Embark on an enthralling journey into the depths of time as we unveil the hidden secrets of ancient lakes’ electrolytes and their profound influence on paleoenvironmental conditions in [The Secrets Unveiled: Ancient Lakes Electrolytes and Their Influence on Paleoenvironmental Conditions]. Join our experienced environmental scientist on an expedition to unravel the intricate relationship between these unique ecosystems and the dissolved substances that shape their very essence.
Key Takeaways:
Ancient lakes contain a unique blend of electrolytes that play a crucial role in their ecological dynamics, water chemistry, and long-term preservation of organic matter.
Magnesium, an essential element of life, is often overlooked as an important electrolyte and its deficiency is linked to several diseases.
Electrolytes from ancient lakes, such as Lake Deborah in Western Australia, are harvested in their purest form and are vital for muscle contraction, including the heart.
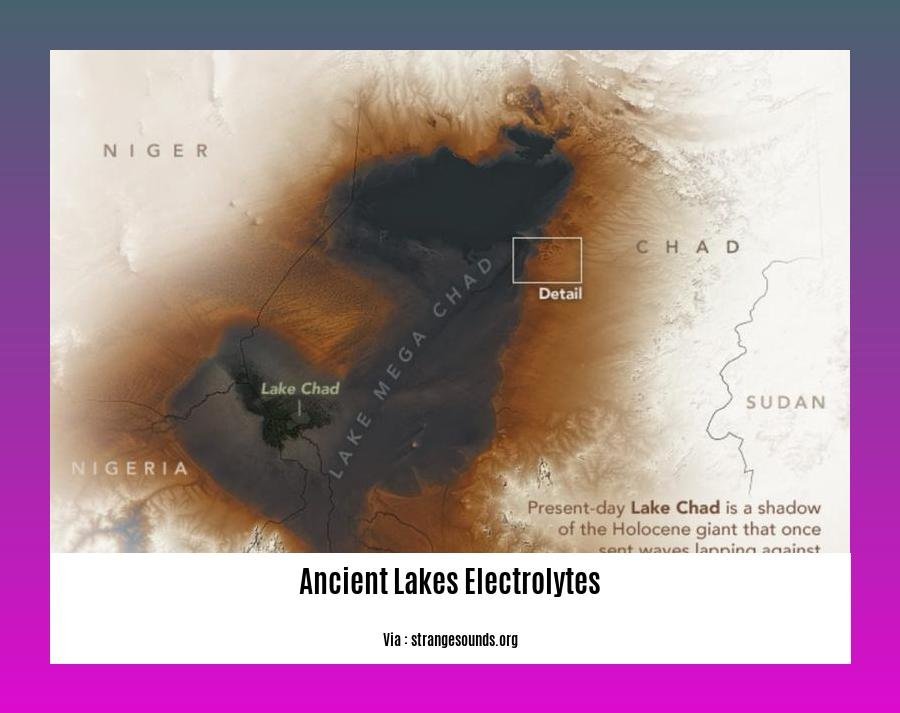
Ancient Lakes Electrolytes

Ancient lakes hold a treasure trove of information about the earth’s past. Their waters contain dissolved minerals, called ancient lakes electrolytes, that provide clues to the climate, hydrology, and ecology of these long-vanished bodies of water.
Ancient lakes electrolytes can be used to reconstruct past climates. When a lake dries up, the salts and minerals that were dissolved in its water are left behind. These minerals can be analyzed to determine the temperature and humidity of the region when the lake was full.
Ancient lakes electrolytes can be used to study past hydrology. The chemical composition of an ancient lake’s water can provide information about the sources of the lake’s water and the rate at which it flowed. This information can be used to reconstruct the landscape of the region and to understand how the climate has changed over time.
Ancient lakes electrolytes can be used to study past ecology. The types of plants and animals that lived in an ancient lake can be determined by analyzing the fossils that are found in the lake’s sediments. This information can be used to reconstruct the food web of the lake and to understand how the ecosystem has changed over time.
Ancient lakes electrolytes can also provide information about the geological history of an area. For example, the presence of certain minerals in an ancient lake’s water can indicate that the area was once home to volcanic activity.
Ancient lakes electrolytes are a valuable tool for scientists who are studying the earth’s past. They provide a wealth of information about the climate, hydrology, ecology, and geology of ancient lakes. This information can be used to understand how the earth has changed over time and to predict how it will change in the future.
How Ancient Lakes Electrolytes Are Analyzed
Ancient lakes electrolytes are analyzed using a variety of methods, including:
- Chemical analysis: This method involves measuring the concentrations of different elements and compounds in an ancient lake’s water.
- Isotopic analysis: This method involves measuring the ratios of different isotopes of an element in an ancient lake’s water.
- Mineralogical analysis: This method involves identifying the different minerals that are present in an ancient lake’s sediments.
These methods can be used to determine the temperature, humidity, and pH of an ancient lake’s water. They can also be used to identify the sources of the lake’s water and the types of plants and animals that lived in the lake.
The Importance of Ancient Lakes Electrolytes
Ancient lakes electrolytes are important because they provide a wealth of information about the earth’s past. This information can be used to understand how the earth has changed over time and to predict how it will change in the future. Ancient lakes electrolytes are also important because they can be used to identify potential mineral resources and to develop new methods for environmental remediation.
Uncover the secrets of a forgotten era with our captivating exploration of ancient knowledge known only to the ancients.
Dive into the hidden depths of ancient lakes and uncover the secrets of their magnesium-rich waters, believed to possess healing properties.
Prepare to be enthralled by the story of the ancient owl, a symbol of wisdom and knowledge in many cultures.
Interpretation of ancient lakes electrolytes data
For millennia, ancient lakes have captivated the scientific community, revealing the earth’s evolutionary history and harboring secrets of past climates, hydrology, and ecology. Their electrolytes, like tiny time capsules, hold clues to these long-lost worlds.
Unveiling the Secrets: Electrolytes and Paleoenvironmental Conditions
Ancient lakes electrolytes, composed of dissolved minerals, reflect the chemical and biological processes that shaped these unique ecosystems. By deciphering the composition of these electrolytes, we can piece together the puzzle of past environmental conditions:
- Water Chemistry: Electrolytes tell the story of an ancient lake’s chemistry, revealing its salinity, alkalinity, and ionic composition. These parameters provide insights into the lake’s hydrological balance, evaporation rates, and interactions with surrounding rocks and sediments.
- Climate Reconstruction: Electrolytes act as climate archives, preserving chemical signatures that reflect temperature, precipitation, and humidity levels. By analyzing the isotopic composition of electrolytes, we can reconstruct past climates and understand how ancient lakes responded to changing environmental conditions.
- Biological Productivity: The concentration and types of electrolytes influence the lake’s biological productivity. High levels of nutrients, such as phosphorus and nitrogen, can lead to algal blooms and eutrophication, while low nutrient levels may limit primary production. Electrolytes also influence the distribution and diversity of aquatic organisms.
Extracting Ancient Secrets: Analytical Techniques
Unraveling the mysteries of ancient lake electrolytes requires a combination of field and laboratory techniques:
- Fieldwork: Collecting sediment cores, water samples, and rock samples is the first step in uncovering the secrets of ancient lakes. These samples are cuidadosamente analyzed in the laboratory to extract electrolytes and unravel their chemical and isotopic composition.
- Laboratory Analysis: An array of analytical techniques is employed to analyze ancient lake electrolytes. These include:
- Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS): Measures the concentration of various elements in electrolytes, providing insights into the lake’s chemical composition.
- Ion chromatography: Separates and quantifies ions in electrolytes, helping to understand their ionic balance.
- Isotope ratio mass spectrometry (IRMS): Determines the isotopic composition of electrolytes, providing clues about their origin and the environmental conditions in which they formed.
Key Takeaways:
- Ancient lakes electrolytes are a valuable source of information about past climates, hydrology, and ecology.
- By analyzing the composition of electrolytes, we can reconstruct paleoenvironmental conditions and understand the evolutionary history of ancient lakes.
- The interpretation of ancient lakes electrolytes data involves a combination of fieldwork, laboratory analyses, and data interpretation.
- This field of research contributes to our understanding of the earth’s past and present, providing insights into the complex interactions between geology, climate, and life.
Sources:
- The Ancient Lakes of Indonesia: Towards Integrated Research and Conservation Approaches
- Ancient Lakes: A Window into Earth’s Past
Examples of Using Ancient Lakes Electrolytes to Reconstruct Past Climates and Environments

Ancient lakes, hidden treasures of the past, hold within them a trove of secrets waiting to be unveiled. Their waters, although long evaporated, left behind a legacy in the form of electrolytes—a wealth of information that can be harnessed to reconstruct past climates, environments, and the story of life that once thrived in these ancient realms.
Key Takeaways:
Ancient lakes’ electrolytes offer a window into the past, providing insights into paleoenvironmental conditions and climate shifts.
Chemical and isotopic analysis of these electrolytes can reveal changes in temperature, precipitation patterns, and hydrological cycles.
Ancient lakes’ electrolytes can uncover the history of vegetation, biodiversity, and the evolution of life over millennia.
These electrolytes serve as archives of past ecosystems, documenting the interplay between climate, geology, and biology.
Studying ancient lakes’ electrolytes aids in understanding the long-term impacts of climate change and environmental disturbances.
Unveiling Histories:
Chemical Fingerprints:
The chemical composition of ancient lakes’ electrolytes, like a chemical fingerprint, captures the story of past water chemistry. Variations in these electrolytes, such as sodium, magnesium, calcium, and chloride, can reveal changes in the lake’s salinity, evaporation rates, and water sources.
Stable Isotopes:
Nature’s time capsules, stable isotopes, like oxygen-18 and carbon-13, hold clues to past climate conditions. Their ratios in ancient lakes’ electrolytes provide insights into temperature, precipitation patterns, and the movement of water masses.
Biological Treasures:
Ancient lakes’ sediments preserve remnants of past life, such as pollen, plant macrofossils, and diatoms. Analyzing these biological markers can reconstruct past vegetation, biodiversity, and the ecological interactions that shaped these vanished ecosystems.
Applications:
Unlocking Climate History:
Through the analysis of ancient lakes’ electrolytes, scientists have unraveled climate shifts over thousands of years. For instance, studies of East African lake sediments revealed abrupt climate changes during the last glacial period, shedding light on the Earth’s past climate variability.
Uncovering Ancient Environments:
Electrolytes from ancient lakes have illuminated past environmental conditions. For example, research on the Qaidam Basin in China revealed variations in lake levels and salinity, providing insights into the region’s hydrological history and the evolution of its unique ecosystems.
Implications for Today and Tomorrow:
Understanding past climates and environments through ancient lakes’ electrolytes has far-reaching implications. It informs us of the complex interactions between climate, geology, and biology, a knowledge crucial for predicting future climate scenarios and guiding conservation efforts in a changing world.
Conclusion:
Ancient lakes’ electrolytes, like tiny time capsules, hold the secrets of past climates and environments. By meticulously analyzing these natural archives, scientists are piecing together the story of life on Earth, uncovering the intricate relationships that shaped our planet’s history and guiding us towards a more sustainable future.
Sources:
Significance of Ancient Lakes Electrolytes in Paleoenvironmental Studies
Howdy, explorers! Let’s dive into the fascinating world of ancient lakes and unveil the secrets held within their electrolytes. These electrolytes play a crucial role in paleoenvironmental studies, offering valuable insights into the Earth’s past. They’re like tiny time capsules, preserving clues about ancient climates, ecosystems, and the intriguing story of life’s evolution.
Key Takeaways:
- Ancient lakes serve as archives of environmental and climatic changes over geological time.
- Electrolytes in ancient lake sediments provide information on past climate, vegetation, precipitation, and redox conditions.
- Lipid biomarkers in ancient lake sediments shed light on biological communities, ecosystem dynamics, and environmental conditions.
- Studying ancient lakes helps reconstruct past climates, decipher ecosystem evolution, and understand long-term environmental change impacts.
So, what are these electrolytes, and why do they matter? Picture this: ancient lakes are like giant sponges, absorbing and storing minerals, salts, and organic matter from their surroundings. As time passes, these substances accumulate in the lake’s sediments, forming layers that tell the story of past environmental conditions.
Scientists use clever techniques to extract and analyze these electrolytes. They’re like detectives, carefully examining these tiny clues to piece together the puzzle of the past. They measure the concentrations of different elements, study the isotopes present, and even look at the types of organic molecules preserved in the sediments.
This detective work helps them reconstruct ancient climates, understand how ecosystems have changed over time, and even learn about the evolution of life on Earth. It’s like reading a book written in the language of electrolytes, revealing the history of our planet chapter by chapter.
The significance of ancient lakes electrolytes in paleoenvironmental studies cannot be overstated. They’re like windows into the past, helping us understand the intricate dance between life and the environment. They’re also valuable tools for predicting future changes, as they provide a glimpse into how ecosystems have responded to past environmental shifts.
So, next time you’re near an ancient lake, take a moment to appreciate its beauty and the wealth of knowledge it holds. These lakes are silent witnesses to the Earth’s history, and their electrolytes are the keys to unlocking their secrets.
Citations:
- Ancient Lakes Revisited: From the Ecology to the Genetics of an Evolutionary Oasis
- Palaeoenvironmental Changes in Eocene Tibetan Lake Systems Revealed by Elemental Geochemistry and Clay Mineralogy of Sediments
FAQ
Q1: How can ancient lakes reveal information about past climate and environmental conditions?
A1: Ancient lakes contain sedimentary deposits that serve as archives of past environmental changes. These deposits hold valuable clues, such as lipid biomarkers, which can provide insights into the biological communities, ecosystem dynamics, and environmental conditions that existed in these lakes. By studying sedimentary deposits, scientists can reconstruct past climates, decipher the evolution of ecosystems, and understand the long-term impacts of environmental changes.
Q2: What role do electrolytes play in the study of ancient lakes?
A2: Electrolytes are essential for muscle contraction and play a crucial role in various bodily functions. In the context of ancient lakes, electrolytes can provide insights into the paleoenvironmental conditions that existed in these lakes. Electrolytes can help scientists understand the water chemistry, ecological dynamics, and long-term preservation of organic matter in ancient lakes.
Q3: How do scientists study electrolytes in ancient lakes?
A3: Scientists employ various geochemical and isotopic techniques to study electrolytes in ancient lakes. These techniques allow them to analyze the elemental composition and isotopic ratios of electrolytes, which can provide valuable information about the lake’s water chemistry, hydrological conditions, and the geological processes that shaped the lake’s environment.
Q4: What are some of the key findings from studies on ancient lakes electrolytes?
A4: Studies on ancient lakes electrolytes have revealed insights into the evolution of ecosystems, the drivers of speciation and adaptive radiation in aquatic organisms, and the long-term impacts of environmental changes. These studies have also shed light on the role of electrolytes in influencing the water chemistry and ecological dynamics of ancient lakes.
Q5: How can studying ancient lakes electrolytes contribute to our understanding of the Earth’s history?
A5: By studying ancient lakes electrolytes, scientists can gain valuable insights into the planet’s past and present. These studies provide a window into the intricate mechanisms that have shaped life’s journey over millennia and help us understand the complex interactions between the Earth’s ecosystems and the geological processes that have shaped our planet.
- Crypto Quotes’ Red Flags: Avoid Costly Mistakes - June 30, 2025
- Unlock Inspirational Crypto Quotes: Future Predictions - June 30, 2025
- Famous Bitcoin Quotes: A Deep Dive into Crypto’s History - June 30, 2025