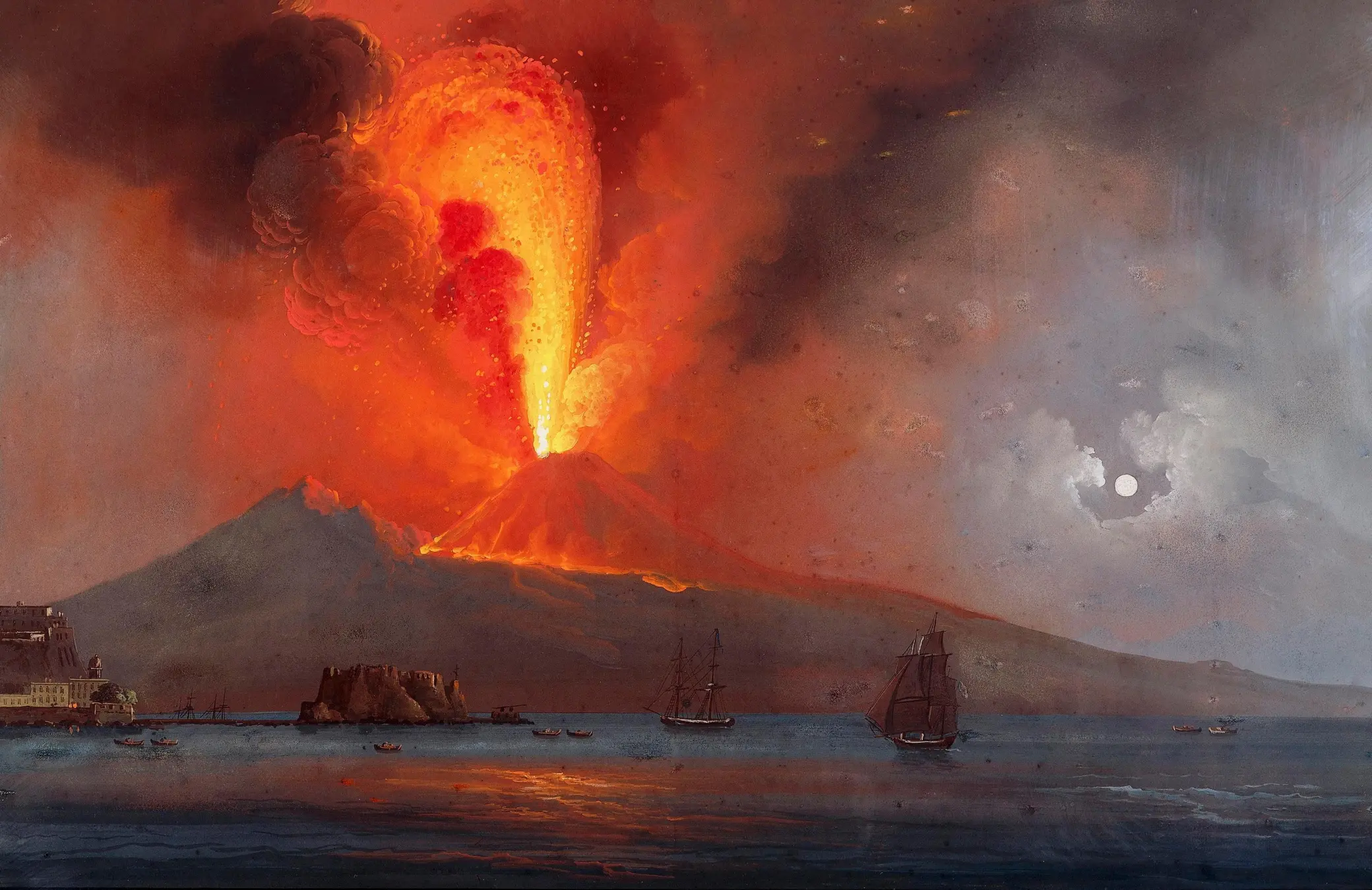Picture this: a volcanic eruption so powerful, it blankets a thriving city in ash, preserving it for centuries to come. Or an explosion so deafening, it rattles windows thousands of miles away. These are just a few of the famous volcanic eruptions that have shaped history. Join us as we delve into the fiery depths of these geological titans, uncovering the captivating stories behind their eruptions and the lasting impact they’ve had on human civilizations and the planet itself.
Volcanic Explosions That Rocked History
Volcanoes, those fiery mountains that erupt with molten rock and ash, have been shaping our planet’s destiny since the dawn of time. Some of their outbursts have left an unforgettable mark on human history, shaping nations, altering the climate, and leaving behind tales of both awe and devastation.
The Mount Tambora Tantrum (1815): The Ultimate Volcanic Superpower
When Mount Tambora in Indonesia let loose in 1815, it was a cataclysmic explosion that hurled ash into the sky, reaching a record-breaking height of 40 kilometers. The eruption was so powerful that it caused a worldwide chill known as the “Year Without a Summer” in 1816. Temperatures plummeted, crops failed, and famine spread like wildfire.
Krakatoa’s Fiery Demise (1883): A Tsunami of Destruction
In 1883, Krakatoa, an Indonesian island volcano, erupted with a fury that shook the world. The explosion created a deafening roar and triggered a series of towering tsunamis that crashed onto coastal shores, claiming the lives of over 36,000 people. The violent eruption wiped out the entire island and left a crater that’s still visible today.
Mount St. Helens: A Wake-Up Call in 1980
When Mount St. Helens in the United States erupted in 1980, it was a spectacle of nature’s wrath. The blast killed 57 people, devastated forests, and caused billions of dollars in damage. It also offered scientists a fascinating glimpse into the inner workings of volcanic eruptions, helping them better understand these geological giants.
Laki’s Toxic Breath (1783): An Invisible Threat
In Iceland, the eruption of Laki in 1783 unleashed a relentless torrent of sulfur dioxide into the atmosphere. This invisible gas spread far and wide, causing climate change that chilled temperatures and poisoned crops. Livestock died in droves, leading to famine and misery across the region.
Mount Pinatubo’s Global Embrace (1991)
In 1991, Mount Pinatubo in the Philippines erupted, sending ash high into the sky. The ash plume circled the globe, causing temporary cooling of the Earth’s temperatures. The eruption also spewed out sulfuric gases, which can have long-term effects on the ozone layer.
Iconic Volcanic Eruptions have played a pivotal role in shaping our planet. They’ve inspired awe, fueled scientific research, and left an enduring legacy on human history. As we learn more about these geological behemoths, we gain a deeper appreciation for the power they wield and the importance of recognizing and mitigating the risks they pose.
Explore the famous volcanoes that have shaped our planet, from the awe-inspiring Mount Everest to the majestic Mount Fuji. Delve into the Types of volcanoes and discover their unique characteristics, from explosive stratovolcanoes to gentle shield volcanoes. Understand the Volcanic hazards and risks associated with these powerful natural wonders, from pyroclastic flows to ash clouds. Investigate the complex relationship between Volcanoes and climate change, examining their role in shaping our planet’s atmosphere and temperature. Embark on a Volcano tourism and safety adventure, discovering the thrill of witnessing these eruptions firsthand while learning about the importance of safety precautions. Explore the breathtaking Volcanic islands and archipelagos that have emerged from volcanic activity, creating unique ecosystems and stunning landscapes. Discover the fascinating Volcanic rocks and minerals that form during volcanic eruptions, revealing the secrets of the Earth’s interior. Harness the power of Geothermal energy from volcanoes as a sustainable energy source, tapping into the Earth’s natural heat. Venture beyond our planet to explore the captivating Volcanoes on other planets, unlocking the mysteries of the solar system. Stay informed about the latest breakthroughs in Volcano monitoring and prediction techniques, ensuring communities are prepared for potential eruptions.
Which Volcanic Eruptions Had the Most Devastating Consequences?
Volcanoes, powerful forces of nature, have the potential to unleash unimaginable destruction, shaping the course of civilizations and leaving an enduring mark on our planet. Throughout history, countless volcanic eruptions have occurred, each with its own unique impacts and consequences. Let’s delve into the annals of time to explore some of the most devastating volcanic eruptions that have left a profound imprint on humanity.
1. Mount Tambora: The Year Without a Summer
In 1815, the Indonesian volcano Mount Tambora erupted with an explosive force that sent ash plumes soaring into the atmosphere, blotting out the sun for months. The eruption’s impact was far-reaching, causing global cooling and famine. Known as the “Year Without a Summer,” 1816 brought widespread crop failures, societal unrest, and hardship across Europe and North America.
2. Krakatoa: The Thunderous Explosion
In 1883, the Indonesian island of Krakatoa was shattered by a cataclysmic explosion that released the energy of millions of nuclear bombs. The volcanic eruption triggered colossal tsunamis that ravaged coastal areas, claiming over 36,000 lives. The thunderous explosions reverberated across the globe, disrupting weather patterns and casting the world into darkness for days.
3. Laki: The Toxic Cloud
In 1783, the Icelandic volcano Laki embarked on a protracted eruption that spewed vast amounts of toxic sulfur dioxide into the atmosphere. The poisonous cloud spread far beyond Iceland, causing respiratory ailments and crop failures in distant lands. The resulting famine and devastation left an indelible mark on Icelandic history and beyond.
4. Nevado del Ruiz: The Deadly Mudflow
In 1985, Colombia’s Nevado del Ruiz volcano erupted, triggering a catastrophic mudflow that buried the town of Armero. The mudflow, composed of volcanic debris and melted snow, surged down the mountainside with terrifying speed, claiming the lives of over 20,000 people. This tragedy serves as a sobering reminder of the secondary hazards associated with volcanic activity.
5. Mount Pinatubo: The Global Impact
In 1991, Mount Pinatubo in the Philippines erupted with explosive force, releasing an enormous column of ash and gas into the atmosphere. The eruption temporarily altered global temperatures and disrupted ozone layer chemistry. The fallout from Pinatubo’s eruption served as a stark reminder of the profound impact that volcanic eruptions can have on our planet.
These devastating volcanic eruptions have left an indelible mark on human history and continue to shape our understanding of volcanic activity. Through scientific study and preparedness, we can mitigate the risks associated with these natural disasters and work towards a future where we can coexist with the awesome power of our planet’s volcanoes.
Volcanic Eruptions: Causing Widespread Destruction and Loss of Life?
Volcanic eruptions are nature’s wild card, capable of unleashing unimaginable devastation. They spew out sulfur dioxide, ash, and gases into our atmosphere, disrupting everything in their path.
Remember the catastrophic 1815 eruption of Mount Tambora? It wiped out entire villages, leaving a trail of destruction that sent the global climate into a tailspin. And who could forget Krakatoa’s thunderous eruption in 1883? It triggered monstrous tsunamis that ravaged coastlines, with the sound of the blast reverberating for thousands of miles around the globe.
More recently, in 1991, Mount Pinatubo let loose an eruption of unprecedented magnitude, unleashing an enormous cloud of sulfur dioxide into the atmosphere. Not only did it disrupt global weather patterns, but it also temporarily sent Earth into a cooling cycle.
These are just a few of the many volcanic eruptions that have left a scarring impact on our planet and its inhabitants. They’re harsh reminders of nature’s formidable power, showing us how crucial it is to be prepared and have early warning systems in place. By knowing what to do and where to go, we can minimize the devastating consequences of these natural disasters and save lives.
How have volcanic eruptions influenced the course of human history and shaped our understanding of the natural world?
Volcanoes, like fiery giants, have been leaving their mark on our planet and our lives for as long as we can remember. From the tragic destruction of Pompeii to the awe-inspiring landscapes they create, volcanic eruptions have played a pivotal role in shaping human history and deepening our understanding of the natural world.
Environmental Impacts:
When volcanoes erupt, they hurl a mix of ash, gases, and molten rock high into the sky. This can be a destructive force, leaving behind a trail of devastation. But these eruptions also have a creative side. They can give birth to new islands, enrich the soil with nutrients, and release minerals that breathe life into ecosystems.
Climate Change:
Volcanoes release gases like sulfur dioxide into the atmosphere. These gases can act like a sunshade, blocking sunlight and causing a cooling effect. They can also mess with precipitation patterns, making one place rainy while drying out another.
Impact on Human Civilizations:
Volcanic eruptions have shaped human history in ways both terrible and fascinating. Take Pompeii, for example. The eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD preserved this ancient Roman city in ash, giving us an incredible glimpse into their lives and culture. On the flip side, the Minoan civilization on the island of Santorini met its end when a volcanic explosion ravaged their world around 1600 BC.
Scientific Advancements:
Volcanoes have been like a textbook for scientists, teaching us about the Earth’s composition, geological processes, and the history of life. By studying volcanic activity, we’ve learned how to date geological events, uncover the secrets of the mantle, and gain insights into the formation of our planet.
Key Takeaways:
- Volcanic eruptions can be destructive, but they can also create new land and fertile soil.
- They influence the climate, potentially causing cooling or changes in precipitation patterns.
- Volcanoes have played a major role in shaping human history, both through destruction and preservation.
- Studying volcanic eruptions has helped us understand the Earth and its geological processes.
Remember, volcanic eruptions are a force of nature that we can’t control, but by understanding them, we can better prepare ourselves for their potential risks and marvel at the incredible power they possess.
FAQ
Q1: What was the deadliest volcanic eruption in history?
A1: The deadliest volcanic eruption in history was the eruption of Mount Tambora in Indonesia in 1815. The eruption killed an estimated 120,000 people.
Q2: What was the largest volcanic eruption in history?
A2: The largest volcanic eruption in history was the eruption of the Yellowstone supervolcano in the United States approximately 640,000 years ago. The eruption released an estimated 2,000 cubic kilometers of ash and pumice.
Q3: What are the most common types of volcanic eruptions?
A3: The most common types of volcanic eruptions are effusive eruptions and explosive eruptions. Effusive eruptions are characterized by the gentle outpouring of lava, while explosive eruptions are characterized by the violent ejection of ash, pumice, and gas.
Q4: What are the hazards associated with volcanic eruptions?
A4: The hazards associated with volcanic eruptions include ashfall, pyroclastic flows, lahars, and tsunamis. Ashfall can block out the sun and cause respiratory problems, pyroclastic flows are fast-moving clouds of hot gas and ash that can incinerate everything in their path, lahars are mudflows that can destroy buildings and infrastructure, and tsunamis are waves that can be generated by volcanic eruptions and can cause widespread damage.
Q5: How can we protect ourselves from volcanic eruptions?
A5: We can protect ourselves from volcanic eruptions by staying informed about volcanic activity in our area, evacuating if necessary, and taking steps to protect our homes and property from volcanic hazards.