Get ready to explore the fascinating landscape within your mouth! It’s a world of its own, complete with mountains, valleys, and even a river. Join us as we uncover the wonders of mouth geography, from the structures that help you eat and speak to the intricate ecosystems they support.
Defining Mouth Geography
Mouth geography is the study of the structures in your mouth and how they work together. Just like a bustling city, your mouth has distinct “neighborhoods” that contribute to its overall health and function. Let’s take a tour:
The Tongue: A Jack of All Trades
The tongue, a muscular multitasker, plays a vital role in tasting, speaking, and swallowing. Covered in tiny bumps called papillae, the tongue houses your taste buds. Interestingly, different areas of the tongue are more sensitive to specific tastes. The back is for bitter flavors, the sides for sour and salty, and the tip for sweet and savory.
The Palate: Your Mouth’s Ceiling
The palate forms the roof of your mouth and comes in two parts: the hard palate in the front and the soft palate in the back. The hard palate, a bony structure, provides support for the teeth and shapes the mouth. The soft palate, with its dangling uvula, helps with swallowing and speech.
The Teeth: More Than Just a Pretty Smile
Your teeth, lined up along your jaw, are essential for chewing and play a crucial role in digestion. Each type of tooth has a specific function:
- Incisors: These sharp, front teeth cut food into bite-sized pieces.
- Canines: The pointy teeth next to your incisors tear into tougher foods.
- Molars: Located in the back, molars crush and grind food into a paste.
Why Should We Care About Mouth Geography?
Understanding your mouth’s geography is key to maintaining good oral health. The mouth is home to a diverse community of microbes known as the microbiome. When in balance, this ecosystem contributes to overall well-being. However, imbalances can lead to issues like:
- Cavities
- Gum disease
- Other health problems
By knowing the different parts of your mouth, you can clean them more effectively, making brushing and flossing more targeted. Regular dental visits become like check-ups with an explorer, ensuring your mouth’s landscape stays healthy.
Keep Exploring!
The field of mouth geography is constantly evolving as scientists uncover new links between oral health and overall health. Keep exploring, stay curious, and prioritize your oral health!
What is the definition of mouth in geography?
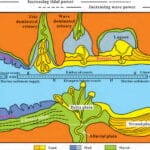
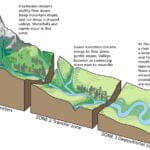
In geography, the “mouth” doesn’t refer to the one on your face. Instead, it describes the point where a river flows into a larger body of water like a lake, sea, or ocean. It’s a dynamic area where freshwater and saltwater mix, creating a unique habitat.
River mouths are more than just endpoints; they are:
- Transition zones: Where freshwater and saltwater ecosystems converge.
- Sediment deposition sites: As rivers slow down, they deposit sediment, shaping landforms like deltas and estuaries.
- Biodiversity hotspots: The mix of fresh and saltwater attracts a wide range of species adapted to these unique conditions.
What is the mouth of a river in geography?
The mouth of a river is the point where it discharges its flow into a larger body of water. This meeting point is a dynamic environment shaped by the river’s sediment load, water flow, and the characteristics of the receiving water body.
River mouths often feature distinctive landforms:
- Deltas: Fan-shaped deposits of sediment that form as a river branches out into a larger body of water.
- Estuaries: Partially enclosed coastal bodies of water where freshwater and saltwater mix, creating highly productive ecosystems.
Why is it called the mouth of the river?
The term “mouth” is used to describe the end of a river for a couple of key reasons:
1. Visual Analogy: Just like our mouths are openings where we take in food, a river’s mouth is an opening where it “empties” its water and sediment into a larger body.
2. Functional Similarity: The mouth is where a river “releases” its contents, much like how our mouths release words and food.
What is the meaning of river mouth?
The meaning of “river mouth” extends beyond a simple definition. It encompasses:
- Ecological Significance: River mouths are crucial habitats supporting diverse species, including fish, birds, and invertebrates.
- Geomorphological Processes: Sedimentation and erosion at river mouths shape coastlines and create landforms that influence ecosystems and human activities.
- Human Interactions: Humans have long settled near river mouths, taking advantage of resources like fish, fertile land, and transportation routes.
How do you define “mouth”?
In the context of human anatomy, the “mouth” refers to the oral cavity, the opening through which we take in food and air. It’s a complex structure with several key components:
- Tongue: Responsible for taste, speech, and manipulating food.
- Teeth: Break down food through biting and chewing.
- Palate: Forms the roof of the mouth and aids in swallowing and speech.
- Salivary Glands: Produce saliva, which moistens food, aids in taste, and starts the digestive process.
What is the mouth region called?
The scientific term for the mouth region is the oral cavity. It’s the gateway to both the digestive and respiratory systems, playing a vital role in:
- Ingestion: Taking in food and fluids.
- Digestion: The initial stages of breaking down food.
- Respiration: The passage of air into and out of the body.
- Speech: The articulation of sounds.
What is the definition of by word of mouth?
“Word of mouth” refers to the informal sharing of information through spoken communication. It’s a powerful form of communication because:
- Trustworthy Source: We’re more likely to believe information from people we know and trust.
- Organic Reach: Word of mouth can spread quickly and organically, reaching a wide audience through personal networks.
What is the word of mouth easy definition?
In simple terms, “word of mouth” is when people tell other people about something. It’s like passing along a message through conversation, whether it’s a recommendation, a warning, or a funny story.
Which term refers to the mouth?
Both “mouth” and “oral cavity” refer to the same structure. “Mouth” is the more common term, while “oral cavity” is the scientific term.
What is Mouth in Science Definition?
In scientific terms, the mouth, or oral cavity, is the initial part of the alimentary canal (digestive tract) responsible for:
- Food intake
- Taste perception
- Mechanical and Chemical Digestion
It’s a complex structure with specialized components that work together to process food and initiate digestion.
Key Points:
- Mouth Geography: Understanding the structures and functions within the mouth.
- River Mouths: Dynamic areas where rivers meet larger bodies of water.
- Oral Cavity: The scientific term for the mouth, gateway to the digestive and respiratory systems.
- Word of Mouth: Informal communication that spreads through personal interactions.
This comprehensive guide has covered everything from the anatomy of your mouth to the geographical significance of river mouths. By appreciating the complexities of these structures, we can better understand their importance in our lives and the natural world.
- Unveiling the Enigma: Mansoureh Khojasteh Bagherzadeh’s Public Appearances & Private Life in Iran - July 18, 2025
- Unveiling the Mystery: Mansoureh Khojasteh Bagherzadeh’s Husband: A Rare Glimpse into a Private Life - July 18, 2025
- Unveiling Masoud Khamenei’s Mother: Power, Influence, and Iran’s Future - July 18, 2025