This guide provides a comprehensive approach to understanding and memorizing the citric acid cycle, a crucial metabolic pathway. We’ll explore mnemonics, visual aids, and learning strategies to help you conquer this biochemical marvel.
Decoding the Citric Acid Cycle
The citric acid cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a central metabolic pathway essential for cellular respiration. It occurs within the mitochondria and serves to oxidize acetyl-CoA, ultimately producing energy-rich molecules like NADH and FADH2, which fuel the electron transport chain for ATP synthesis. This intricate eight-step process can seem daunting, but with the right tools, you can master it. Discover the secrets of cell functionality with our comprehensive cell organelles worksheet.
Understanding the Cycle’s Significance
The citric acid cycle isn’t just about energy production. It also plays a crucial role in:
- Anabolism: Providing building blocks for synthesizing essential molecules like amino acids.
- Metabolic Integration: Connecting with other pathways, forming a complex regulatory network within the cell.
Key Players: Intermediates and Enzymes
The cycle involves a series of intermediates and enzymes:
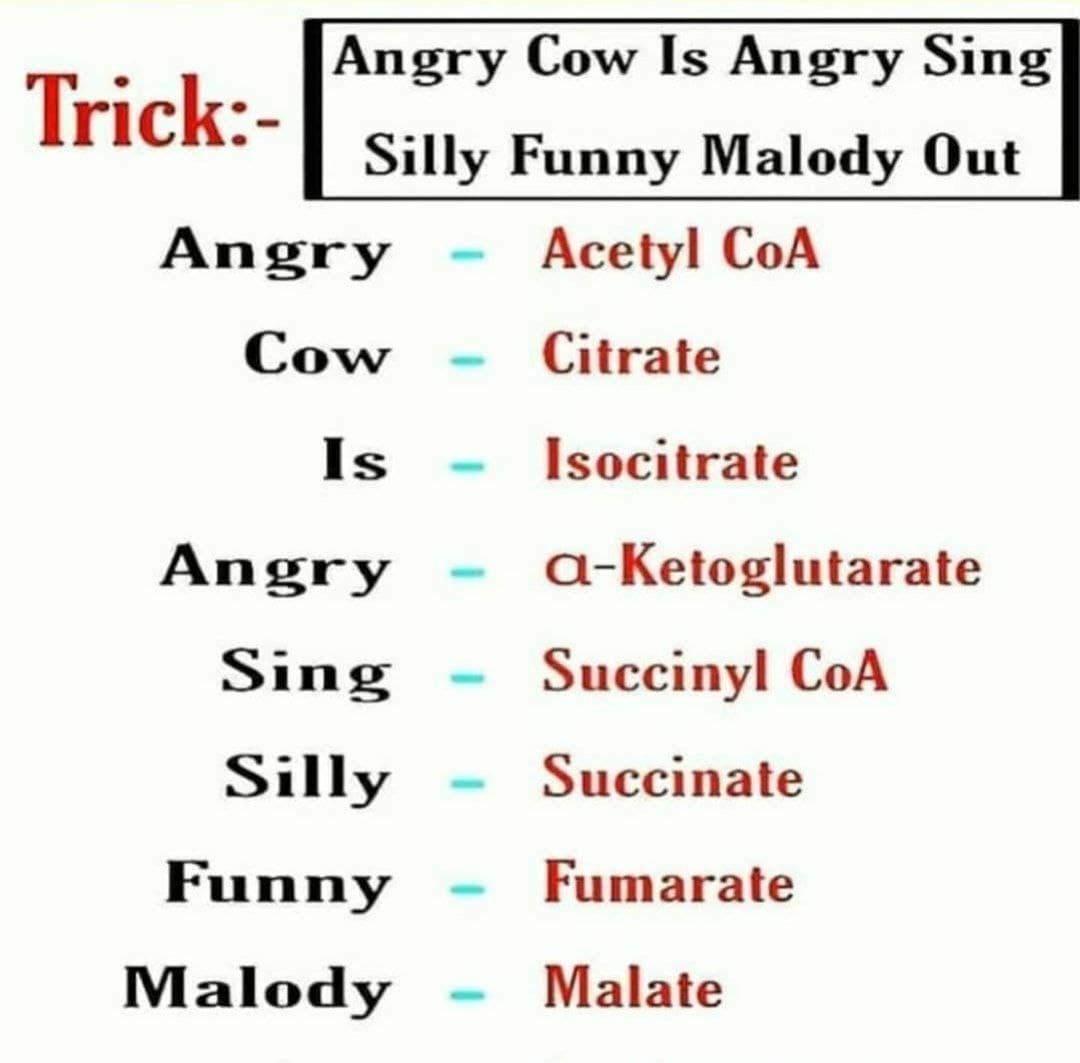
Intermediates: Citrate, Isocitrate, α-Ketoglutarate, Succinyl-CoA, Succinate, Fumarate, Malate, Oxaloacetate.
Enzymes: Each step is catalyzed by a specific enzyme, many of which are dehydrogenases or synthases. Aconitase, acting on citrate, is a notable exception.
Memory Mastery: Mnemonics and More
Mnemonic Devices for Intermediates
- “Citrate Is Krebs’ Starting Substrate For Making Oxaloacetate.” This mnemonic directly links the intermediates to the cycle’s function.
- “Can I Keep Selling Seashells For Money, Officer?” This more quirky version can be particularly memorable.
Mnemonic Devices for Enzymes
- “Cool Aunts In Kansas Sell Special Fudge Monthly.” This mnemonic aligns with the enzymes: Citrate synthase, Aconitase, Isocitrate dehydrogenase, α-Ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, Succinyl-CoA synthetase, Succinate dehydrogenase, Fumarate Hydratase (adapted), Malate dehydrogenase.
- Consider developing personalized mnemonics that resonate with you.
Visual Learning
Draw the cycle repeatedly. Visual aids, including diagrams, flowcharts, and animations (available on platforms like YouTube from various educational channels) can greatly enhance understanding and retention.
Memorization Strategies for the MCAT
Strategic Approach for the MCAT
While complete memorization of every detail isn’t strictly necessary for the MCAT, a strategic approach combining understanding and targeted memorization is highly recommended.
Prioritize Understanding
Focus on the cycle’s role in cellular respiration, its connection to oxidative phosphorylation, and its regulation. The MCAT emphasizes application of knowledge, not just recall.
Key Elements for Memorization
- Intermediates: Use a mnemonic like “Can I Keep Selling Sex For Money, Officer?”
- Enzymes: Focus on their general function (e.g., synthase, dehydrogenase) and associated reactants/products. Aconitase, which converts citrate to isocitrate, is an exception worth noting.
- Products: CO2, NADH, FADH2, GTP. Know where they are generated and their roles in subsequent energy production.
Enhance Retention
Use mnemonics and visual aids to improve memorization. Practice applying your knowledge with MCAT-style questions.
Deep Dive into the TCA Cycle
Acetyl-CoA and Oxaloacetate: The Cycle’s Foundation
Acetyl-CoA initiates the cycle, while oxaloacetate acts as both a starting and ending compound, highlighting its catalytic nature.
Connection to the Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
The NADH and FADH2 produced in the TCA cycle are crucial for the ETC, the final stage of cellular respiration where the majority of ATP is generated. This connection underscores the TCA cycle’s importance in energy production.
Regulation of the TCA Cycle
Several factors regulate the TCA cycle, including ATP, ADP, and NADH levels. Understanding these regulatory mechanisms can help you unravel how the cycle responds to cellular energy demands.
Clinical Relevance
Dysfunction within the TCA cycle can lead to various metabolic disorders. Exploring this clinical relevance can provide a deeper appreciation of the cycle’s importance in human health.
Advanced Learning Strategies
Creating Personalized Mnemonics
Develop your own mnemonics to strengthen memory.
Spaced Repetition
Use flashcards or online tools to reinforce learned information over time.
Integrating with Other Metabolic Pathways
Connect the TCA cycle to glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, and other pathways for a broader metabolic context.
Addressing Common Misconceptions
Avoid confusing intermediates or neglecting the cyclical nature of the process. Actively seek clarification on areas of uncertainty.
Ongoing Research and Future Directions
Research continues to uncover new insights into the citric acid cycle’s regulation, connections to disease, and potential therapeutic targets. This evolving understanding underscores the importance of staying curious and keeping up with current research.
By utilizing these strategies, you can move beyond rote memorization to a deeper understanding of this essential metabolic pathway. Remember, learning the citric acid cycle is a journey, not a race. Embrace curiosity, remain persistent, and celebrate your progress along the way.