Pregnancy is a journey filled with anticipation, but sometimes, unexpected challenges arise. Anhydramnios, a condition characterized by critically low levels of amniotic fluid, is one such challenge. This fluid plays a vital role in your baby’s development, acting as a protective cushion, regulating temperature, and facilitating lung and digestive system maturation. This comprehensive article will explore the causes, diagnosis, management, and potential impact of anhydramnios on both the developing baby and expectant parents.
Decoding the Causes of Anhydramnios
The causes of anhydramnios can be complex, and sometimes, a definitive cause remains elusive. Several factors may contribute to this condition:
- Fetal Kidney Problems: A significant portion of amniotic fluid comes from fetal urine. If your baby’s kidneys aren’t developing properly or there’s a blockage in their urinary tract, they may not produce enough urine, leading to low fluid levels. Conditions like kidney dysplasia or a blocked urethra can contribute to this.
- Placental Issues: The placenta is the lifeline between you and your baby, providing essential nutrients and oxygen. If the placenta isn’t functioning correctly, it can disrupt the delicate balance of fluid exchange, potentially leading to anhydramnios. This can occur in conditions like placental abruption or preeclampsia.
- Premature Rupture of Membranes (PROM): The amniotic sac, a tough membrane encasing your baby and the amniotic fluid, can sometimes tear or rupture prematurely (often called “water breaking”). This can lead to a leakage of fluid, causing low levels or even anhydramnios. Sometimes, a small, undetectable tear can cause a slow leak that’s difficult to notice.
- Maternal Dehydration: While less common, severe maternal dehydration might contribute to low amniotic fluid. Staying well-hydrated is crucial, especially during hot weather or illness.
- Certain Medications: Some medications, especially those used to treat high blood pressure, may have the side effect of reducing amniotic fluid. Discuss any medications you are taking with your doctor to understand potential risks.
Diagnosing Anhydramnios: Ultrasound and Beyond
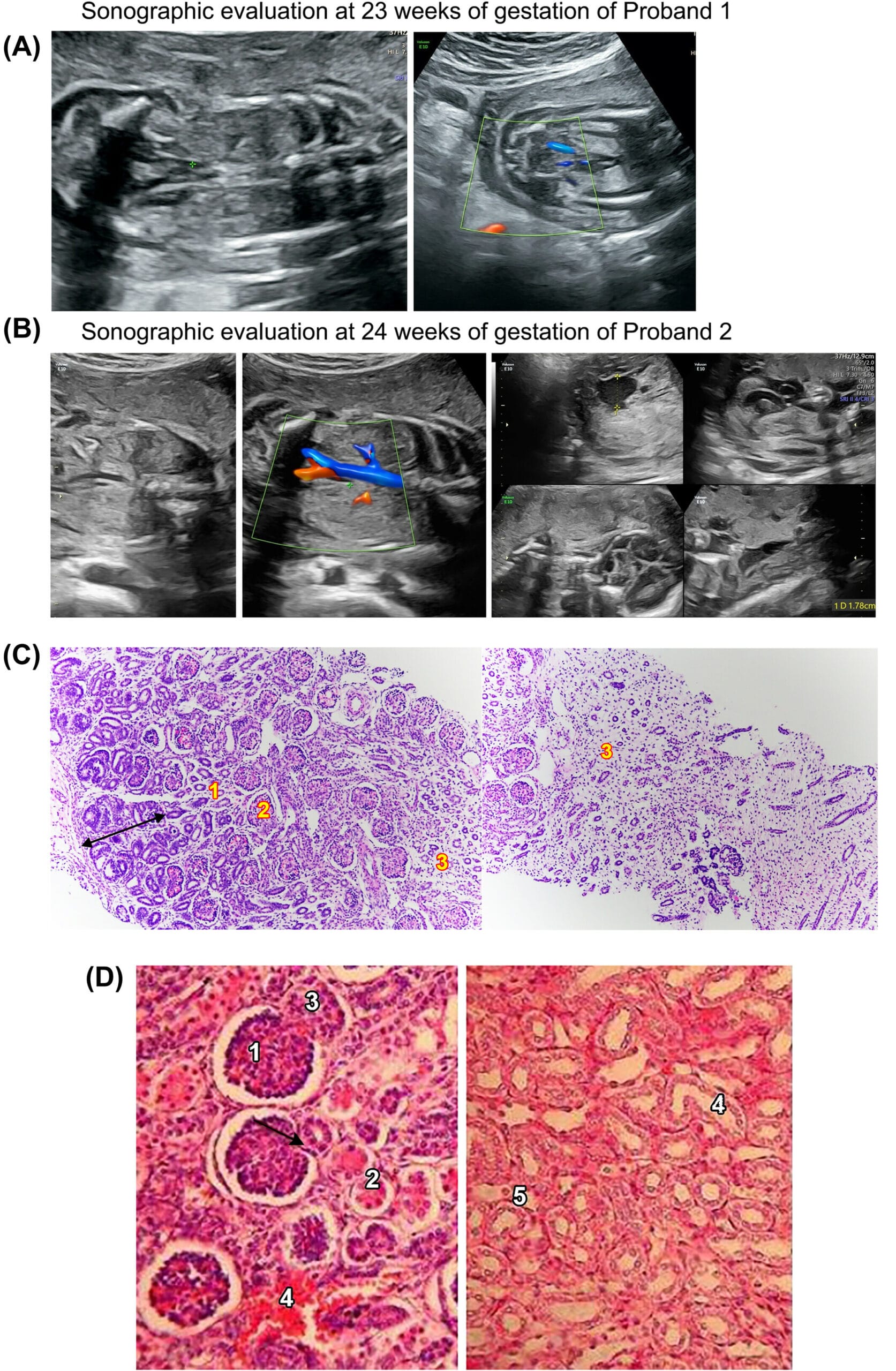
Anhydramnios is typically diagnosed through an ultrasound. During the ultrasound, your doctor will measure the amniotic fluid index (AFI), which assesses the total amount of fluid. They may also measure the single deepest pocket (SDP) of fluid. These measurements help determine if the fluid level falls below the normal range. Additional tests, like Doppler flow studies, might be used to assess blood flow to the baby and the placenta.
Managing Anhydramnios: A Balancing Act
Managing anhydramnios requires a careful, individualized approach depending on factors like how far along your pregnancy is, the suspected cause of the low fluid, and your baby’s overall health. Possible approaches include:
- Close Monitoring: Regular ultrasounds and other tests allow doctors to closely monitor your baby’s development, particularly lung development, and identify any potential complications early.
- Amnioinfusion: In some cases, doctors may infuse fluid directly into the amniotic sac through a procedure called amnioinfusion. This can temporarily increase fluid levels, offering additional cushioning for the baby and potentially supporting lung development.
- Early Delivery: If your baby’s lungs are severely underdeveloped or other serious complications arise, your doctor may recommend early delivery. This is a carefully considered decision, balancing the risks of prematurity with the risks of remaining in a low-fluid environment. Sometimes, expectant management with close observation is the best approach.
Potential Complications: Understanding the Risks
Anhydramnios can pose several risks to a developing baby. Some potential complications include:
- Pulmonary Hypoplasia (Underdeveloped Lungs): Amniotic fluid is crucial for lung development. Without enough fluid, your baby’s lungs may not mature fully, possibly leading to breathing difficulties after birth.
- Skeletal Deformities: In severe cases of prolonged low fluid, the baby may experience compression, potentially leading to skeletal abnormalities.
- Pregnancy Loss: In rare and severe cases, particularly early in pregnancy, anhydramnios may, tragically, result in pregnancy loss. This underscores the importance of early diagnosis and proactive management.
- Umbilical Cord Compression: Low amniotic fluid can increase the risk of the umbilical cord becoming compressed, potentially restricting blood flow and oxygen to the baby.
- Preterm Birth: If anhydramnios poses significant risks to your baby, your doctor may recommend early delivery, even if it means your baby will be born prematurely. Premature babies face their own set of health challenges.
- Birth Asphyxia: The lack of amniotic fluid’s protective cushioning can increase the risk of birth asphyxia, a condition where the baby doesn’t receive enough oxygen during labor and delivery.
The Prognosis: Navigating Uncertainty
The outlook for pregnancies complicated by anhydramnios is highly variable. It depends on factors like the underlying cause, when the condition develops, and the severity of any complications. With careful monitoring and appropriate management, many babies thrive despite this challenge. Ongoing research, such as the RAFT trial (Renal Anhydramnios Fetal Therapy Trial), investigates innovative interventions for anhydramnios related to renal malformations, offering potential hope for future advancements.
“I wrote these words almost exactly a year before an ultrasound scan presented us with a brand new word: anhydramnios. The amniotic fluid was all gone… With no fluid, our baby would develop no strength in its lungs and would only survive his birth by minutes or hours.” This poignant statement highlights the emotional toll an anhydramnios diagnosis can take on expectant parents. While medical advancements offer hope, the emotional and psychological impact necessitates compassionate support and informed decision-making.
If you’re interested to know more about cody sargent brain tumor, continue reading.
It’s essential to discuss your specific situation with your healthcare provider. They can offer the best guidance and support based on your individual circumstances. While anhydramnios can be a source of anxiety, advancements in prenatal care and treatment provide hope and positive outcomes for many families facing this challenge. Remember, every pregnancy is unique, and it’s crucial to maintain open communication with your doctor throughout your journey.
- Unlock Filipino Culture: A Deep Dive into Traditions and Practices - April 23, 2025
- Unlock Spanish Culture: Insights & Opportunities Now - April 23, 2025
- White Spirit Uses & Substitutes: A Deep Dive for Pros & DIYers - April 23, 2025