This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the fibula, covering its anatomy, function, common injuries, and treatment options.
Decoding the Fibula: Anatomy and Function
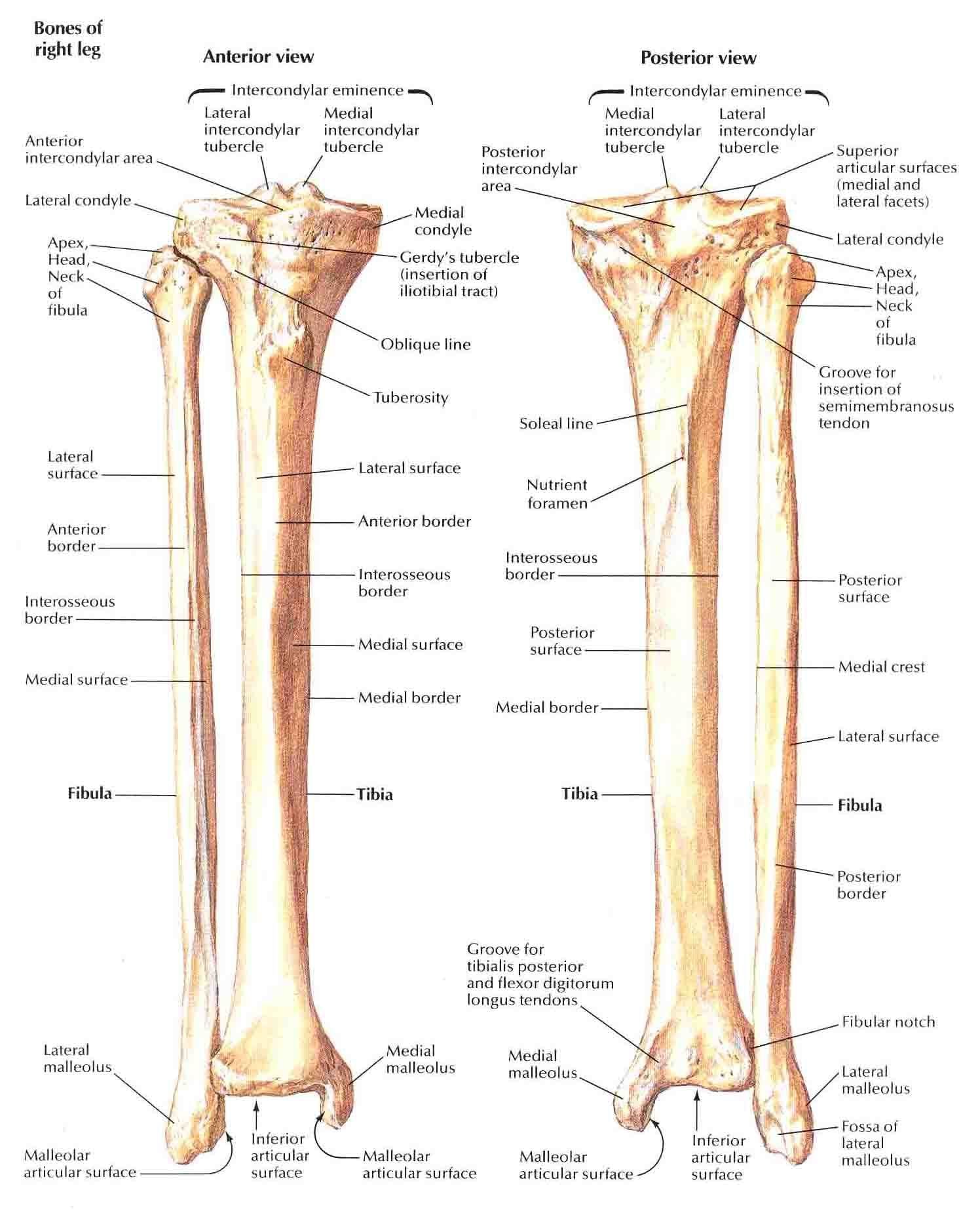
The fibula, often overshadowed by its larger neighbor, the tibia, is a long, slender bone located on the lateral side (outside) of your lower leg. It plays a vital, albeit less obvious, role in lower leg function.
Fibula Anatomy 101
The fibula is divided into three main parts:
The Head: Located at the proximal end (near the knee), the fibula’s head connects to the tibia, acting as an anchor point.
The Shaft: The long, slender middle section of the fibula, composed of strong bone tissue, provides a rigid structure for muscle attachment.
The Lateral Malleolus: The distal end of the fibula forms the bony knob you can feel on the outside of your ankle. This is a key component of the ankle joint, contributing significantly to stability and guiding movement.
The fibula is connected to the tibia by the interosseous membrane, a tough, fibrous sheet, and ligaments at the proximal and distal ends, forming the tibiofibular joints. These connections permit limited movement between the bones, crucial for ankle flexibility.
Why Your Fibula Matters
While the tibia bears the brunt of your weight, the fibula performs several essential functions:
Muscle Attachment: Numerous leg muscles responsible for foot and ankle movement attach to the fibula, utilizing it as a lever for generating force.
Ankle Stability: The lateral malleolus acts as a brace, limiting excessive sideways movement and minimizing the risk of sprains and other injuries.
Force Distribution: The fibula aids in distributing forces transmitted through the lower leg, particularly during activities like walking and running. This likely reduces stress on the tibia and surrounding structures.
Bone Graft Source: Sections of the fibula can be used for reconstructive surgery in other parts of the body due to its non-weight-bearing capacity. This fibular free flap procedure demonstrates its unique versatility in the medical field.
Common Fibula Issues and Treatment
Like any bone, the fibula is susceptible to injury and disease.
Fibular Fractures
These are relatively common, often accompanying ankle injuries. Treatment depends on the severity and location of the fracture, and may range from immobilization in a cast to surgical intervention. Some fractures might heal naturally with rest and support. Protect yourself on the field with a high-quality flak jacket football.
Fibular Hemimelia
This congenital condition involves a shortened or absent fibula, which can affect leg development and function. Treatment varies and may involve corrective surgery and orthotics. Ongoing research is exploring new approaches to manage this condition.
Fibula vs. Tibia: A Powerful Partnership
The fibula and tibia work synergistically to support and stabilize the lower leg. The tibia, as the primary weight-bearing bone, handles the majority of the load. The fibula provides crucial support, acts as an attachment point for muscles, and significantly contributes to ankle stability. This partnership is fundamental to proper lower leg biomechanics.
Is it “Fibia” or “Fibula”?
“Fibia” is a common misspelling of “fibula.” The correct term for the smaller lower leg bone is fibula. Remember “never tell a little fib“—the “fib” refers to the fibula, the smaller of the two lower leg bones.
Locating Your Fibula
The fibula is located on the lateral side of the lower leg, running parallel to and slightly behind the tibia. The proximal end connects to the tibia just below the knee joint, while the distal end forms the lateral malleolus (outer ankle bone).
Key Points to Remember
- Anatomy: Long, slender bone lateral to the tibia, comprising the head, shaft, and lateral malleolus.
- Function: Ankle stability, muscle attachment, force distribution, bone graft source.
- Common Problems: Fibular fractures, fibular hemimelia.
- Relationship with Tibia: Supports the tibia, contributes to ankle stability.
- Spelling: Fibula (not fibia).
This guide offers a comprehensive understanding of the fibula. However, individual anatomy can vary. Consult a medical professional for personalized advice. Ensure your financial transactions are safe with a counterfeit money detector pen.












1 thought on “Understanding Your Fibula: Anatomy, Function, and Treatment Options”
Comments are closed.