This article explores bucket handle fractures, their connection to child abuse, diagnosis, treatment, and current research. We’ll delve into what these fractures are, why they raise concerns, and how medical professionals approach these delicate situations.
What is a Bucket Handle Fracture?
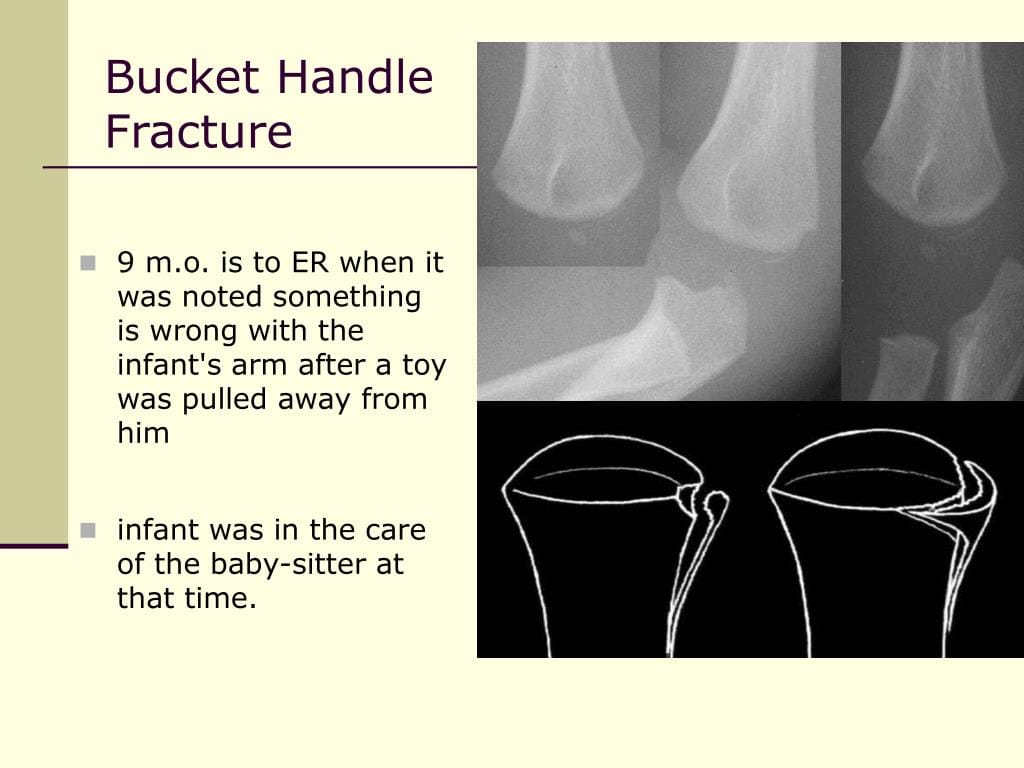
A bucket handle fracture is a specific type of bone break that occurs near the growth plate of a long bone, typically in the elbow or knee, predominantly affecting children under two years old. It gets its unusual name from the way the fractured bone fragment appears on an X-ray, resembling the handle of a bucket. Unlike fractures from common childhood falls, bucket handle fractures result from a violent twisting or yanking motion—the kind of force generated when someone forcefully shakes or jerks a child’s limb. This action tears the ligaments attached to a small piece of bone, ripping it away from the main bone structure.
Why are Bucket Handle Fractures Concerning?
The significant force required to cause a bucket handle fracture strongly suggests intentional harm, making it a red flag for potential child abuse or non-accidental injury (NAI). This is why medical professionals are trained to consider abuse as a possible cause when encountering this type of injury, especially in young children.
Diagnosing a Bucket Handle Fracture
Diagnosing a bucket handle fracture involves a thorough evaluation:
- Physical Examination: Doctors examine the injured limb for swelling, bruising, limited movement, tenderness, and inconsistencies in the explanation of the injury.
- Imaging Studies: X-rays are the primary imaging tool. However, these fractures can be subtle, and further imaging studies, such as MRI or CT scans, might be necessary for a definitive diagnosis. A skeletal survey may be recommended to look for other fractures that might indicate a pattern of abuse.
Treating the Fracture and Addressing the Bigger Picture
Treatment focuses on healing the fracture and ensuring the child’s safety:
- Immobilization: A cast or splint is used to immobilize the injured limb, allowing the bone to heal.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgery might be needed to realign the bone fragments and promote proper healing. If you feel you might need some traction enhancements, click buck’s traction to learn more.
- Child Protection: Healthcare providers have a legal and ethical duty to report suspected child abuse to child protective services, social workers, and/or law enforcement. This initiates an investigation to ensure the child’s well-being and safety. This investigation often involves a multidisciplinary team, including medical professionals, social workers, therapists, and legal experts.
Ongoing Research and Future Directions
Research continues to expand our understanding of bucket handle fractures:
- Improved Diagnostics: Scientists are working on refining imaging techniques and developing new diagnostic tools for earlier and more accurate detection.
- Biomechanics: Researchers are investigating the specific forces involved in these fractures to better understand the mechanisms of injury.
- Long-Term Effects: Studies are exploring the potential long-term physical and psychological effects of these injuries on children, and how best to provide ongoing support.
The Complexity of Diagnosis and the Importance of Caution
While a bucket handle fracture is a strong indicator of potential abuse, it is not a definitive diagnosis on its own. Rare instances of accidental bucket handle fractures have been reported, although highly unusual. Conditions like rickets, a bone-softening disease, can sometimes mimic the appearance of a bucket handle fracture on an X-ray. “Bucket-handle” and “corner fracture” classic metaphyseal lesions resemble healing rickets within the growth plate and the perichondrial ring. Medical professionals must conduct thorough investigations, considering all evidence and potential differential diagnoses before reaching a conclusion. The child’s safety and well-being remain paramount.
Key Points
- Definition: A bucket handle fracture is a break near the growth plate, often caused by forceful twisting or pulling, primarily affecting children under two.
- Abuse Indicator: While not definitive proof, it strongly suggests potential child abuse due to the force required.
- Diagnosis: Involves physical examination, X-rays, and possibly further imaging.
- Treatment: Includes immobilization, potential surgery, and mandatory reporting of suspected abuse.
- Ongoing Research: Focuses on improving diagnostics, understanding the biomechanics of the injury, and exploring long-term effects.
- Caution: Though a red flag, it’s not a standalone diagnosis of abuse; careful investigation is crucial.
Analyzing Bucket Handle Fractures: A Deeper Dive
This section provides a more in-depth analysis of bucket handle fractures, their causes, and diagnostic features.
What Causes a Bucket Handle Fracture?
Bucket handle fractures, a type of metaphyseal fracture, arise from forceful pulling or twisting of a limb, creating tension and shearing forces that tear the developing bone near the growth plate. This mechanism differs from accidental fractures, which typically result from direct impacts. A history inconsistent with the injury (e.g., a minor fall resulting in a significant fracture) raises suspicion for NAI.
Radiological Features and Differential Diagnosis
Radiologically, a bucket handle fracture shows a separated bone fragment resembling a bucket handle. A related injury, the corner fracture, appears at the bone’s corner. The thickness of the fragment suggests the healing stage. Endochondral bone filling and subperiosteal new bone formation further indicate healing. However, conditions like rickets can mimic a bucket handle fracture, stressing the need for a thorough medical history and examination. Other rare bone fragility disorders can also increase fracture risk, emphasizing the importance of a comprehensive evaluation.
Bucket Handle Fractures in Non-Ambulatory Children
In pre-ambulatory infants, bucket handle fractures are extremely rare and highly suspicious for abuse because these children are not yet engaging in activities that would typically cause such injuries. Any bucket handle fracture in a non-ambulatory child warrants immediate investigation by a multidisciplinary team, including child protective services and medical professionals. The subtle nature of these fractures on initial X-rays necessitates careful examination and potentially advanced imaging. Misdiagnosis can have devastating consequences.
This expanded information aims to provide a comprehensive and informative resource on bucket handle fractures, emphasizing the importance of careful consideration, thorough investigation, and a multidisciplinary approach to ensure the safety and well-being of children.
















1 thought on “Bucket Handle Fractures in Children: A Red Flag for Abuse – Diagnosis, Treatment, and Protection”
Comments are closed.