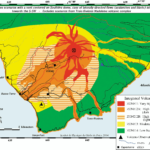
Prepare to be amazed by the world’s most epic volcanoes! These colossal mountains of fire and fury have been erupting for ages, leaving behind mind-blowing stories of creation, destruction, and survival. We’ll dig deep into the biggest volcanic blasts ever and how they rocked ancient civilizations. We’ll also meet the brave scientists who study these sleeping giants, using their smarts to predict when they’ll wake up. Plus, we’ll explore the most active volcanoes on Earth, understand how they impact nearby cities, and marvel at how they’ve transformed our planet over time. Get ready for a wild ride into the fiery heart of nature’s most powerful forces!
Famous Volcanoes: Earth’s Majestic and Mysterious Giants
Volcanic Titans
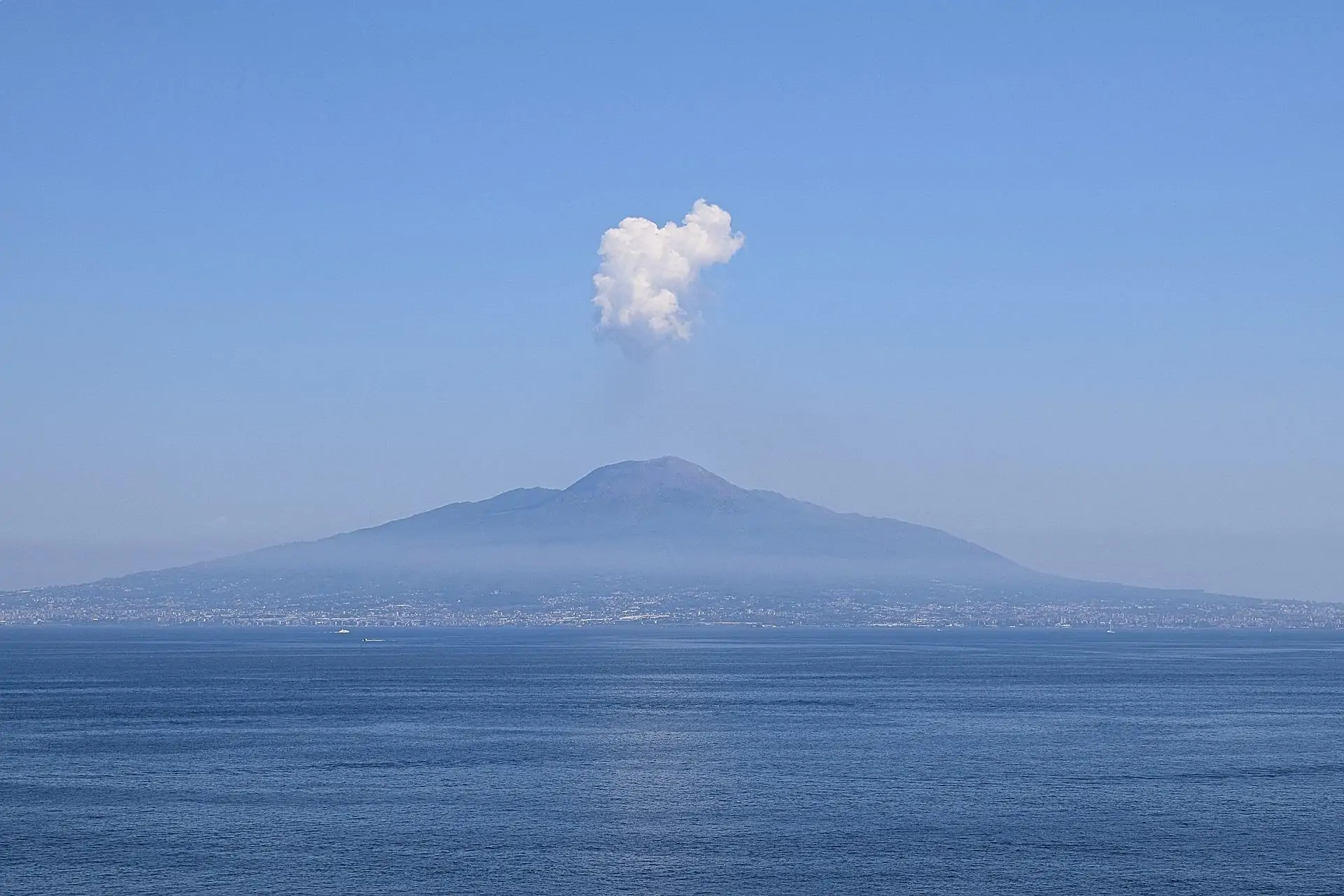
Throughout history, awe-inspiring volcanoes have captivated us with their fiery power and colossal presence. From the legendary peaks of Mount Fuji to the catastrophic eruptions of Mount Vesuvius, these geological behemoths have sculpted landscapes, influenced civilizations, and captured our imagination.
Icons of Nature’s Might
- Mount St. Helens: This towering stratovolcano in the Pacific Northwest made headlines with its explosive eruption in 1980, reshaping the landscape and serving as a stark reminder of nature’s untamed fury.
- Mount Vesuvius: Located close to Naples, Italy, this stratovolcano is etched into history for its devastating eruption in 79 AD, burying the ancient Roman cities of Pompeii and Herculaneum in a tragic shroud of volcanic ash.
- Kīlauea: A shield volcano on the Hawaiian island, Kīlauea is a Polynesian wonder that has captivated visitors with its mesmerizing lava flows and active eruptions, painting the night sky with an ethereal glow.
Diversity in Volcanic Form
Famous volcanoes come in all shapes and sizes, boasting a remarkable range of forms:
- Stratovolcanoes: Imagine a steep, cone-shaped mountain built from layers of lava and ash, towering over the surroundings.
- Shield Volcanoes: These gentle giants are like broad, sloping shields formed by low-viscosity lava flows that spread out widely.
- Cinder Cones: These smaller, steeper volcanoes are formed by the accumulation of cinder, a type of volcanic rock, creating conical hills that add to the volcanic tapestry.
Unveiling Earth’s Secrets
Studying famous volcanoes is like opening a window into the inner workings of our planet. Scientists analyze volcanic materials and monitor activity to decode the mysteries of these geological enigmas.
Harnessing Volcanic Energy
While volcanic eruptions can be destructive forces, they also hold potential benefits:
- New Land Formation: Volcanic eruptions can create new islands and extend coastlines, shaping the Earth’s geography.
- Geothermal Energy: The heat from volcanic areas can be harnessed to generate clean, renewable energy.
- Soil Enrichment: Volcanic ash contains valuable minerals that can enrich the soil, benefiting agriculture.
Lessons from the Past, Preparing for the Future
Examining famous volcanoes teaches us invaluable lessons for the future:
- Eruption Preparedness: Understanding volcanic behavior helps us prepare for potential eruptions, protecting lives and property.
- Mitigation Strategies: By studying past eruptions, we can develop strategies to mitigate risks and reduce their impact.
- Environmental Protection: Volcanoes are integral parts of ecosystems, and their study helps us safeguard their delicate balance.
As we continue to explore the secrets of famous volcanoes, we gain a profound appreciation for the awe-inspiring power and fragility of our planet. These geological giants remind us that Earth is a dynamic, ever-changing masterpiece, and we are fortunate to witness their majesty from afar.
- Did you know that different types of volcanoes can form depending on the composition of magma and the style of eruption?
- Discover the various volcanic hazards and risks that can impact communities living near active volcanoes: Volcanic hazards and risks
- Travel back in time to learn about some of the most famous volcanic eruptions in history, which have shaped landscapes and influenced human civilizations.
- Explore the potential impacts of volcanoes and climate change, examining how volcanic activity can affect global temperatures and atmospheric conditions.
- Plan your adventure responsibly with our guide to Volcano tourism and safety, ensuring an unforgettable and safe experience while visiting active volcanic sites.
- Embark on a geological journey to discover the Volcanic islands and archipelagos formed by volcanic activity, showcasing their unique landscapes and ecosystems.
- Delve into the world of Volcanic rocks and minerals, unlocking the secrets of their formation and exploring their applications in various industries.
- Investigate the potential of Geothermal energy from volcanoes as a sustainable energy source, harnessing the heat generated by volcanic activity.
- Expand your horizons beyond Earth with our exploration of Volcanoes on other planets, discovering the fascinating volcanic landscapes of our solar system.
- Stay informed and prepared with an overview of Volcano monitoring and prediction techniques, empowering communities to mitigate risks associated with volcanic activity.
What are the largest volcanic eruptions in history and their impact
Volcanic eruptions are no joke. They can unleash mind-boggling destruction, wipe out entire towns, and even leave a lasting mark on the planet. We’ve seen some real whoppers throughout history, and here’s a look at a few of the biggest and baddest:
Mount Tambora, 1815: This volcano in Indonesia threw an almighty tantrum, sending ash and debris high into the atmosphere. It caused a global “year without a summer” in 1816, with bizarre weather patterns and famine worldwide.
Krakatoa, 1883: This Indonesian volcano blew its top with such force that it triggered massive tsunamis, wiping out coastal communities and killing over 36,000 people. The eruption also sent shockwaves around the world, causing changes in weather patterns and atmospheric pressure.
Mount Pinatubo, 1991: This Philippine volcano had a volcanic temper tantrum that spewed ash 20 miles high. It’s like it was trying to reach the moon! The eruption caused widespread damage, killed hundreds, and even cooled down the planet for a while.
The Impact of Volcanic Eruptions
These volcanic giants don’t just make a mess; they can have serious consequences:
Local destruction: Towns and villages can be buried, people can lose their lives, and even entire ecosystems can be destroyed. It’s like a natural apocalypse!
Global effects: Volcanic eruptions can mess with the planet’s weather, even triggering famines. They can also disrupt trade and transportation, making it hard for people to get what they need.
Volcanic Eruption Studies
Lucky for us, smart scientists are studying volcanic eruptions to understand what makes them tick. They’re trying to figure out:
- Why these volcanoes get so angry?
- How to predict when they’re going to blow their tops?
- How to minimize the damage when they do.
By getting to know these volcanic beasts better, scientists can help us prepare for and avoid getting caught in their fiery crossfire.
How do scientists monitor and predict volcanic eruptions?
Volcanoes are fascinating and powerful natural phenomena, but they can also be unpredictable and dangerous. That’s why scientists work hard to monitor and predict volcanic eruptions, so that we can protect ourselves and our communities.
Here’s a closer look at some of the tools and techniques scientists use:
- Earthquakes Galore: Volcanic rumbles often signal upcoming eruptions. Scientists place earthquake detectors near volcanoes to catch these seismic tremors.
- Gas Sniffers: Eruptions release gases like sulfur dioxide and carbon dioxide. Scientists use sensors to measure gas levels, giving them clues about the volcano’s activity.
- Groundwork Groundwork: Magma makes its way up through volcanoes, pushing the ground. Scientists use tiltmeters and GPS to measure these tiny shifts, providing insights into magma’s location and size.
- Satellite Snoopers: Satellites have a bird’s-eye view of volcanoes, tracking changes in temperature, gas emissions, and ground deformation. This data helps scientists understand the volcano’s condition.
- AI Superpowers: Artificial intelligence and machine learning are stepping into the volcanic arena. Scientists use these algorithms to analyze data from earthquakes, gases, and ground deformation, improving eruption predictions.
By combining these methods, scientists can monitor volcanoes closely and forecast eruptions with greater accuracy. This knowledge is invaluable for warning communities, allowing them to prepare for potential hazards.
Remember, volcanic eruptions are part of Earth’s natural rhythm, but with science on our side, we can live safely alongside these fiery giants.
What are the most active volcanoes in the world and the risks they pose?
Volcanic eruptions are like nature’s fireworks, awe-inspiring but with a darker side. The world is home to a multitude of active volcanoes, keeping geologists and scientists on their toes. Let’s dive in and uncover the volcanoes that pose the greatest risks.
Hotspots of Volcanic Activity
Indonesia, a land of stunning islands, is the volcanic champion. With over 13,000 volcanoes, it’s no wonder it’s known as the “Ring of Fire.” Around the globe, an estimated 1,350 active volcanoes are under watchful eyes.
The Danger Zones
Volcanic eruptions are not all created equal. They come in various forms, each posing unique threats:
- Lava flows: Imagine a river of molten rock flowing down the side of a volcano, consuming everything in its path like a hungry monster.
- Ash clouds: These clouds can reach high into the sky, disrupting air travel, coating the ground like a thick blanket, and causing breathing problems.
- Lahars: Superheated mudflows that can race down mountainsides, destroying everything in their wake.
- Pyroclastic flows: A deadly mix of ash and gas that blasts out of a volcano at supersonic speeds, incinerating anything caught in its path.
Monitoring the Beasts
Scientists use advanced techniques to keep tabs on these volcanic monsters:
- Seismic activity: Like a secret code, tremors and earthquakes give clues about an impending eruption.
- Gas emissions: Sulphur dioxide and other gases released by magma act as warning signs of volcanic unrest.
- Ground deformation: When a volcano’s shape changes, it’s a sign that magma is on the move.
- Satellite observations: Space-based eyes keep a close watch, tracking temperature changes and surface deformation.
- Advanced modeling: Supercomputers are like volcanic whisperers, simulating eruption scenarios to help us prepare and evacuate.
Keeping Communities Safe
Those living in the shadow of these volcanic giants need a solid game plan. Mitigation strategies are the key to minimizing the risks:
- Hazard mapping: Mapping out areas that could be affected by lava, ash, and other dangers.
- Early warning systems: Like the sirens in tornado movies, these systems provide timely alerts so people can run for cover.
- Evacuation plans: Clear instructions for how to get out of harm’s way quickly and safely.
- Education and awareness: Empowering communities with knowledge about volcanic risks and safety measures.
The Bottom Line
Volcanic eruptions are a force of nature, capable of both awe-inspiring spectacles and devastating consequences. But by understanding these active volcanoes and the risks they pose, we can prepare and protect ourselves. Monitoring, planning, and educating are our weapons against these volatile giants. Remember, knowledge is power, especially when it comes to volcanoes.
FAQ
Q1: Which are the most famous volcanoes around the world and why?
A1: Some of the most famous volcanoes include Mount Vesuvius (Italy), Mount Fuji (Japan), Krakatoa (Indonesia), Mount St. Helens (USA), and Kīlauea (Hawaii, USA). These volcanoes are renowned for their historical eruptions, cultural significance, and geological impact. Mount Vesuvius is infamous for its 79 AD eruption that buried the Roman cities of Pompeii and Herculaneum. Mount Fuji is an iconic symbol of Japan and a popular tourist destination. Krakatoa’s 1883 eruption was one of the largest and most devastating in recorded history. Mount St. Helens’ 1980 eruption was a major scientific event and a reminder of the power of volcanoes. Kīlauea is an active volcano that has been erupting continuously since 1983, creating new land and reshaping the landscape of Hawaii’s Big Island.
Q2: What are the largest volcanic eruptions in history and their impact?
A2: The largest volcanic eruptions in history include the 1815 eruption of Mount Tambora (Indonesia), the 1883 eruption of Krakatoa (Indonesia), and the 1991 eruption of Mount Pinatubo (Philippines). These eruptions had profound impacts on global climate, leading to years without summer and widespread famines. The Tambora eruption is estimated to have killed over 71,000 people, while the Krakatoa eruption generated tsunamis that killed over 36,000 people. The Pinatubo eruption injected vast amounts of sulfur dioxide into the stratosphere, causing a temporary cooling effect on the Earth’s temperature.
Q3: How do scientists monitor and predict volcanic eruptions?
A3: Scientists use various methods to monitor and predict volcanic eruptions, including: seismic monitoring, gas monitoring, ground deformation monitoring, and satellite observations. Seismic monitoring involves detecting and analyzing seismic waves generated by volcanic activity, which can indicate magma movement and impending eruptions. Gas monitoring measures the composition and volume of gases released by volcanoes, as certain gases can indicate changes in volcanic activity. Ground deformation monitoring uses instruments to detect changes in the shape or elevation of the ground around volcanoes, which can be caused by magma movement or pressure buildup. Satellite observations provide data on temperature changes, gas emissions, and surface deformation, which can also be used to track volcanic activity and predict eruptions.
Q4: What are the most active volcanoes in the world and the risks they pose?
A4: Indonesia has the highest number of active volcanoes in the world, with over 13,000 volcanoes. Other countries with significant volcanic activity include the United States, Japan, Russia, and Italy. Active volcanoes pose various risks, including lava flows, ashfall, pyroclastic flows, lahars (volcanic mudflows), and volcanic gases. Lava flows can destroy buildings and infrastructure, while ashfall can disrupt transportation and agriculture. Pyroclastic flows are fast-moving clouds of hot gas and ash that can incinerate everything in their path. Lahars can bury entire villages and cause widespread damage. Volcanic gases can be toxic and can cause respiratory problems and other health issues.
Q5: How do iconic volcanoes shape landscapes and influence human history?
A5: Iconic volcanoes have shaped landscapes and influenced human history in numerous ways. Volcanic eruptions can create new land, such as the Hawaiian Islands, which were formed by the eruptions of the Mauna Loa and Kīlauea volcanoes. Volcanic ash and lava can also enrich soils, making them more fertile for agriculture. In some cultures, volcanoes are considered sacred or mystical places and have played a significant role in mythology and folklore. For example, Mount Fuji in Japan is considered a sacred mountain and is a popular destination for pilgrims and tourists. Volcanic eruptions can also have negative impacts on human history, causing widespread destruction and loss of life. The eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD buried the Roman cities of Pompeii and Herculaneum, preserving them as archaeological treasures that provide insights into ancient Roman life.
- Sept 31 Myth: Unveiling Calendar Secrets - March 18, 2025
- How Long & Till December 18, 2025: Accurate Countdown Guide - March 18, 2025
- Discover Japanese Artists: A Complete History - March 18, 2025