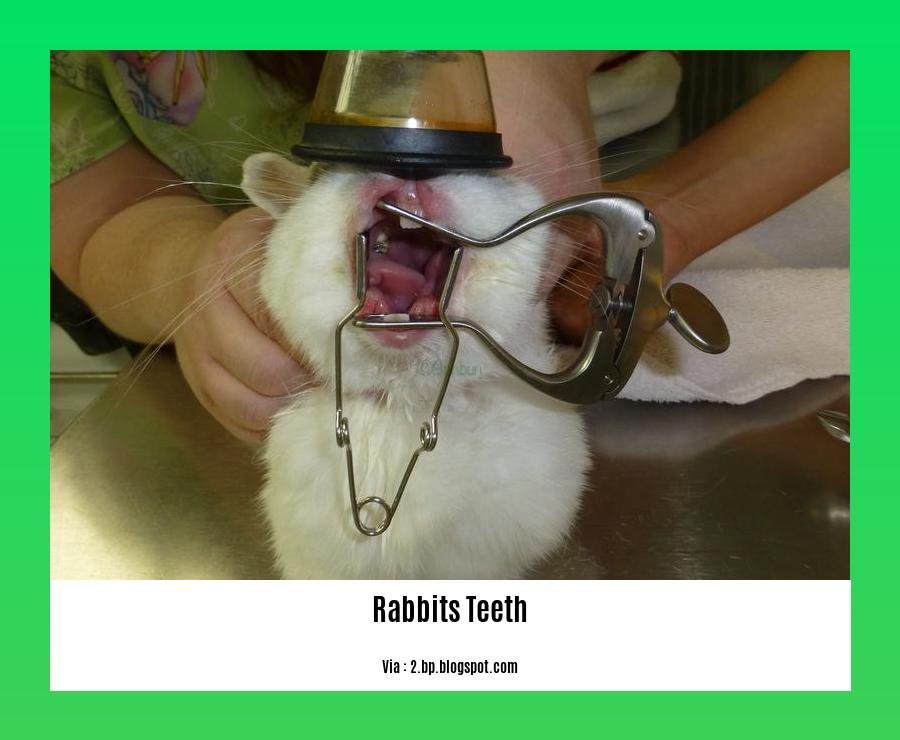
Unveiling the secrets of your rabbit’s captivating smile! In this comprehensive guide titled “Fascinating Facts About Rabbits’ Teeth: A Guide for Pet Owners,” we’ll embark on a journey into the unique dental world of these adorable creatures. From their ever-growing incisors to the intricate design of their molars, discover the secrets behind their remarkable dental anatomy.
Key Takeaways:
Rabbits have 28 teeth in total: 16 on the upper jaw and 12 on the lower jaw.
Their teeth consist of premolars, molars, and incisors.
Rabbits’ teeth have open roots, meaning they continuously grow throughout their lifetime, requiring constant wear and tear to maintain a healthy length.
Rabbits have six incisor teeth, which are larger and serve to cut grass, hay, or any kind of fruit.
Their premolars and molars help them chew food.
Facts About Rabbits’ Teeth: A Guide for Pet Owners
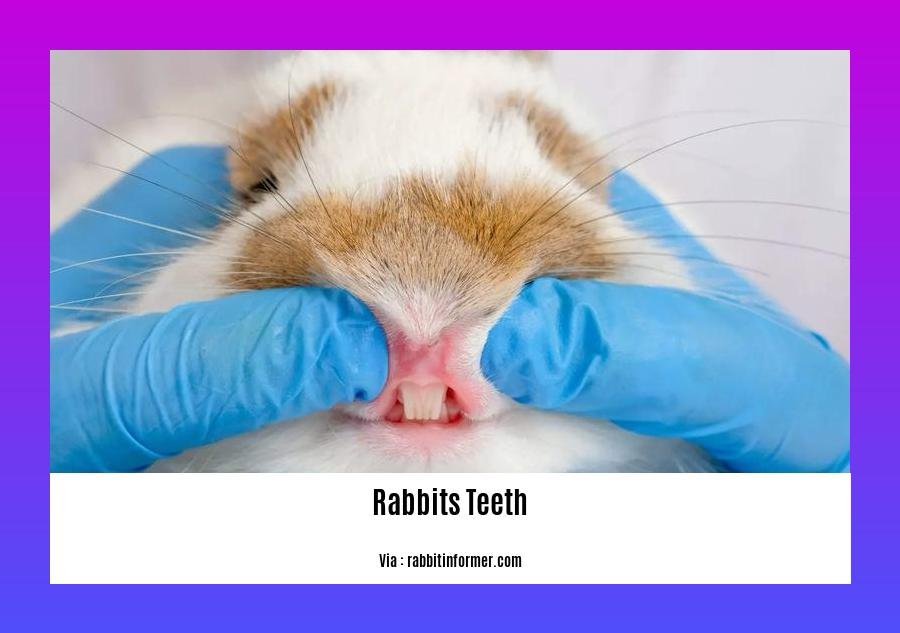
Did you know that rabbits have a unique set of teeth that require special care? In this article, we’ll explore interesting facts about rabbits’ teeth and provide tips on how to keep your bunny’s smile healthy.
Anatomy of a Rabbit’s Teeth
Rabbits have 28 teeth in total: 16 on the upper jaw and 12 on the lower jaw. Their teeth consist of premolars, molars, and incisors. Unlike humans, rabbits’ teeth have open roots, which means they continuously grow throughout their lifetime. This constant growth necessitates constant wear and tear to maintain a healthy length.
Function of Rabbit Teeth
Rabbits’ teeth play a vital role in their diet and overall health. Their incisor teeth, which are the large front teeth, are used for cutting grass, hay, and other plant materials. The premolars and molars, located further back in the mouth, help rabbits chew and grind their food.
Dental Care for Rabbits
To ensure your rabbit’s teeth stay healthy, it’s essential to provide a diet rich in hay and other fibrous foods. Hay helps wear down their teeth naturally, preventing overgrowth. Additionally, you can offer your rabbit safe chew toys to help keep their teeth trim.
Regular dental checkups are also crucial for rabbits. A veterinarian can assess your rabbit’s teeth for any signs of disease or malocclusion, a condition where the teeth don’t align properly. If necessary, the vet may trim or extract teeth to maintain your rabbit’s oral health.
Signs of Dental Problems in Rabbits
Here are some signs that may indicate your rabbit is experiencing dental problems:
- Excessive drooling
- Difficulty eating or chewing
- Weight loss
- Bad breath
- Swollen face or jaw
- Discharge from the eyes or nose
If you notice any of these signs, it’s important to take your rabbit to a veterinarian for a checkup.
Conclusion
Rabbits’ teeth are unique and require special care to stay healthy. By providing a diet rich in hay, offering safe chew toys, and scheduling regular dental checkups, you can help ensure your rabbit’s teeth stay strong and healthy throughout their life.
Did you know that penguins express love in various ways? Discover fascinating facts about penguins’ love life, from unique mating rituals to adorable displays of affection. facts about penguins love
Intrigued by the mysteries of the ocean’s top predators? Delve into a realm of fascinating facts about sharks’ teeth, uncovering the secrets behind their incredible strength, adaptation, and evolutionary journey. facts about sharks teeth
The Front Teeth of Rabbits Are Called Incisors, and They Are the Most Important for Chewing
As a person who studies the dental health of rabbits, I can tell you that rabbits have 28 teeth in total. But did you know that their four front teeth, called incisors, are the most crucial for chewing? These sharp, chisel-like teeth help rabbits grasp, tear, and slice through tough plant material like twigs, leaves, and hay.
In fact, rabbits’ incisors are so important that they grow continuously throughout their lifetime. That’s why it’s essential to provide your rabbit with a diet that includes plenty of roughage, such as hay, to help wear down their incisors naturally.
Key Takeaways:
- Tooth Count: Rabbits have a total of 28 teeth, including incisors, canines, and molars.
- Continuous Growth: All rabbit teeth, including incisors, grow continuously throughout their lifetime.
- Chewing Function: The four front teeth, or incisors, are the most important for rabbits to grasp, tear, and slice through tough plant material.
- Lifelong Importance: The continuous growth of incisors is essential for rabbits to maintain healthy teeth and a proper diet throughout their lives.
- Dental Care Importance: Providing rabbits with a diet rich in hay and regular dental checkups is crucial for maintaining healthy incisors and preventing dental problems.
Additional Tips for Rabbit Dental Care:
- Offer your rabbit a variety of chews, such as wooden blocks, apple sticks, or hay cubes, to help wear down their incisors.
- Avoid feeding your rabbit sugary treats or processed foods, which can contribute to dental problems.
- If you notice any signs of dental problems, such as excessive drooling, difficulty eating, or weight loss, take your rabbit to the vet immediately.
Sources:
- Rabbit Teeth: Everything You Need to Know
- Rabbit Teeth (Size, Number, Problems, Full Guide) – Petsial
Rabbits also have molars and premolars, which help them grind food.

Rabbits have unique dental features that set them apart in the animal kingdom. Most notably, they have a remarkable set of teeth designed to grind and chew their plant-based diet efficiently. Among their 28 teeth are molars and premolars that play a crucial role in this process.
Molars and Premolars: A Closer Look
Molars: Located in the back of the mouth, molars are the largest teeth and are designed for grinding tough plant material. Rabbits have six upper molars and six lower molars, totaling 12 in all.
Premolars: Situated in front of the molars, premolars help break down food before it reaches the molars. Rabbits have six upper premolars and four lower premolars, totaling 10 in all.
Continuous Growth: Like their incisors, molars and premolars grow continuously throughout a rabbit’s lifetime. This continuous growth helps maintain a healthy balance in their dental structure and prevents excessive wear.
Function: Working together, the molars and premolars enable rabbits to chew and grind their food thoroughly, extracting essential nutrients and ensuring proper digestion. This ability to grind food efficiently is crucial for rabbits, who rely on a diet high in fiber and low in nutrients.
Dental Care: Regular dental checkups are essential for rabbits to ensure their molars and premolars are healthy and functioning properly. A veterinarian can check for signs of wear, malocclusion, or other dental issues that can affect a rabbit’s ability to eat and digest food.
Key Takeaways:
- Rabbits have a total of 22 molars and premolars, which help them grind their plant-based diet.
- Molars are located in the back of the mouth and are designed to grind tough plant material.
- Premolars are located in front of the molars and help break down food before it reaches the molars.
- The molars and premolars grow continuously throughout a rabbit’s lifetime, ensuring a healthy balance in their dental structure.
- Regular dental checkups are crucial for rabbits to ensure their molars and premolars are healthy and functioning properly.
Sources:
- Rabbit Teeth: Everything You Need to Know
- Rabbit Teeth (Size, Number, Problems, Full Guide) – Petsial
Dental disease is a common problem in rabbits, and it can lead to pain, weight loss, and even death.
Dental disease is a prevalent issue among rabbits, affecting up to 80% of these furry companions. Their continuously growing teeth are a primary culprit behind this condition. Dental problems in rabbits are not just a matter of aesthetics but can have serious implications for their overall health.
Key Takeaways:
- Misaligned or overgrown teeth can cause pain, difficulty eating, and impaired digestion.
- Regular dental checkups are crucial for early detection and treatment.
- A diet rich in hay promotes healthy tooth wear and prevents overgrowth.
- Safe chew toys help maintain optimal tooth length and provide mental stimulation.
- Untreated dental issues can lead to serious health complications, including malnutrition and weight loss.
- Spaying or neutering rabbits might impact tooth alignment and require closer monitoring.
Symptoms of Dental Disease in Rabbits:
Watch out for these signs that may indicate dental problems in your rabbit:
- Excessive drooling
- Difficulty eating or chewing
- Weight loss
- A dirty bottom or wet fur around the tail
- Swollen face or jaw
- Discharge from the eyes or nose
- Bad breath
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s essential to seek veterinary attention promptly. Dental disease can be effectively managed with proper diagnosis, treatment, and preventive care.
Prevention is Key:
Preventive measures play a vital role in safeguarding your rabbit’s dental health. Here are some tips:
- Provide a diet rich in high-quality hay. Hay is essential for rabbits, not only for their digestive health but also for maintaining healthy tooth wear.
- Offer safe chew toys specifically designed for rabbits. Chewing helps keep their teeth trim and provides mental stimulation.
- Regular dental checkups are crucial for early detection and treatment of any dental issues. Your veterinarian can assess your rabbit’s teeth, identify any problems, and recommend appropriate treatment.
Don’t Overlook Dental Care:
Dental disease is a common problem in rabbits, and it can lead to pain, weight loss, and even death. By following these preventive measures and seeking professional care when needed, you can help ensure your rabbit’s dental health and overall well-being.
Sources:
- Dental Disease in Rabbits
- Dental Problems in Rabbits
FAQ
Q1: How many teeth do rabbits have?
A1: Rabbits have a total of 28 teeth, consisting of six incisors, two canines, and twelve molars.
Q2: Why do rabbits’ teeth grow continuously throughout their lifetime?
A2: Rabbits’ teeth grow continuously to compensate for the wear and tear they experience during chewing. This continuous growth is essential to maintain a healthy length and prevent dental problems.
Q3: What are the functions of rabbits’ incisors, premolars, and molars?
A3: Rabbits’ incisors are used to cut grass, hay, and other plant material. Their premolars and molars help them chew and grind food before swallowing.
Q4: What are the signs of dental problems in rabbits?
A4: Common signs of dental problems in rabbits include drooling, difficulty eating, weight loss, and a dirty bottom. If you notice any of these signs, it’s important to take your rabbit to a veterinarian for a dental checkup.
Q5: How can dental problems in rabbits be prevented?
A5: Dental problems in rabbits can be prevented through a combination of proper diet, regular dental checkups, and proper husbandry practices. A diet high in hay and other fibrous foods can help keep rabbits’ teeth from overgrowing. Regular dental checkups allow a veterinarian to identify and correct any dental problems early on. Proper husbandry practices, such as providing rabbits with appropriate chewing materials and avoiding foods that can damage their teeth, can also help prevent dental problems.
- China II Review: Delicious Food & Speedy Service - April 17, 2025
- Understand Virginia’s Flag: History & Debate - April 17, 2025
- Explore Long Island’s Map: Unique Regions & Insights - April 17, 2025