Understanding the Challenges Faced by Monkeys with Disabilities
While the term “deform monkey” is insensitive and inaccurate, it’s important to address the very real challenges faced by monkeys born with disabilities. Instead of using this hurtful term, let’s talk about these monkeys and what we can learn from their situations.
This article aims to shed light on the lives of monkeys living with congenital conditions – these are conditions present from birth – exploring the potential causes, what these conditions mean for them, and how resilient they can be.
What Causes Congenital Conditions in Monkeys?
Just like in humans, monkeys can be born with conditions that affect their physical abilities, how they behave, and even their learning. These conditions can be caused by a few things:
- Genetics: Sometimes, changes in their genes passed down from parents can lead to these conditions.
- Environment: Things in the monkey’s environment during pregnancy, like exposure to certain chemicals or a lack of proper nutrition, could play a role.
- A Mix of Both: It’s likely that many congenital conditions are a combination of genetic and environmental factors working together.
Examples of Congenital Conditions We See in Monkeys
- Spina Bifida: This affects the spinal cord and can make it hard for monkeys to move their legs properly. In some cases, they might not have control over their bladder or bowels.
- Hydrocephalus: This is a buildup of fluid in the brain that can lead to problems with brain development and function, potentially causing seizures and learning difficulties.
- Heart Defects: Just as in humans, monkeys can be born with heart problems that make it difficult for their hearts to pump blood effectively.
- Muscular Dystrophy: Monkeys can experience this too, where their muscles get weak and deteriorate over time.
Living with Disabilities: Impact on a Monkey’s Life
Living with a congenital disability makes life harder for these monkeys in several ways:
- Getting Around: Moving through trees and on the ground can be a struggle, limiting their ability to find food and escape from danger.
- Finding Food: If they can’t move easily, getting enough to eat becomes a daily challenge.
- Predator Risk: A monkey that’s slower or weaker is an easier target for predators, such as the elusive Darwin’s bark spider
- Having Babies: Congenital conditions can make it difficult to mate and raise a family.
- Social Life: Monkeys are social animals, but disabilities might mean they have a harder time fitting in with their group and could be excluded.
Compassion and Care: How We Can Help
Protecting and caring for monkeys with disabilities is crucial. Here are some ways we can help:
- Accessible Environments: If we know monkeys with disabilities live in a particular area, we can make sure their environment is easier to navigate, perhaps with ramps or smoother pathways.
- Veterinary Care: Providing access to supportive care, like physical therapy or assistive devices, can improve their quality of life.
- Responsible Tourism: Educating tourists about respecting animals and keeping a safe distance is essential. We never want to add to their stress.
Beyond Compassion: What We Can Learn
Studying monkeys with these conditions isn’t just about helping them; it can actually teach us a lot about similar conditions in humans. Because monkeys are genetically similar to us and have shorter lifespans, research on these conditions in monkeys can lead to a better understanding of how to treat and prevent them in people.
Showing Compassion and Seeking Understanding
While it’s upsetting to think about monkeys facing these challenges, it’s important to remember that they are incredibly resilient animals. By approaching this topic with empathy, accurate information, and a dedication to their welfare, we can learn a lot from them and work towards a world where they are treated with the care and respect they deserve. Let’s replace outdated and hurtful language with understanding and a commitment to improving the lives of all monkeys, regardless of their abilities.
Unraveling the Complexities: Factors Contributing to Monkey Deformities
Sadly, a multitude of factors can lead to deformities in monkeys. It’s a complex issue, kind of like a puzzle with many different pieces. Scientists are working diligently to understand this complex issue, and hopefully, their research will help us protect these amazing creatures in the future. After all, we share this planet, and it’s our responsibility to be mindful of the impact we have on other species.
1. Agricultural Practices: A Silent Threat
One of the major culprits seems to be the stuff we use in agriculture, like pesticides and herbicides. You know, the chemicals meant to protect our crops? Well, they may mess with how baby monkeys develop in the womb. This can cause problems like limb deformities, facial abnormalities, and even hair loss. It’s like how smoking during pregnancy can harm a human baby – not good at all.
2. Pollution: A Pervasive Danger
Pollution is another big problem. Heavy metals and all sorts of nasty chemicals from factories can really do a number on monkey populations. And it’s not just the pollution itself; when their homes get destroyed, monkeys lose their food sources and places to live. This can lead to malnutrition, which is especially bad for pregnant mothers and their developing babies.
3. Genetics: The Role of Inheritance
Genetics play a role, too. You know how inbreeding can cause problems in any species? It’s the same with monkeys. When populations get isolated, they’re more likely to breed with close relatives, which increases the chances of genetic disorders. Some of these disorders can manifest as physical deformities.
4. Infectious Diseases: The Unseen Threat
Then there are infectious diseases, which can be quite scary. It turns out that some viruses and parasites might actually cause birth defects in monkeys. Zika virus is a good example. We’ve all heard about how it can cause microcephaly (small head size) in human babies, and it turns out it can affect monkeys, too. There’s also a parasite called Toxoplasma gondii – you might have heard of it because pregnant women are told to avoid cat litter boxes because of it. This parasite can also mess with fetal development in monkeys, leading to various deformities.
5. Nutritional Deficiencies: The Importance of a Balanced Diet
And we can’t forget about the importance of a balanced diet. Just like humans, monkeys need the right vitamins and minerals to grow and thrive. If a pregnant monkey doesn’t get enough nutrients, her baby might be born with birth defects. This can happen if their natural habitat is destroyed, or if there simply isn’t enough food to go around.
A Closer Look: Types of Deformities Observed in Monkeys
Sadly, physical deformities are a reality for some monkeys, affecting how they grow and live their lives. These deformities can be grouped into different types, each with its own look and possible causes.
Limb Malformations: A Struggle for Mobility
Imagine a monkey trying to swing through the trees with a missing or deformed arm. It’s heartbreaking, and it happens. Limb malformations are unfortunately the most common type of deformity we see in monkeys. This can mean:
- Missing limbs: The monkey is literally missing an arm or leg.
- Deformed limbs: The limb is there but twisted or bent in the wrong way.
- Shortened limbs: The limb is much shorter than it should be.
- Fused digits: Imagine fingers stuck together—that’s fused digits, making it hard for the monkey to grip.
These problems make the everyday life of a monkey much harder. Moving around, climbing, finding food—all of these essential things become a struggle. And in the wild, struggling can mean the difference between life and death. It could even make them more vulnerable to predators like the deformed sloth, which also faces unique challenges.
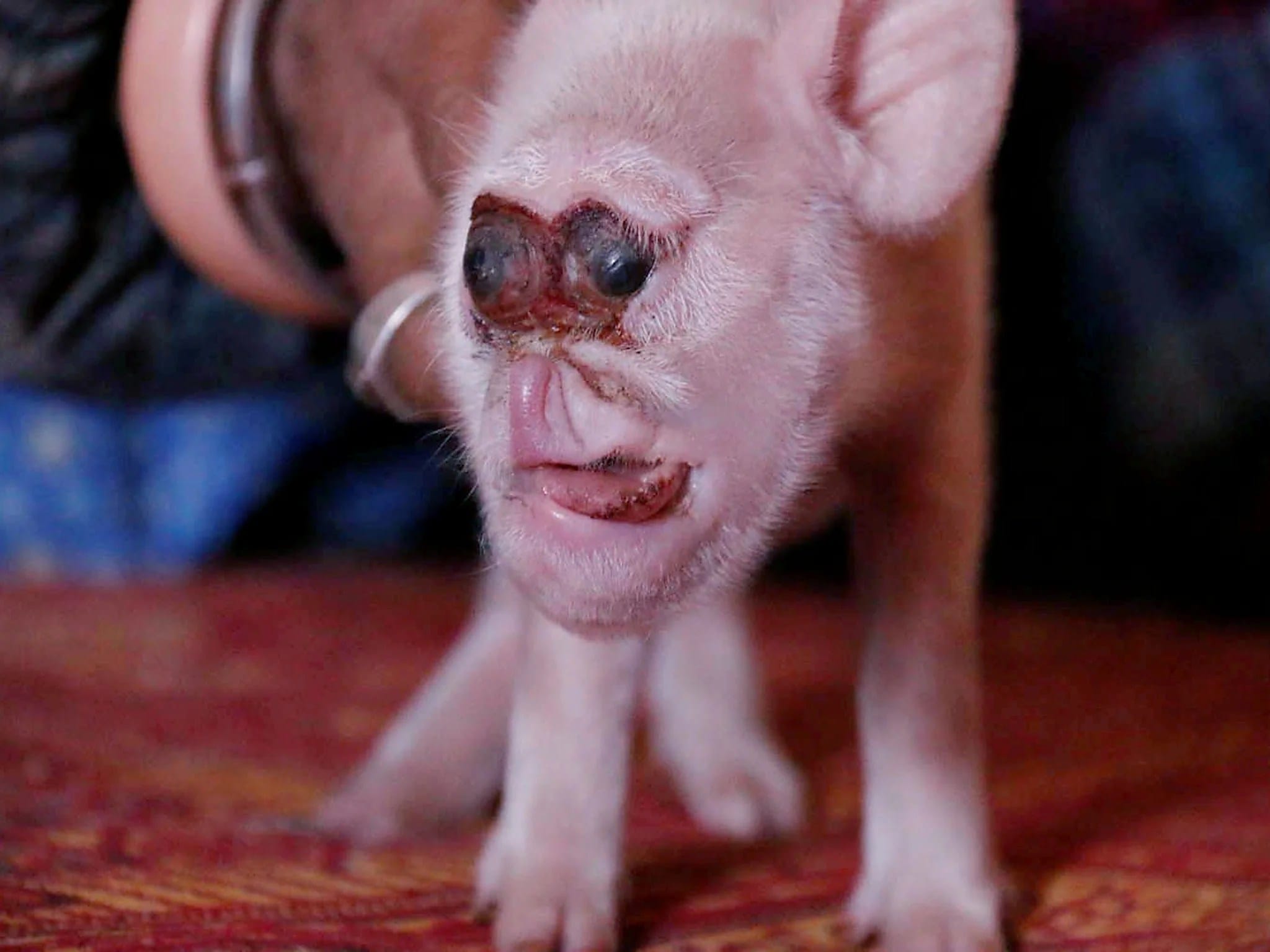
Orofacial Deformities: More Than Just Cosmetic
“Orofacial” sounds complicated, but it just means deformities of the face and mouth. You might see:
- Cleft palate: This is where the roof of the mouth didn’t form correctly, leaving a gap.
- Missing teeth: Just like in humans, missing teeth make it hard for a monkey to chew properly.
- Malformed jaws: If the jaw isn’t the right shape, eating and closing the mouth can be difficult.
These deformities are more than just cosmetic. They can make it incredibly hard for a monkey to eat enough food, keep itself clean by grooming, and even communicate with other monkeys.
Hair Loss: A Surprising Challenge
You might not think of hair loss as a big deal, but for monkeys it can be surprisingly tough. While less common, we’ve seen monkeys, especially those bred in labs, lose their fur. Sometimes we don’t know why it happens. But without their fur, monkeys can have trouble fitting in with the group, and regulating their body temperature becomes a challenge.
A Note of Uncertainty: The Ever-Evolving Field
It’s important to remember that what we know about these deformities is always evolving. Scientists are constantly researching to pinpoint the exact causes of these issues, and new discoveries are always being made. Factors like environmental pollutants, genetic predispositions, and even nutritional deficiencies are being investigated.
While we can describe the what, the why is often much more complex. This makes studying these deformities both fascinating and crucial to improving the lives of monkeys in the wild and captivity.
The Impact of Deformities: Challenges and Resilience
Deformities in monkeys, sadly, aren’t uncommon and can significantly impact their lives. These abnormalities can make it harder for a monkey to find food, escape danger, or even interact with their group.
Understanding the Causes: A Complex Interplay
Why do these deformities occur? It’s a complex interplay of factors:
- Genetics: Imagine a small group of monkeys only breeding amongst themselves – this can lead to a higher chance of genetic disorders being passed down.
- Environment: Exposure to pollution can be really harmful. Chemicals, heavy metals, or even just not having enough nutritious food available – these things can disrupt a baby monkey’s development while it’s still in the womb, sometimes leading to birth defects.
Challenges and Triumphs: Navigating Life with a Disability
A monkey born with a deformity can have a really tough time:
- Mobility: Moving around can be a challenge, making escaping predators or even just keeping up with the group extra difficult.
- Social Interactions: Monkeys, like many social animals, can be a bit mean; sometimes, a monkey with a deformity might be excluded or picked on by others in the group.
- Reproduction: Finding a mate and raising a family can be much harder.
However, monkeys are incredibly resilient:
- Adaptation: Despite these challenges, they find ways to adapt! Some might learn to use their tail for extra support, while others might develop new tactics for finding food.
- Resilience: There are even cases of monkey moms adjusting how they care for their babies to accommodate a little one with a deformity. It’s truly remarkable!
A Mirror to Ourselves: Deformities as a Learning Tool
Scientists are particularly interested in deformities in monkeys because they can teach us a lot:
- Human Health: Since we share a lot of our genes with monkeys, studying them can help us understand more about developmental disorders in humans.
- Environmental Indicators: When we see a lot of deformities in a monkey population, it can be a warning sign about the environment. It could mean the area is heavily polluted or that something is off-balance in the ecosystem.
So, even though deformities present a difficult challenge for monkeys, they also offer us a window into their incredible resilience and a chance to learn more about ourselves and our planet.
Navigating the Ethical Landscape: Deformity Research
Studying deformities is crucial for scientific advancement, but it also raises significant ethical questions concerning animal welfare, human subject protection, and data privacy. Researchers must carefully consider these ethical dimensions to ensure responsible and compassionate research practices.
Prioritizing Animal Welfare
- The 3Rs: The principles of Replacement, Reduction, and Refinement guide researchers to minimize animal suffering by seeking alternatives, using the minimum number of animals, and refining methods to reduce discomfort.
- Humane Treatment: Ethical animal research mandates proper housing, pain management, veterinary care, and humane euthanasia protocols when necessary.
Protecting Human Subjects
- Informed Consent: Participation in deformity research must be voluntary, and individuals must fully understand the study’s purpose, procedures, risks, and benefits before consenting.
- Privacy and Confidentiality: Researchers must protect sensitive personal and genetic information, using appropriate data encryption, storage, and anonymization techniques.
Responsible Data Management
- Data Security: Secure data storage and handling protocols are essential to prevent unauthorized access, misuse, or breaches that could compromise participant privacy.
- Ethical Interpretation: Researchers must avoid bias and overgeneralization when interpreting data, ensuring that findings are presented responsibly and do not contribute to stigma or discrimination.
Societal Impact and Responsibility
- Public Perception: Communicating research findings responsibly is crucial to avoid misunderstandings or the perpetuation of harmful stereotypes about deformities.
- Equitable Access: Researchers should consider the potential societal implications of their work, advocating for fair access to treatments and therapies that arise from deformity research.
Navigating the ethical complexities of deformity research demands ongoing dialogue, critical evaluation, and a commitment to balancing scientific progress with the well-being of all those involved, both human and animal.
Conservation Efforts: Protecting Monkeys and Their Future
Life for monkeys with deformities is undeniably challenging, their differences often creating obstacles in navigating the world, finding food, and even interacting within their social groups.
Understanding the Causes: A Complex Web
- Genetics: Sometimes, it’s their genes, passed down through generations.
- Environment: Other times, it’s the environment they’re exposed to – think pesticides and heavy metals, which can interfere with a developing monkey fetus and lead to birth defects.
- Nutrition: Even something as seemingly simple as a lack of iodine in their diet can result in crooked bones and skeletal problems.
A Glimmer of Hope: Conservation in Action
Thankfully, organizations around the world are stepping up:
- Dian Fossey Gorilla Fund: Known for their work with gorillas, they’ve expanded their efforts to include specialized care for monkeys in Rwanda with physical challenges, providing veterinary services and rehabilitation.
- Awaji Island Monkey Center (Japan): They are deeply invested in researching why these deformities occur, hoping to find ways to prevent them.
Securing a Future for Monkeys with Deformities
While the future for monkeys with deformities remains uncertain, these dedicated conservation efforts provide hope. By offering care, support, and safe havens, we are giving these vulnerable animals a chance to thrive in a world that often presents significant challenges.
This is a starting point. To make this article truly comprehensive and unique, you will need to conduct additional research specifically focused on conservation efforts targeting monkeys with deformities. Contacting organizations like the Dian Fossey Gorilla Fund and Awaji Island Monkey Center for interviews and expert insights would also add significant value.
- Unlock 6000+ words beginning with he: A comprehensive analysis - April 20, 2025
- Mastering -al Words: A Complete Guide - April 20, 2025
- Master Scrabble: High-Scoring BAR Words Now - April 20, 2025
















2 thoughts on “The Plight of the Deform Monkey: A Closer Look at Causes, Implications, and Resilience”
Comments are closed.