Embark on a captivating historical odyssey with [- Uncovering the Enigmatic Ancient Ghana Empire: A Historical Journey]. Delve into the annals of West Africa and unravel the mysteries of a civilization that left an indelible mark on the continent.
Key Takeaways:
- The Ghana Empire, also known as the Wagadou Empire, was a powerful trading empire in West Africa.
- It existed from the 6th to 13th century CE in the region of present-day southeastern Mauritania, western Mali, and eastern Senegal.
- The empire was founded by the Soninke people under King Dinga Cisse.
- It had a feudal government with local kings paying tribute to a high king.
- The empire’s economy was based on the control of gold and salt trade routes across the Sahara Desert.
- The Ghana Empire was located between the Sahara Desert and the rainforests of West Africa.
Ancient Ghana Empire
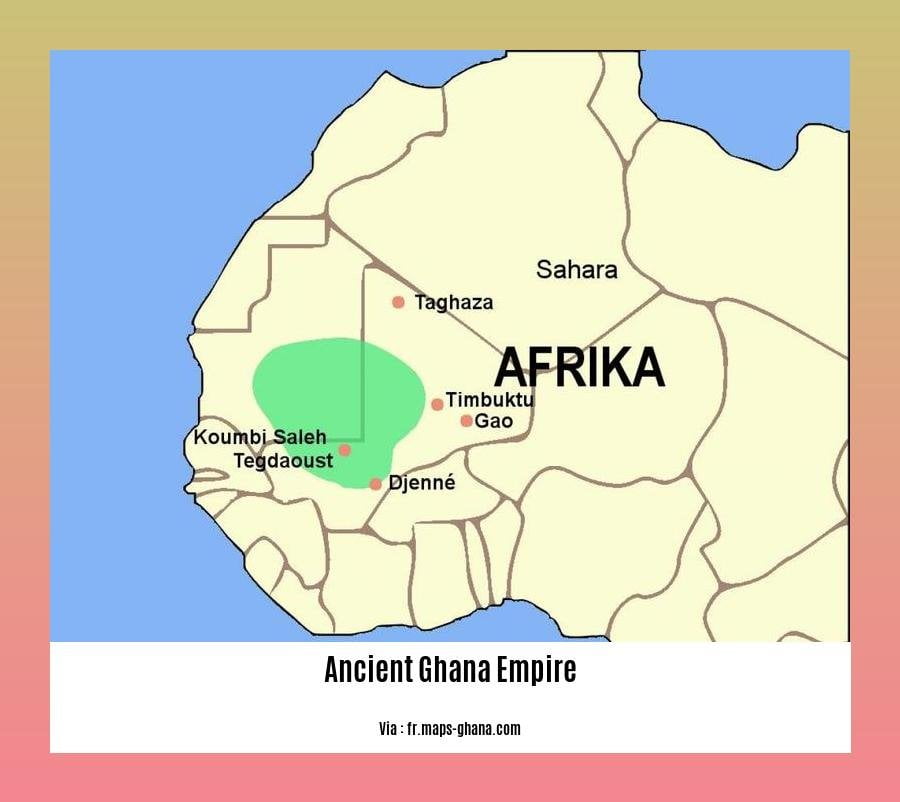
The Ancient Ghana Empire, also known as the Wagadou Empire, flourished from the 6th to 13th centuries CE in western Africa.
Origins and Rise to Power
The Ghana Empire found its genesis among the Soninke people and traced its lineage back to King Dinga Cisse. Straddling the trans-Saharan trade routes and strategically positioned between the Sahara desert and West Africa’s rainforests, the empire flourished on the wealth accrued from controlling the gold and salt trade.
Political Structure
The Ghana Empire operated a feudal system, where local kings paid tribute to the emperor, known as the Ghana. This centralized rule ensured stability and maintained the empire’s influence over its vast territories.
Economic Prowess
The empire’s economic might stemmed from its dominance of the trans-Saharan trade routes. Ghana emerged as a trading hub, connecting West Africa with North Africa and beyond. Gold, salt, and other commodities flowed through the empire, enriching its cities and amassing immense wealth.
Cultural Legacy
Beyond its economic prowess, the Ghana Empire left an indelible cultural mark on the region. Its artisans were renowned for their intricate goldsmithing and skilled metalworking. Islam gained prominence during the empire’s later years, influencing its architecture and social structure.
Decline and Legacy
By the 13th century, the Ghana Empire began to wane. Factors such as drought, competition from neighboring powers, and internal strife contributed to its decline. Despite its eventual demise, the Ghana Empire left a lasting legacy as one of the most significant empires in West African history.
If you’re curious about the rich and diverse past of Ghana, be sure to delve into the History of Ghana. Additionally, learn more about the country’s momentous Ghana’s independence from Britain and the visionary leadership of Kwame Nkrumah.
Economic Systems and Trade Networks

The Ghana Empire was a powerful West African kingdom that flourished from the 6th or 7th century CE. Its prosperity was largely due to its control over trade and access to natural resources such as gold and iron ore.
The empire’s economic system was based on agriculture, trade, and mining. The main crops were millet, sorghum, and rice. The empire also traded in gold, ivory, and slaves. The capital of the empire was likely Koumbi Saleh, which was a major trading center.
The Ghana Empire had an extensive trade network that stretched across West and North Africa. The empire traded with the Berbers of North Africa, the Arabs of the Middle East, and the people of the Sahel region. The empire’s main exports were gold and slaves. In exchange, the empire imported salt, cloth, and other goods.
The Ghana Empire’s economic success allowed it to build a powerful army. The army was well-trained and had cavalry units. The empire also had a strong navy that patrolled the Niger River.
Key Takeaways:
- The Ghana Empire’s prosperity was based on its control of trade and access to natural resources.
- The empire had an extensive trade network that stretched across West and North Africa.
- The empire’s economic success allowed it to build a powerful army and navy.
Relevant URL Sources:
- World History Encyclopedia: Ghana Empire
- Britannica: Ghana
Cultural Practices and Religion
Step into the enigmatic realm of the Ghana Empire, where diverse cultural practices and religion intertwined to shape the very fabric of society.
Traditional Indigenous Beliefs: The empire embraced a rich tapestry of animist and traditional beliefs, honoring ancestors, spirits, and the natural world.
Influence of Islam: As trade routes flourished, the empire came into contact with Islam, which gained significant influence during the reign of King Tenkamenin. The adoption of Islam brought new spiritual practices and architectural marvels like mosques.
Syncretism and Coexistence: Rather than displacing traditional beliefs, Islam coexisted harmoniously with indigenous practices, creating a unique blend of spirituality.
Rituals and Ceremonies: Religious rituals and ceremonies played a vital role in daily life, marking important events like births, marriages, and funerals. Elaborate festivals celebrated the harvest, honored ancestors, and appeased the gods.
Religious Leaders: Known as marabouts, religious leaders held great power and influence within the empire. They consulted on spiritual matters, provided healing, and interpreted dreams.
Key Takeaways:
- The Ghana Empire embraced a diverse array of cultural practices and religion, including traditional indigenous beliefs, Islam, and Christianity.
- Religious ceremonies and rituals marked important events and played a central role in daily life.
- The empire experienced a harmonious coexistence of Islam and traditional beliefs.
- Religious leaders, known as marabouts, wielded significant power and influence.
- The unique blend of cultural practices and religion left a lasting legacy on the Ghana Empire and beyond.
Relevant URL Sources:
- Ghana Empire – Wikipedia
- Ghana | History, Culture & Legacy | Britannica
Decline and Legacy of the Ghana Empire
The Ghana Empire, a beacon of wealth and power in West Africa, gradually declined over centuries. This enigmatic empire’s influence waned due to internal conflicts, shifting trade routes, and external invasions.
Internal Strife
Power struggles among royal factions weakened the empire from within. Succession disputes and regional ambitions led to disunity, undermining the central authority.
Shifting Trade Routes
The rise of new trade routes along the coast of West Africa diverted wealth away from the trans-Saharan trade routes that had sustained the Ghana Empire. The empire’s economic dominance diminished as its control over trade routes weakened.
External Invasions
The Almoravids, a Berber dynasty from North Africa, invaded the Ghana Empire in the mid-11th century CE. Their military superiority and zeal for religious conversion dealt a significant blow to the empire, leading to the sacking of its capital, Koumbi Saleh.
Legacy
Despite its decline, the Ghana Empire left an enduring mark on West Africa. It established a strong administrative system, facilitated trade networks, and fostered cultural exchange. Its legacy continues to inspire historians and scholars who seek to understand the rise and fall of ancient civilizations.
Key Takeaways:
- Internal strife: Power struggles and regional ambitions weakened the empire from within.
- Shifting trade routes: The rise of coastal trade routes diverted wealth away from the empire’s trans-Saharan routes.
- External invasions: The Almoravids’ invasion dealt a significant blow to the empire’s power and prestige.
- Legacy: Despite its decline, the Ghana Empire left an enduring mark on West African history.
Citations:
- History of Ghana – Historical Empires and Kingdoms
- Ghana Empire – Wikipedia
















