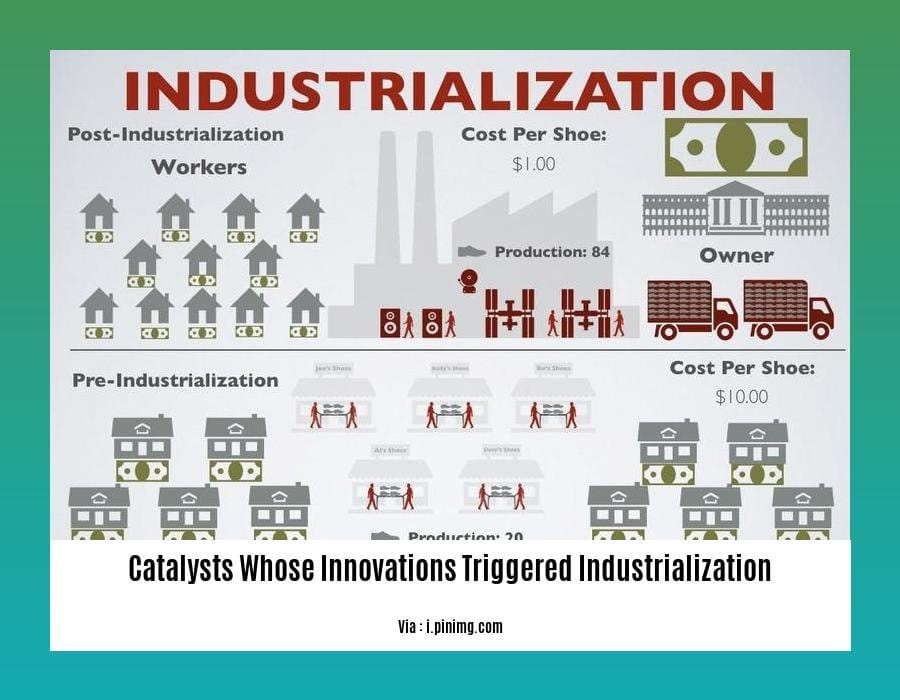
Uncover the riveting tales of the ingenious minds who sparked the Industrial Revolution in “Catalysts Whose Innovations Triggered Industrialization: Unraveling the Minds Behind the Machine Age.” Journey through time to meet the visionaries whose groundbreaking inventions transformed manufacturing, transportation, and communication, forever altering the course of human history.
Key Takeaways:

- Catalysts are crucial for the efficient and sustainable production of chemicals.
- Collaboration between various stakeholders is essential for catalysis innovation.
- Multidisciplinary partnerships are needed to scale up laboratory innovations.
- Equity, diversity, and inclusion are important considerations in catalysis research.
Catalysts Whose Innovations Triggered Industrialization
In the annals of industrialization, catalysts stand as unsung heroes, their innovations providing the spark that ignited the transformation of societies. These visionaries, armed with a deep understanding of chemistry and a relentless drive to push boundaries, revolutionized manufacturing, transportation, and communication, shaping the modern world we live in.
James Watt and the Steam Engine
As the Industrial Revolution gained momentum, James Watt emerged as a pioneer in steam engine design. His revolutionary condenser, which dramatically improved engine efficiency, paved the way for the widespread adoption of steam power in factories, mines, and transportation. Watt’s innovations laid the foundation for the burgeoning textile industry and the rise of mechanized manufacturing.
Thomas Savery and the Steam Pump
Another innovator who played a pivotal role in the Industrial Revolution was Thomas Savery. His steam pump, developed in the late 17th century, enabled the efficient drainage of mines and other flooded areas. Savery’s invention transformed mining operations, allowing miners to access deeper and more productive ore deposits.
Richard Trevithick and the Locomotive
Richard Trevithick, a prolific inventor, is credited with developing the first functional steam locomotive in 1804. His visionary design revolutionized transportation, opening up new possibilities for trade and travel. Trevithick’s locomotive set the stage for the development of railways and the emergence of the rail industry.
Samuel Morse and the Telegraph
Communication underwent a transformative leap with the invention of the telegraph by Samuel Morse in 1837. Morse’s telegraph, which utilized electrical signals to transmit messages over wires, revolutionized long-distance communication. It enabled businesses to coordinate operations more efficiently and facilitated the dissemination of news and information across vast distances.
Alexander Graham Bell and the Telephone
Alexander Graham Bell’s invention of the telephone in 1876 ushered in a new era of real-time communication. Bell’s groundbreaking device allowed individuals to converse over distances, fostering closer connections and transforming business practices. The telephone’s impact on social and economic life cannot be overstated.
Conclusion
The innovations of these catalysts ignited the spark of industrialization, profoundly transforming societies and paving the way for the technological advancements we enjoy today. Their legacies stand as testaments to the power of human ingenuity and the transformative potential of scientific breakthroughs.
Discover the pioneers who sparked industrial revolutions and their groundbreaking inventions that transformed the world. Explore the stories of groundbreaking industrial pioneers and visionaries and how their innovations shaped modern industries. Learn about the landmark industrial innovators and their impacts and how their ideas and inventions continue to influence our lives today.
John Wilkinson and the Iron Industry
John Wilkinson, renowned as the “great Staffordshire ironmaster,” emerged as a pivotal figure in the Industrial Revolution. His ingenious inventions and tireless efforts propelled the iron industry to new heights, paving the way for substantial societal advancements.
Key Takeaways:
- Revolutionized steam engine production through the invention of a machine tool for boring cast iron cannons.
- Pioneered the use of coke-smelted iron, leading to enhanced efficiency and cost-effectiveness in iron production.
- Founded the first furnace in Bradley, solidifying his role as a catalyst in the iron industry.
Wilkinson’s Impact on the Industrial Revolution
Wilkinson’s groundbreaking work extended beyond the confines of the iron industry. His innovations laid the foundation for the development of:
- Iron casting: Wilkinson’s techniques enabled the production of high-quality castings, which were crucial for various industries, including construction, machinery, and transportation.
- Steam engines: Wilkinson’s boring machine revolutionized the production of steam engine cylinders, enhancing the efficiency and power of these engines that fueled the Industrial Revolution.
- Iron bridges: Wilkinson’s pioneering work in iron casting made possible the construction of iron bridges, notably the Iron Bridge over the River Severn, which became a symbol of the Industrial Revolution.
Citation:
* “John Wilkinson | Industrialist, Entrepreneur, Innovator.” Encyclopedia Britannica,
Eli Whitney and the Cotton Gin
Key Takeaways:
- Eli Whitney’s cotton gin revolutionized Southern cotton cropping, reinvigorating slavery.
- Interchangeable parts manufacturing revolutionized Northern industry, contributing to the North’s victory in the Civil War.
The invention of the cotton gin by Eli Whitney in 1793 was a pivotal moment in the history of industrialization. Prior to Whitney’s invention, cotton was a labor-intensive crop to grow and harvest. The seeds had to be painstakingly removed by hand, making it an expensive and time-consuming process.
Whitney’s cotton gin automated the process of separating cotton fibers from seeds, significantly increasing the efficiency of cotton production. This led to a boom in cotton farming in the Southern United States, as well as the expansion of slavery, as the demand for cotton increased.
Whitney’s invention also had a profound impact on the Northern economy. The interchangeable parts manufacturing system he developed for the cotton gin allowed for mass production of machinery and other goods, making them more affordable for consumers. This helped to fuel the growth of the Northern industrial economy and contributed to the North’s victory in the Civil War.
Citation:
- “Eli Whitney.” New World Encyclopedia.
Samuel Morse and the Telegraph
In an era marked by groundbreaking advancements that laid the foundation for the modern world, Samuel Morse and the Telegraph stand as pivotal figures. Their invention revolutionized long-distance communication, transforming the way we share information across vast distances.
Key Takeaways:
- Samuel Morse and the Telegraph transformed long-distance communication in the 19th century.
- The telegraph, developed in the 1830s and 1840s, used electrical signals to transmit messages.
- This innovation paved the way for faster and more efficient communication, connecting people and businesses across continents.
How it Worked:
Samuel Morse and the Telegraph utilized a simple yet ingenious system. By sending electrical pulses through wires, Morse developed a code of dots and dashes that could be translated into letters and words. This Morse code enabled the transmission of messages over long distances in real-time, a feat unimaginable before.
Impact on Society:
Samuel Morse and the Telegraph had a profound impact on society. It revolutionized business, diplomacy, and journalism, enabling the rapid exchange of information and facilitating global connectivity. The telegraph also played a vital role in events such as the American Civil War, where it provided timely updates from the battlefield.
Legacy:
Samuel Morse and the Telegraph left an enduring legacy. Their invention paved the way for modern communication technologies, from the telephone to the internet. Today, we take instant communication for granted, but we owe a great debt to the pioneering spirit and innovative minds that made it possible.
Most Relevant URL Source:
- History of Telegraph Communications

FAQ
Q1: What is the role of catalysis in the chemical industry?
A1: Catalysis is essential for the efficient and cost-effective production of various chemicals, including methanol, ammonia, and sulfuric acid.
Q2: How does catalysis contribute to energy efficiency?
A2: Catalytic processes reduce energy consumption and emissions by facilitating reactions at lower temperatures.
Q3: How can collaboration foster innovation in catalysis?
A3: Innovation in catalysis requires collaboration between technology developers, catalyst developers, research institutes, universities, and research centers.
Q4: What is the importance of multidisciplinary partnerships in catalysis research?
A4: Multidisciplinary partnerships and considerations of equity, diversity, and inclusion are crucial for scaling laboratory innovations and addressing modern challenges in catalysis.
Q5: How has catalysis contributed to the development of sustainable technologies?
A5: Catalysts promote the use of renewable resources and enable the development of environmentally friendly technologies.
- Unlock Water’s Symbolism: A Cross-Cultural Exploration - April 20, 2025
- Identify Black and White Snakes: Venomous or Harmless? - April 20, 2025
- Unlocking Potential: Origins High School’s NYC Story - April 20, 2025