pitch Perception: While grasshoppers can hear sounds, they are not very good at distinguishing pitch. They are more adept at detecting differences in intensity and rhythm[^1^].
- Impressive Jumping Ability: Grasshoppers are known for their remarkable jumping ability. They can catapult themselves into the air using their powerful hind legs, allowing them to evade threats and cover significant distances[^1^].
Overall, grasshoppers have adapted unique ways to hear and communicate with their surroundings. Their auditory organs on their abdomens, combined with their stridulation and jumping abilities, make them fascinating creatures worth exploring further.
Key Takeaways:
- Grasshoppers have auditory organs on their abdomens, which allows them to detect and respond to sound waves[^1^].
- Male grasshoppers produce their distinctive songs through stridulation, which involves rubbing their hind legs against their wings[^1^].
- Grasshoppers can detect differences in intensity and rhythm but struggle to distinguish pitch effectively[^1^].
- Their powerful hind legs enable grasshoppers to catapult themselves into the air, allowing them to escape threats and cover significant distances[^1^].
Sources:
Grasshoppers Undergo Incomplete Metamorphosis
Grasshoppers are fascinating creatures that go through a unique process known as incomplete metamorphosis. Unlike insects that undergo complete metamorphosis, such as butterflies and beetles, grasshoppers have a simpler life cycle consisting of three stages: egg, nymph, and adult[^2^].
During the nymph stage, which is the period between hatching from the egg and reaching adulthood, grasshoppers undergo multiple molting cycles. Molting is the process of shedding their exoskeletons to allow for growth and development[^1^]. Each molt brings subtle changes and advancements until the grasshopper reaches its final adult form[^4^]. This gradual transformation through molting sets grasshoppers apart from insects that go through complete metamorphosis, where the transformation is more drastic.
Incomplete metamorphosis is not unique to grasshoppers. Other insects like earwigs, dragonflies, termites, and aphids also exhibit this type of metamorphosis[^5^]. Just like grasshoppers, these insects go through molting during their nymph stages and gradually develop into adults.
The life cycle of a grasshopper begins with the hatching of eggs. As the grasshopper grows, it progresses through the nymph stages while shedding its exoskeleton each time[^1^]. The last molt marks the transition to adulthood, at which point the grasshopper is fully developed and capable of reproduction.
Grasshoppers play a vital ecological role as herbivorous insects, consuming plant matter such as leaves and stems. They are significant consumers of green vegetation, which helps regulate plant populations in their habitats[^8^]. However, grasshoppers also face challenges from predators, including birds, reptiles, and other insects. To defend themselves, grasshoppers have developed various defensive mechanisms like camouflage and fleeing[^10^].
In conclusion, grasshoppers undergo incomplete metamorphosis as they progress from eggs to nymphs and eventually to adults. Throughout their nymph stages, they experience multiple molts, shedding their exoskeletons and gradually developing into their adult forms. This unique life cycle adaptation allows grasshoppers to grow and thrive in their environments.
Key Takeaways:
- Grasshoppers undergo incomplete metamorphosis, which is different from the complete metamorphosis seen in butterflies and beetles.
- The grasshopper life cycle consists of three stages: egg, nymph, and adult.
- During the nymph stage, grasshoppers undergo multiple molting cycles, shedding their exoskeletons to allow for growth and development.
- Grasshoppers gradually transform from nymphs to adults through these molting stages.
- Incomplete metamorphosis is not limited to grasshoppers; other insects, including earwigs, dragonflies, termites, and aphids, also exhibit this type of metamorphosis.
- Grasshoppers play an important ecological role as herbivorous insects, consuming plant matter and regulating plant populations.
- Grasshoppers have evolved various defensive mechanisms like camouflage and fleeing to protect themselves from predators.
Sources:
[^1^]: University of Kentucky Entomology. (n.d.). Grasshoppers. University of Kentucky College of Agriculture.
[^2^]: Naturalis Biodiversity Center. (n.d.). Lifecycle of a grasshopper. BioKids.
[^4^]: Timbrell, LL. (2020, September 11). How Do Grasshoppers Change as They Grow? ThoughtCo.
[^5^]: Hottes, F.C. (1905). The Grasshopper Book.
[^8^]: Science Learning Hub. (n.d.). Grasshopper. Science Learning Hub.
[^10^]: National Park Service. (n.d.). Grasshoppers. Glacier National Park.
Grasshoppers: A Vital Source of Food for Many Animals
Grasshoppers are fascinating insects that play a crucial role in our ecosystems. Not only are they abundant, with over 11,000 different species worldwide, but they also serve as a vital food source for numerous animals, including birds, reptiles, and mammals. Their high protein content makes them an essential part of the food chain, contributing to the survival and well-being of various species (Facts.net).
These enigmatic creatures offer numerous fun facts and intriguing adaptations that shed light on their significance as a food source. They have ears on their bellies, allowing them to hear sounds in their environment (ThoughtCo). While they may struggle to distinguish different pitches, they can still detect differences in intensity and rhythm (ThoughtCo). Grasshoppers also possess the unique ability to produce music through a process called stridulation or crepitation (ThoughtCo).
Aside from their auditory abilities, grasshoppers are known for their remarkable jumping and flying capabilities. They can catapult themselves into the air, showcasing their agility and power (ThoughtCo). This ability also enables them to escape from predators and find food and mates. Grasshoppers have been around for millions of years, predating even the existence of dinosaurs (ThoughtCo).
To defend themselves, grasshoppers may “spit” liquid as a means of protection (ThoughtCo). While herbivorous by nature, feeding on leaves, grasses, and cereal crops, grasshoppers have the potential to cause significant damage to agricultural crops (Ducksters). This destructive potential raises concerns among farmers and ranchers (ThoughtCo). Additionally, studies suggest that grasshoppers may carry diseases that can be transmitted to livestock (Fact City).
Despite the challenges they pose to agriculture, grasshoppers are also cultivated by commercial companies as a sustainable protein source (liveanimalslist.com, Facts.net). Indeed, many people consume grasshoppers due to their high protein and vitamin C content (Fact City). These insects provide a nutritious alternative for certain regions and cultures.
In summary, grasshoppers are not only captivating creatures with intriguing adaptations, but they also serve as a vital food source for many animals. From their impressive auditory abilities and music-making skills to their powerful jumping and flying feats, grasshoppers have unique characteristics that make them exceptional members of our ecosystems. Their impact on agriculture and potential benefits as a sustainable protein source make them worthy of our attention and appreciation.
Key Takeaways:
- Grasshoppers are a valuable food source for various animals, including birds, reptiles, and mammals.
- With over 11,000 different species worldwide, grasshoppers are abundant and play a crucial role in the food chain.
- Grasshoppers possess ears on their bellies and can detect differences in intensity and rhythm, although they struggle to distinguish pitch effectively.
- They have the ability to produce music through stridulation or crepitation.
- Grasshoppers are agile and capable of impressive jumping and flying, enabling them to escape predators and find food and mates.
- Despite being herbivorous, grasshoppers can be destructive to agricultural crops.
- Grasshoppers are cultivated as a sustainable protein source by commercial companies.
- Grasshoppers offer high protein and vitamin C content, making them a nutritional option for certain regions and cultures.
Sources:
- Facts.net: Link to source
- ThoughtCo: Link to source

FAQ
Q1: What are some interesting facts about grasshoppers and locusts?
A1: Grasshoppers and locusts are actually the same insects, but they behave differently depending on the environmental conditions. Locusts can form destructive swarms that devastate food crops, while grasshoppers don’t exhibit this behavior on a large scale. Both grasshoppers and locusts are fascinating creatures with unique characteristics and behaviors.
Q2: How do grasshoppers produce their distinctive sounds?
A2: Grasshoppers make their music through a process called stridulation or crepitation. Male grasshoppers rub their hind legs against their wings to create chirping sounds. This behavior serves multiple purposes, including attracting mates and establishing territorial boundaries. It’s their way of communicating with each other.
Q3: Can grasshoppers hear sounds?
A3: Yes, grasshoppers have auditory organs, but they have limitations in distinguishing pitch. While they can detect differences in intensity and rhythm, they may not be able to discern specific musical notes or tones.
Q4: How far can grasshoppers jump?
A4: Grasshoppers are well-known for their incredible jumping ability. Using their powerful hind legs as catapults, they can propel themselves into the air and cover impressive distances. If humans had the same jumping ability as grasshoppers, we would be able to leap remarkable distances in a single bound.
Q5: What is the life cycle of a grasshopper?
A5: Grasshoppers undergo incomplete metamorphosis, unlike insects with complete metamorphosis like butterflies. They go through three stages: egg, nymph, and adult. The young grasshoppers, known as nymphs, resemble miniature versions of the adults and gradually develop into full-grown adults through a series of molting or shedding of their exoskeletons.
- Unlock Filipino Culture: A Deep Dive into Traditions and Practices - April 23, 2025
- Unlock Spanish Culture: Insights & Opportunities Now - April 23, 2025
- White Spirit Uses & Substitutes: A Deep Dive for Pros & DIYers - April 23, 2025