Are you ready to dive into the fascinating world of compound microscopes? In this article, we will unlock the power of these incredible scientific tools, exploring their functions, components, and numerous applications. Whether you are a curious student, a dedicated scientist, or simply someone intrigued by the wonders hidden in the microscopic realm, you’ve come to the right place. Our knowledgeable and experienced science educator will guide you through the complexities of compound microscopes, breaking down technical jargon into accessible language. Get ready to gain a comprehensive understanding of these remarkable devices and their significance in the scientific field. Let’s embark on this enlightening journey together!
Compound Microscope
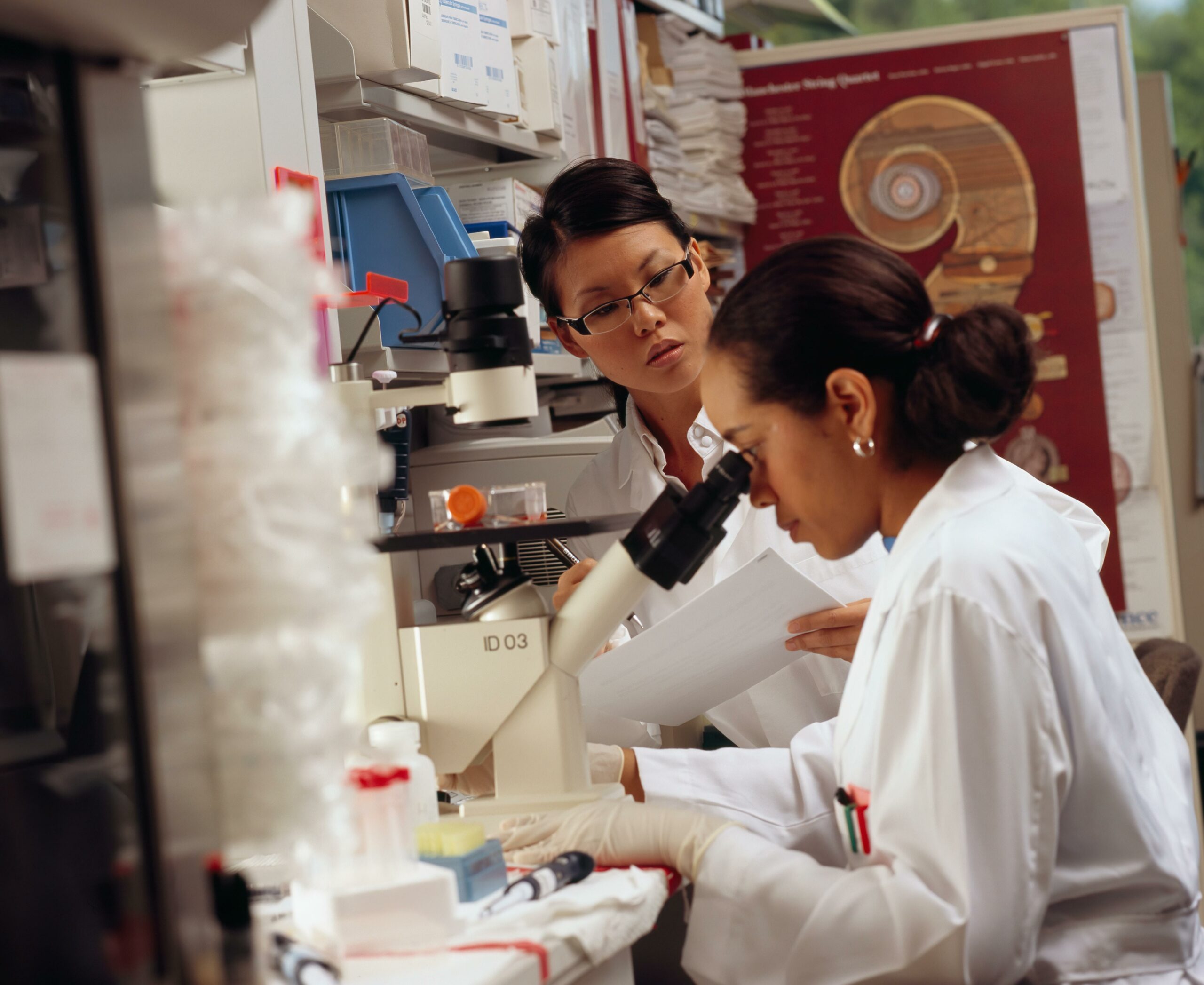
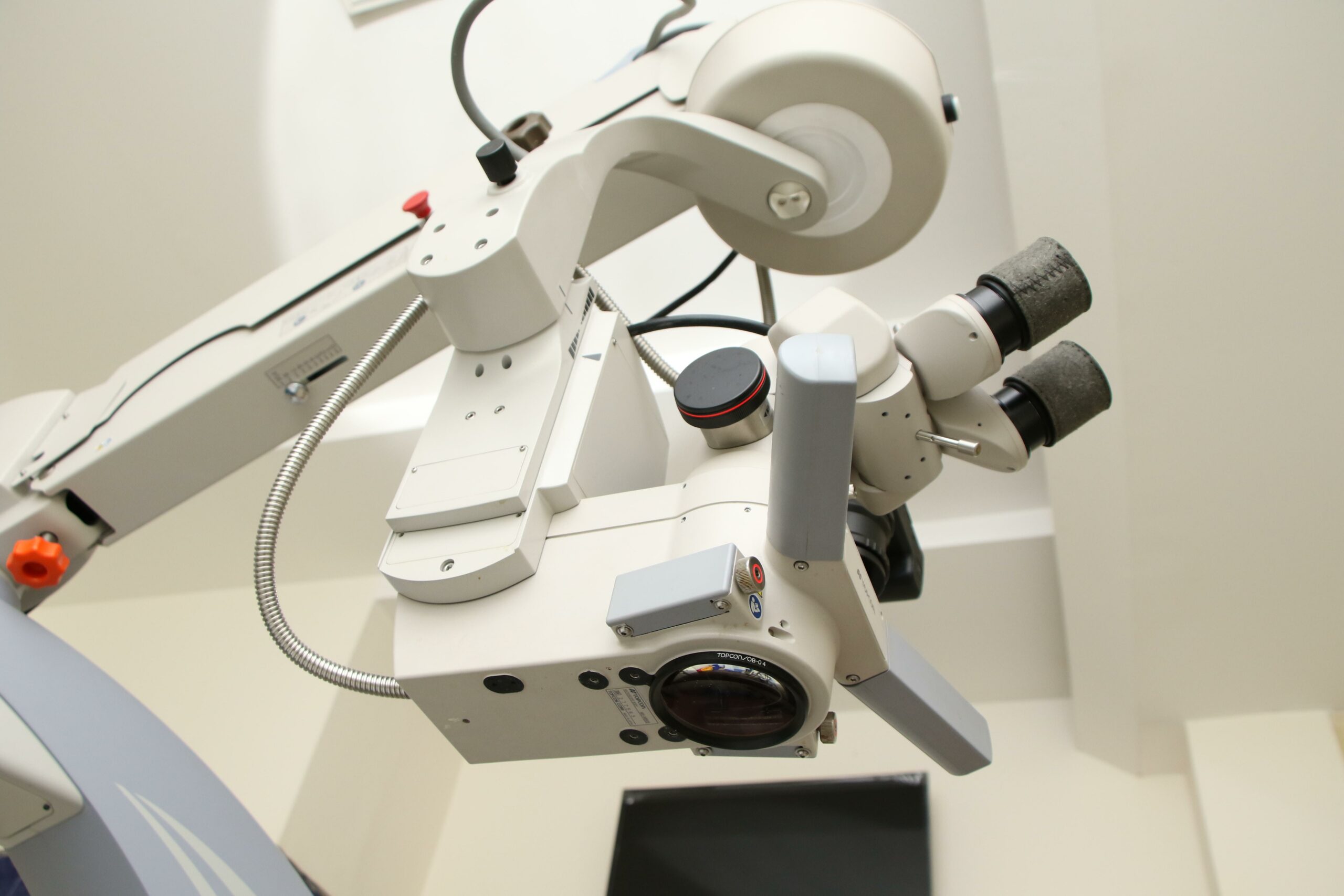
A compound microscope is a versatile scientific tool that allows us to observe and study the microscopic world in incredible detail. By using two sets of lenses, a compound microscope magnifies tiny objects on a slide, revealing a whole new level of complexity and beauty. In this article, we will delve into the functions, components, and applications of the compound microscope, unraveling its power to unlock hidden secrets.
Functions
At its core, the compound microscope functions by utilizing a combination of lenses to enhance the visibility of minute objects. The primary objective of this instrument is to provide magnification, enabling scientists and researchers to observe intricate details that would otherwise be invisible to the naked eye.
To achieve this, a compound microscope consists of several key components that work together harmoniously. These components include the condenser, reflector, objective lenses, ocular lens, and diaphragm. Each element plays a crucial role in optimizing the performance of the microscope.
Components
Let’s take a closer look at the key components of a compound microscope:
Condenser: Situated below the diaphragm, the condenser controls the focus of the light passing through the specimen. By manipulating the position of the condenser, scientists can adjust the illumination and enhance the contrast of the image.
Reflector: Positioned above the base of the microscope, the reflector consists of a plane mirror and a concave mirror. The plane mirror reflects light from an external source, such as a lamp or natural light, while the concave mirror concentrates and directs the light towards the specimen.
Objective Lenses: Located above the nosepiece, the objective lenses come in various forms, such as low power, high power, and oil immersion lenses. These lenses provide different levels of magnification, allowing scientists to choose the optimal lens for their specific research needs.
Ocular Lens: Also known as the eyepiece, the ocular lens is where we observe the magnified image of the specimen. By combining the magnification of the objective lens with the magnification of the ocular lens, the compound microscope delivers a detailed and enlarged view.
Diaphragm: Positioned below the stage, the diaphragm controls the intensity of light that passes through the specimen. By adjusting the diaphragm, researchers can manipulate the brightness and contrast of the image, optimizing the visibility of the microscopic details.
Applications
The applications of compound microscopes are diverse and far-reaching, revolutionizing scientific research across various disciplines. Here are just a few examples of how compound microscopes are utilized in the scientific field:
Biological Research: In the field of biology, compound microscopes are indispensable tools for studying cells, tissues, and microorganisms. By observing these microscopic entities, researchers can gain insights into cellular processes, conduct genetic research, and contribute to vital areas such as disease diagnosis and drug development.
Medicine and Healthcare: Compound microscopes play a vital role in the field of medicine, enabling healthcare professionals to analyze bodily fluids, diagnose diseases, and identify pathogens. Microscopy techniques such as histology and cytology rely heavily on the capabilities of compound microscopes to uncover abnormalities at a cellular level.
Material Science and Nanotechnology: In material science, compound microscopes allow scientists to investigate the structural properties of materials, examine the surface morphology, and analyze microstructures. Moreover, in the field of nanotechnology, compound microscopes are crucial for visualizing nanoscale objects and characterizing their properties.
Education and Research: Compound microscopes have a significant impact on education and research, empowering students and scientists alike to explore the microscopic world. From primary schools to advanced research facilities, these instruments facilitate hands-on learning experiences, foster scientific curiosity, and drive breakthroughs in various scientific disciplines.
In conclusion, compound microscopes are indispensable tools that have revolutionized scientific research. With their ability to magnify tiny objects and reveal hidden details, these instruments have transformed our understanding of the microscopic world. Whether it’s in the field of biology, medicine, material science, or education, compound microscopes continue to unlock new realms of knowledge. So let us embark on a journey through the lens of a compound microscope and uncover the wonders that lie beyond our naked eyes.
“The compound microscope, with its remarkable magnifying power, paves the way for unparalleled discoveries and deepens our understanding of the microscopic universe.”
Microscopes have revolutionized the world of science, allowing us to uncover the tiniest secrets of the universe. Want to learn some fascinating facts about the microscope? Well, look no further! Click here for a list of intriguing facts about the microscope: facts about the microscope. Prepare to be amazed by the incredible capabilities of this scientific marvel!
Compound Microscope
The history of compound microscopes is a fascinating journey through time, unveiling the evolution and breakthroughs of this indispensable scientific instrument. From its humble beginnings to its modern-day applications, the compound microscope has revolutionized our understanding of the microscopic world. Delve into the rich history of compound microscopes to uncover the trailblazers and innovators who shaped this groundbreaking technology. Discover the intriguing stories behind the invention and refinement of this pivotal tool by clicking on this link: history of compound microscopes.
When it comes to the types and applications of compound microscopes, the possibilities are endless. Explore the vast array of specializations and fields that benefit from these powerful instruments. From biological and medical research to material analysis and quality control, compound microscopes offer unparalleled insights into the intricate world of tiny objects. Delve into the diverse uses and discover the endless potential by following this link: types and applications of compound microscopes.
While compound microscopes open a window into the minute details of the microcosmos, understanding their capabilities and limitations is essential for researchers and enthusiasts alike. Uncover the boundaries and constraints that come with these remarkable instruments, allowing for informed decisions and optimal experimentation. Discover the extent of what compound microscopes can achieve and be aware of their limitations by clicking on this link: capabilities and limitations of compound microscopes.
With the article “Compound Microscope” as your starting point, embark on a captivating journey that unravels the history, explores the types and applications, and unveils the capabilities and limitations of these remarkable scientific tools. Let your curiosity guide you as you delve into the fascinating world of compound microscopes, and let these internal links serve as gateways to knowledge and discovery.
How to Effectively Use a Compound Microscope
[youtube v=”uEgM3gk8n6k”]
A compound microscope is an essential tool used in various fields such as biological research, medicine, material science, nanotechnology, and education. With its ability to magnify tiny objects on a slide, it allows us to study cells, tissues, microorganisms, diagnose diseases, visualize nanoscale objects, and facilitate hands-on learning experiences. This article will guide you on how to use a compound microscope effectively.
Understanding the Key Components
To effectively operate a compound microscope, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with its key components. These include:
Condenser and Reflector: The condenser controls the focus of light passing through the specimen, while the reflector reflects and directs light onto the specimen.
Objective Lenses: The compound microscope contains multiple objective lenses that provide different levels of magnification. These lenses include the scanning objective (5X), the 10X objective, the 40X objective, and the 100X objective.
Ocular Lens: The ocular lens is where the magnified image is observed.
Diaphragm: The diaphragm controls the intensity of light passing through the specimen.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using a Compound Microscope
Setting Up the Microscope: Start by plugging in the microscope and turning on the illuminator. Use the rheostat to raise the level of light, starting with it open halfway. This will ensure proper illumination for your specimen.
Preparing the Slide: Use the course focusing knob to lower the stage to its lowest position. Open the clip and place your slide on the stage, then release the arm. Use the stage adjustment knobs to move your specimen over the condenser, ensuring it is centered and in the light.
Rotating the Objectives: Grip the turret to rotate the objectives without pulling or pushing on them. Begin with the lowest power objective, also known as the scanning objective (5X). Rotate the turret until the lowest power objective is above the specimen and it clicks into place.
Focusing and Centering the Specimen: Look through the oculars and use the course focusing knob to slowly raise the stage until your specimen comes into focus. Once it’s in focus, use the stage adjustment knobs to center your specimen in the field of view.
Switching to Higher Magnification: Rotate the turret to switch to the next highest magnification objective. From this point on, use only the fine focus knob for focusing. Refocus the specimen and recenter it in your field of view using the stage adjustment knobs.
Using Immersion Oil: If you need to use the highest magnification objective (100X), place a drop of immersion oil on top of the slide, just above the light source. Move the 100X objective into place without using the immersion oil on the 40X objective, as it may damage it. Refocus and recenter the specimen using the fine focus knob.
Completing the Observation: After viewing the specimen, lower the stage all the way down. Remove the slide and clean off the immersion oil from both the 100X objective and the slide. Finally, move the lowest power objective (10X) into place above the light source, preparing the microscope for the next observation.
Remember, using a compound microscope requires careful handling and attention to detail. By following these steps, you can effectively observe and study various specimens, contributing to advancements in research, healthcare, and education.
“The compound microscope allows us to explore the microscopic world, studying cells, diagnosing diseases, and enabling innovative research.”
FAQ
Question 1
What are compound microscopes used for?
Answer 1
Compound microscopes are used to magnify tiny objects on a slide. They are commonly used in scientific research to observe and study small objects and organisms.
Question 2
What are the main parts of a compound microscope?
Answer 2
The main parts of a compound microscope include the condenser, reflector, objective lenses, and ocular lens. These components work together to magnify and view microscopic objects.
Question 3
What is the function of the condenser in a compound microscope?
Answer 3
The condenser is located below the diaphragm and is used to focus light onto the specimen. It helps to enhance image clarity and resolution.
Question 4
What is the role of the objective lenses in a compound microscope?
Answer 4
Objective lenses are located over the nosepiece and come in different types, including low power, high power, and oil immersion. They contribute to the overall magnification of the microscope and provide different levels of detail in the observed image.
Question 5
Who is credited with inventing the compound microscope?
Answer 5
The invention of the compound microscope is credited to Zacharias Janssen in the late 16th century. His innovation revolutionized scientific research by enabling the observation and study of small objects and organisms.
- Mastering Leader in Spanish: The Complete Guide - April 19, 2025
- Uncovering Surprising Parallels: England Size Compared to US States - April 19, 2025
- Old Mexico Map: Border Shifts 1821-1857 - April 19, 2025
















