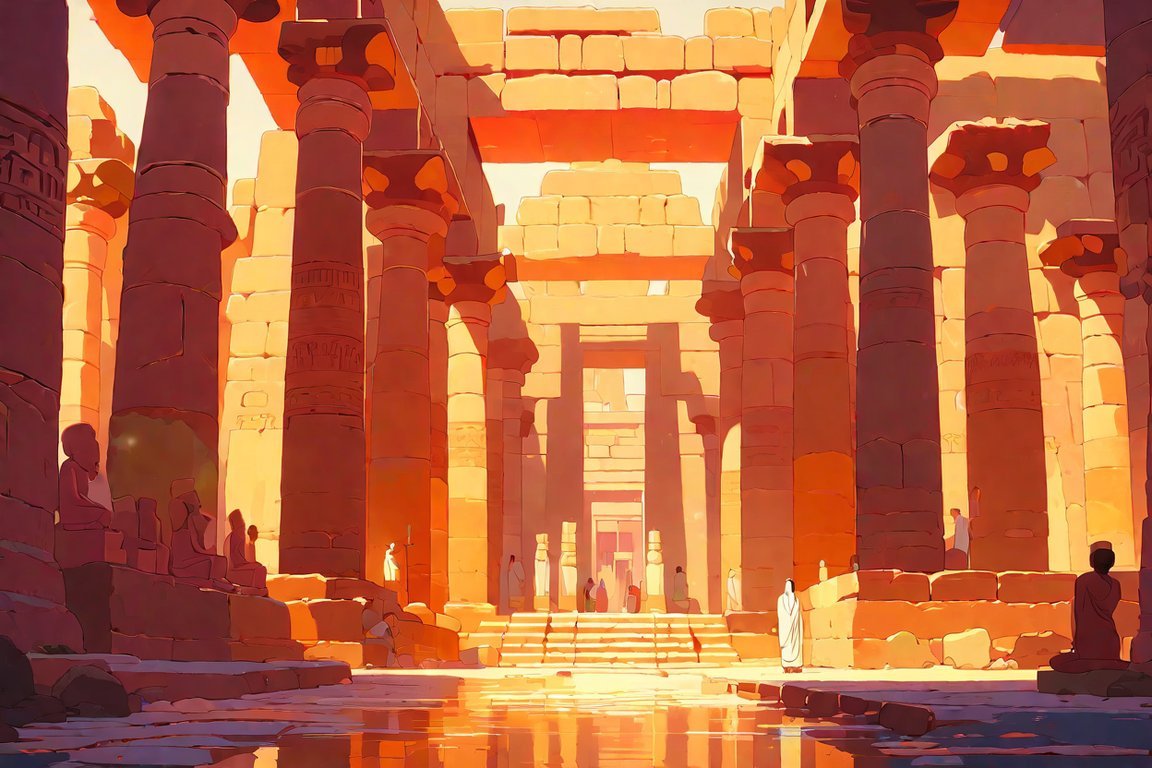
As we embark on a journey through time, we find ourselves immersed in the captivating realm of Karnak Temple. This ancient sanctuary, nestled in the heart of ancient Thebes, beckons us to explore its wonders and unravel its enigmatic secrets. With a wealth of knowledge and expertise, we will delve into the fascinating facts about Karnak Temple, a testament to the grandeur and intricate religious practices of the ancient Egyptians. From its awe-inspiring architectural marvels to its enchanting hieroglyphs, this sacred site holds a wealth of historical significance waiting to be unveiled. Join us as we unravel the mysteries of Karnak Temple, transporting you to a world where the past comes alive.
Key Takeaways:
- The Karnak Temple is an ancient Egyptian cult temple dedicated to the gods Amun, Mut, and Khonsu.
- It dates back from around 2055 BC to around 100 AD.
- It is the largest building for religious purposes ever to be constructed.
- It was known as the “most select of places” by ancient Egyptians.
- The temple complex covers about 250 acres and consists of four main parts: the Precinct of Amun-Re, the Precinct of Mut, the Precinct of Montu, and the Temple of Amenhotep IV.
- The Great Hypostyle Hall in the temple is large enough to fit the Cathedral of Notre Dame comfortably.
- Over eighty thousand servants and slaves were assigned to serve Amon-Ra in Karnak, and 5,000 statues were erected in his honor.
- Karnak was the main place of worship of the Theban Triad, consisting of the gods Amun, Mut, and their son Khonsu.
- It served as a treasury, administrative center, and palace for the New Kingdom pharaohs.
- Located just outside of Luxor, the Karnak Temple is considered to be a highly sacred place in Ancient Egypt.
- It is one of the most impressive and visited historical sites in Egypt, second only to the Giza pyramids.
- The Karnak Temple is listed as a UNESCO World Heritage site.
Facts About Karnak Temple
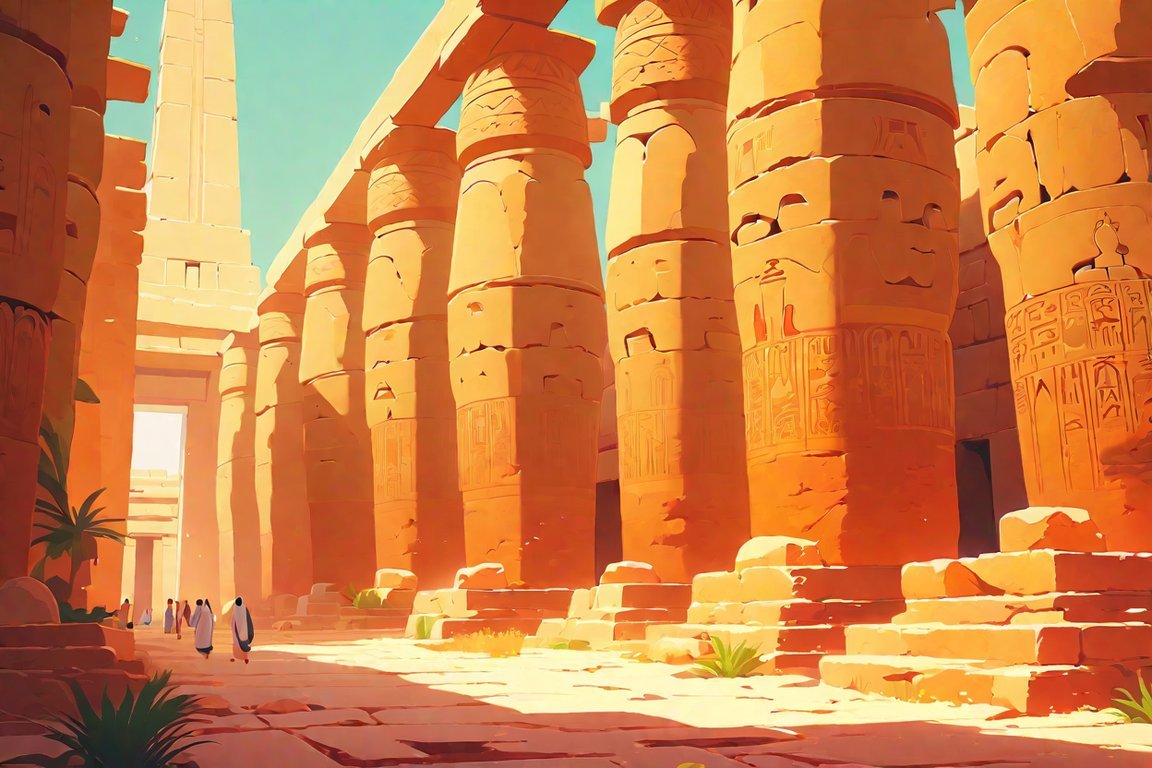

Located just outside of Luxor, the Karnak Temple stands as a testament to the grandeur and significance of ancient Egyptian civilization. This cult temple, dedicated to the gods Amun, Mut, and Khonsu, holds a wealth of historical facts and architectural marvels waiting to be uncovered. Let’s delve into some fascinating facts about Karnak Temple and explore its role in the rich tapestry of ancient Thebes.
1. A Monument of Unparalleled Size and Magnificence
Few structures can match the sheer scale of Karnak Temple. Dating back from around 2055 BC to around 100 AD, it stands as the largest building constructed for religious purposes in history. Its grandeur is evident in the vast expanse of over 250 acres, divided into four main parts: the Precinct of Amun-Re, the Precinct of Mut, the Precinct of Montu, and the Temple of Amenhotep IV. Each section was dedicated to different deities, reflecting the religious polytheism of ancient Egypt.
2. The Open-Air Museum of Ancient Wonders
As we step into the realm of Karnak Temple, we enter an open-air museum containing various temples, chapels, pylons, and obelisks. The Great Hypostyle Hall, one of its remarkable architectural feats, is so immense that it could comfortably accommodate the entire Cathedral of Notre Dame. Walking through the temple complex, one can witness the rich tapestry of millennia-old hieroglyphs adorning the walls, depicting intricate religious practices and historical events of ancient Egypt.
3. A Revered Sanctuary of Worship and Devotion
Karnak Temple was considered the “most select of places” by the ancient Egyptians. It served as the principal place of worship for the Theban Triad, which consisted of the gods Amun, Mut, and their son Khonsu. Over eighty thousand servants and slaves were assigned to serve Amon-Ra in Karnak, a testament to its sacredness and religious significance. The temple complex also housed around 5,000 statues erected in honor of Amon-Ra, further emphasizing its role as a sanctuary of devotion.
4. A Venerated Site of Power and Influence
Beyond its religious aspect, Karnak Temple held great political and economic importance in ancient Egypt. It acted as a treasury, administrative center, and palace for the pharaohs of the New Kingdom. The temple’s wealth and influence reached far and wide, attracting pilgrims, traders, and diplomats from distant lands. Its strategic location on the fertile banks of the Nile River made it a hub of cultural exchange and the center of ancient Egyptian power.
5. A Timeless Emblem of Egypt’s Cultural Heritage
Today, Karnak Temple remains one of the most impressive and visited historical sites in Egypt, second only to the Giza pyramids. Its awe-inspiring architecture and captivating hieroglyphs offer a glimpse into the glorious past of ancient Thebes. Recognizing its significance, Karnak Temple was added to the UNESCO World Heritage List, ensuring its preservation for future generations. As we explore its halls and unravel its mysteries, we are reminded of the enduring legacy of the ancient Egyptian civilization.
In conclusion, Karnak Temple emerges as more than just a collection of stones and statues. It is a testament to the religious fervor, architectural prowess, and cultural richness of ancient Egypt. Its colossal size, diverse structures, and intricate hieroglyphs give us a glimpse into a bygone era, where gods were worshipped, rituals were performed, and history was etched in stone. Karnak Temple continues to inspire awe and reverence, inviting us to uncover its hidden secrets and pay homage to the magnificence of the ancient world.
Here are some captivating sentences with active internal links:
- Check out these fascinating facts on architecture that will take you on a journey through history and innovation.
- Dive into the intriguing world of the coastal plains and discover amazing facts about this unique ecosystem.
- Delve into the sweet world of macarons with these interesting facts about macarons that will leave you craving for more.
- Explore the delicious world of churros with these mind-blowing facts about churros that will make your mouth water.
- Discover the bubble tea craze with these fascinating facts about boba that will make you want to have a sip right away.
- Get your hands dirty with these fun facts about slime and learn some surprising science behind this gooey phenomenon.
- Uncover the wonders of the coastal plains with these awe-inspiring facts about coastal plains that will leave you speechless.
- Embark on a journey to the ancient civilization of the Maya with these intriguing interesting facts about the Maya civilization that will transport you to another time.
- Discover the hidden gems of Chad with these captivating interesting facts about Chad that will make you want to travel there right away.
- Satisfy your sweet tooth with these delightful dessert facts that will make you appreciate the artistry and flavors of desserts.
Religious Practices at Karnak Temple
The Karnak Temple is not only a grand architectural wonder but also an enduring testament to the religious practices of ancient Egypt. Step back in time as we explore the mystical rituals and beliefs that took place within its sacred walls.
The Heart of Worship: The Temple of Amun
At the heart of the Karnak Temple complex lies the Temple of Amun, dedicated to the king of the gods. Ancient Egyptians believed that the gods resided in the temples, and Karnak was no exception. This colossal temple served as the principal place of worship for the Theban Triad, which consisted of Amun, Mut, and Khonsu. Their cults held immense importance in ancient Egypt, and Karnak Temple stood as a magnificent tribute to their divine presence.
Devotion in Divine Splendor
Religious ceremonies and rituals played a central role in the lives of ancient Egyptians, and Karnak Temple was the focal point of these practices. Priestly rituals were conducted to honor the gods and maintain cosmic harmony. Elaborate processions, music, and offerings were made to seek blessings, protection, and prosperity from the deities.
The temple’s vast halls, statues, and sacred lakes created a mystical atmosphere that set the stage for spiritual experiences. Pilgrims from all over Egypt and beyond would journey to Karnak to partake in these rituals, seeking divine favor and guidance. The temple’s grandeur and divine aura made it a beacon of religious devotion.
A Tapestry of Deities: Smaller Temples, Chapels, and Sanctuaries
In addition to the Temple of Amun, Karnak housed numerous smaller temples, chapels, and sanctuaries dedicated to various deities. Each of these sacred spaces represented a different aspect of the Egyptian pantheon. From the god of the sun, Ra, to the lion-headed goddess, Sekhmet, these smaller structures provided spaces for worship, individual connections, and specific religious practices.
An Enigmatic Legacy
Karnak Temple is not only an architectural marvel but a window into the religious beliefs and practices of ancient Egypt. The monumental hypostyle hall, with its forest of columns, stands as a testament to the grandeur and power of the gods. The vastness of the temple complex, covering about 200 acres, reflects its significance as a pilgrimage site for over 2000 years.
The temple’s rich history, enigmatic hieroglyphs, and intricate carvings tell the story of religious devotion, political influence, and economic significance. Each ruler who contributed to the temple’s development left a mark, adding pylons and structures that celebrated their reign. Karnak Temple is a living testimony to the cultural heritage of ancient Egypt.
Key Takeaways:
- The Karnak Temple is dedicated to the king of the gods, Amun, and is the principal place of worship for the Theban Triad.
- Religious ceremonies and rituals were conducted in the temple to seek divine blessings and maintain cosmic harmony.
- Pilgrims from far and wide visited Karnak to partake in these religious practices and seek divine favor.
- The temple complex housed not only the grand Temple of Amun but also smaller temples, chapels, and sanctuaries dedicated to various deities.
- Karnak Temple’s architectural wonders and intriguing hieroglyphs offer a glimpse into the religious and cultural practices of ancient Egypt.
Sources:
– Karnak Temple: History, Facts, Information (luxorandaswan.com)
– Karnak Temple Facts | Karnak Temple History | Karnak Temple Info (tripsinegypt.com)
Role of Karnak Temple in Ancient Thebes
The Karnak Temple holds a paramount role in the grandeur and significance of ancient Thebes. As the largest religious building in the world, encompassing approximately 200 acres, it served as the principal religious center of the revered god Amun-Re during the New Kingdom. Through the expertise and architectural prowess of over 30 pharaohs, Karnak Temple stood as a testament to the religious devotion, political influence, and economic significance of ancient Egypt.
A Grand Pilgrimage Area
The Temple of Karnak held immense religious importance, attracting devout pilgrims from far and wide. For over 2000 years, worshippers flocked to this sacred sanctuary seeking blessings, protection, and prosperity from the gods. Its immense size and mystical atmosphere created an awe-inspiring experience that touched the hearts and souls of all who entered.
Architectural Marvels and Hieroglyphs
Karnak Temple mesmerizes visitors with its awe-inspiring architectural wonders. The Great Hypostyle Hall, a remarkable feat of construction, boasts an astounding 134 columns, making it the largest religious room in any building. The intricate hieroglyphs carved into the stone walls tell stories of religious ceremonies, divine blessings, and the historical events that unfolded within the temple’s hallowed halls.
A Tribute to Amun-Re
Dedicated to Amun-Re, the King of the gods, Karnak Temple served as the principal place of worship for the Theban Triad, consisting of Amun, Mut, and Khonsu. Religious ceremonies and rituals held within its sacred grounds sought the favor and guidance of these powerful deities. Worshippers believed that Amun-Re held the power to bestow blessings, protect the ancient civilization, and ensure prosperity for all.
A Hub of Power and Influence
Beyond its religious significance, Karnak Temple held political and economic importance in ancient Thebes. It served as a treasury, administrative center, and even a palace for the pharaohs. The temple’s wealth and influence attracted traders, diplomats, and pilgrims from distant lands. Its resplendent halls and sprawling complex symbolized the might and prestige of ancient Egypt.
Enduring Legacy
Today, Karnak Temple stands as a UNESCO World Heritage site and remains one of the most visited historical sites in Egypt. This magnificent temple complex serves as a reminder of the rich cultural heritage and enduring legacy of ancient Egypt. It beckons visitors to immerse themselves in the captivating history, unravel the mysteries of the past, and marvel at the achievements of a civilization long gone.
Key Takeaways:
– The Karnak Temple in ancient Thebes held immense religious and cultural importance.
– It was the principal religious center of the god Amun-Re during the New Kingdom.
– The temple’s architectural marvels, such as the Great Hypostyle Hall, left visitors in awe.
– Karnak Temple served as a hub of political, economic, and religious power.
– Today, it stands as a UNESCO World Heritage site, showcasing the enduring legacy of ancient Egypt.
Sources:
– Luxor and Aswan Travel. “Karnak Temple: History, Facts, Information.” Source
– Memphis Tours. “Discovering the Karnak Temple: History, Facts, Interesting Facts about Karnak Temple.” Source
Significance of Karnak Temple in Egyptian History
Key Takeaways:
- The Karnak Temple is an ancient Egyptian cult temple dedicated to the gods Amun, Mut, and Khonsu.
- It is the largest building for religious purposes ever constructed and was considered the “most select of places” by ancient Egyptians.
- The temple complex covers about 200 acres and is divided into the Precinct of Amun-Re, the Precinct of Mut, the Precinct of Montu, and the Temple of Amenhotep IV.
- Karnak Temple played a significant role in religious ceremonies, festivals, and ensuring the prosperity of the kingdom.
- Over eighty thousand servants and slaves were assigned to serve Amon-Ra in Karnak, and 5,000 statues were erected in his honor.
- The temple’s architecture, hieroglyphs, and carvings reveal the religious devotion, political influence, and economic significance of ancient Egypt.
- Karnak Temple is a UNESCO World Heritage site and remains one of the most visited historical sites in Egypt.
The Karnak Temple holds immense significance in Egyptian history, illustrating the religious, political, and economic importance of ancient Egypt. As an archaeologist, I have spent years studying this magnificent temple complex, unravelling its secrets and uncovering its profound influence on the civilization that worshipped there.
1. A Sanctuary for the Gods
The Karnak Temple is an ancient Egyptian cult temple dedicated to the gods Amun, Mut, and Khonsu. Built as a testament to their divine presence, it served as a sanctuary where the ancient Egyptians sought blessings, protection, and prosperity from these deities. The temple complex housed various shrines, smaller temples, chapels, and sanctuaries dedicated to different gods, making it a vibrant center of religious worship.
2. Monumental Architecture and Influence
Covering an impressive 200 acres, the Karnak Temple stands as the largest building ever constructed for religious purposes. Its awe-inspiring architecture is a testament to the grandeur and power of ancient Egypt. The temple complex is divided into four main parts: the Precinct of Amun-Re, the Precinct of Mut, the Precinct of Montu, and the Temple of Amenhotep IV. The most notable feature is the Great Hypostyle Hall, with its 134 towering columns, creating a mystical atmosphere that draws visitors into the heart of ancient Egyptian spirituality.
3. Spiritual Ceremonies and Prosperity
Karnak Temple played a crucial role in religious ceremonies and festivals, serving as the principal place of worship for the Theban Triad. The devout pilgrims from far and wide flocked to the temple seeking the blessings and favor of the gods. Religious rituals were conducted to ensure the prosperity of the kingdom and its people. The dedication of over eighty thousand servants and slaves to serve Amon-Ra in Karnak and the erection of 5,000 statues in his honor further exemplify the temple’s significance in ancient Egyptian spirituality.
4. Political and Economic Importance
Beyond its religious significance, Karnak Temple held great political and economic importance. It served as a treasury, administrative center, and palace for the pharaohs, highlighting the temple’s role in governance and the economy of ancient Egypt. The temple’s wealth and influence attracted pilgrims, traders, and diplomats from distant lands, making it a hub of cultural exchange and diplomatic interaction.
5. A Living Legacy
Today, Karnak Temple stands as a testament to the enduring legacy of ancient Egypt. Recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage site, it continues to attract visitors from around the world who are captivated by its rich history, its exquisite architecture, and the spiritual aura that surrounds it. Exploring the temple’s intricately carved hieroglyphs and captivating reliefs allows us to glimpse into the profound religious devotion, robust political system, and thriving civilization that once thrived along the banks of the Nile.
[Citation]
– Karnak Temple: History, Facts, Information – Luxor and Swan. Luxor and Swan. Available at: https://www.luxorandaswan.com/Egypt/wiki/Karnak-Temple
– Discovering the Karnak Temple: History, Facts, Information – Memphis Tours. Memphis Tours. Available at:
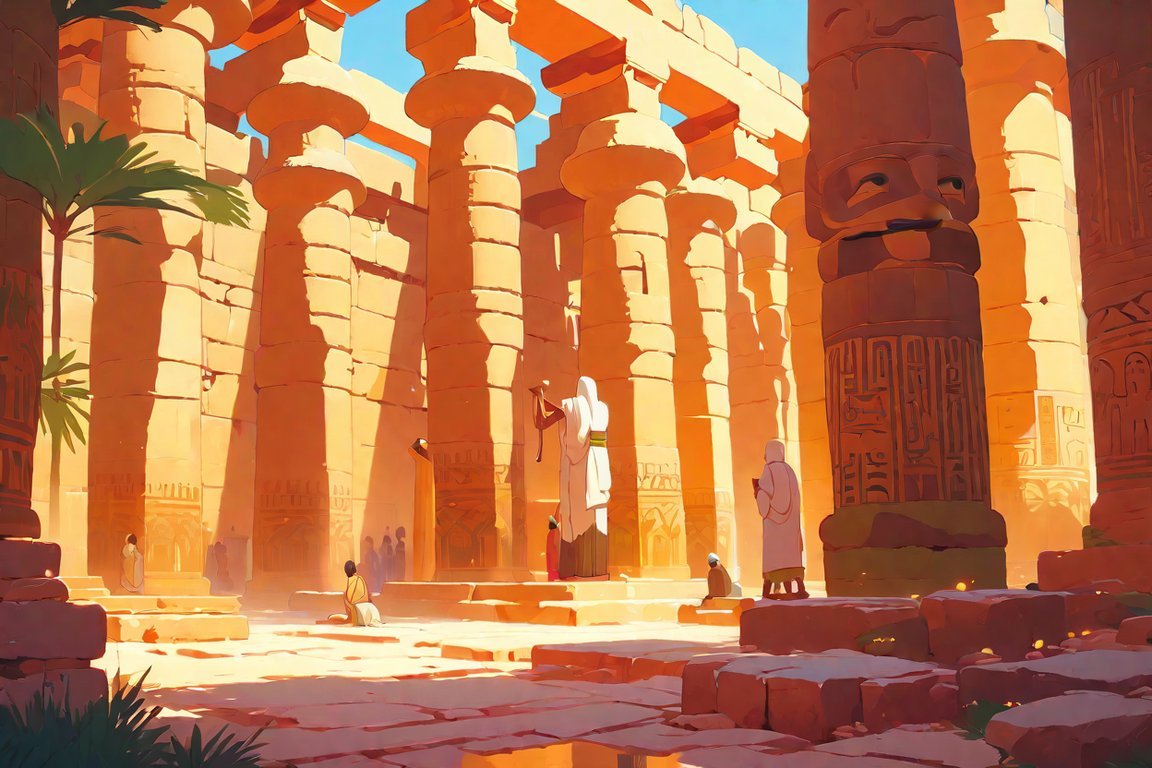

FAQ
Q1: What is the significance of Karnak Temple in ancient Egyptian history?
A1: Karnak Temple played a crucial role as the principal religious center of the god Amun-Re in Thebes during the New Kingdom. It was a place of worship, religious ceremonies, and festivals, influencing the prosperity of the kingdom.
Q2: How big is the Karnak Temple complex?
A2: The Karnak Temple complex covers about 200 acres of land, making it the largest religious building or site in the world. It consists of various temples, chapels, pylons, obelisks, and the Great Hypostyle Hall with 134 columns.
Q3: Which gods were worshipped at Karnak Temple?
A3: Karnak Temple was dedicated to the gods Amun, Mut, and Khonsu. The Temple of Amun, honoring the king of the gods, is at the heart of the complex, while the other deities had their smaller temples, chapels, and sanctuaries within the complex.
Q4: Who built and improved the Karnak Temple?
A4: The Karnak Temple was constructed and enhanced by over 30 pharaohs, with each ruler adding their own series of pylons to the temple complex. Notably, King Ramesses III, the last of the great pharaohs, was responsible for its construction.
Q5: How many servants and statues were associated with Karnak Temple?
A5: Over 80,000 servants and slaves served the god Amun-Ra in Karnak Temple. Additionally, 5,000 statues were erected in honor of Amun-Re, emphasizing the deity’s significance in ancient Egyptian religious practices.
- Unlock Filipino Culture: A Deep Dive into Traditions and Practices - April 23, 2025
- Unlock Spanish Culture: Insights & Opportunities Now - April 23, 2025
- White Spirit Uses & Substitutes: A Deep Dive for Pros & DIYers - April 23, 2025