De Quervain’s tenosynovitis, often referred to as De Quervain’s syndrome, can cause significant wrist pain and limit hand function. It is an inflammatory condition affecting the tendons on the thumb side of your wrist. This comprehensive guide explores the various medical devices and treatment options available to manage De Quervain’s syndrome and regain control of your hand. We’ll cover everything from splints and braces to emerging technologies, helping you navigate your options and find the best path to recovery.
Understanding De Quervain’s Syndrome
De Quervain’s tenosynovitis is characterized by inflammation of the tendons that control thumb movement. These tendons pass through a tunnel-like structure called the sheath, located on the thumb side of your wrist. When these tendons become inflamed, they rub against the sheath, causing pain, swelling, and difficulty gripping or pinching.
Several factors can contribute to De Quervain’s, including:
- Overuse and Repetitive Motions: Activities like gardening, playing racquet sports, or even excessive smartphone use can irritate and inflame the tendons.
- Direct Injury: A sudden impact or sprain to the wrist can trigger De Quervain’s.
- Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy and menopause can increase the risk due to hormonal fluctuations.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: This inflammatory condition can increase susceptibility to De Quervain’s.
Effective Medical Devices for De Quervain’s
Splints and Braces: Your First Line of Defense
Splints and braces play a vital role in managing De Quervain’s syndrome. By immobilizing the thumb and wrist, they reduce tendon irritation and promote healing. Let’s explore the different types available:
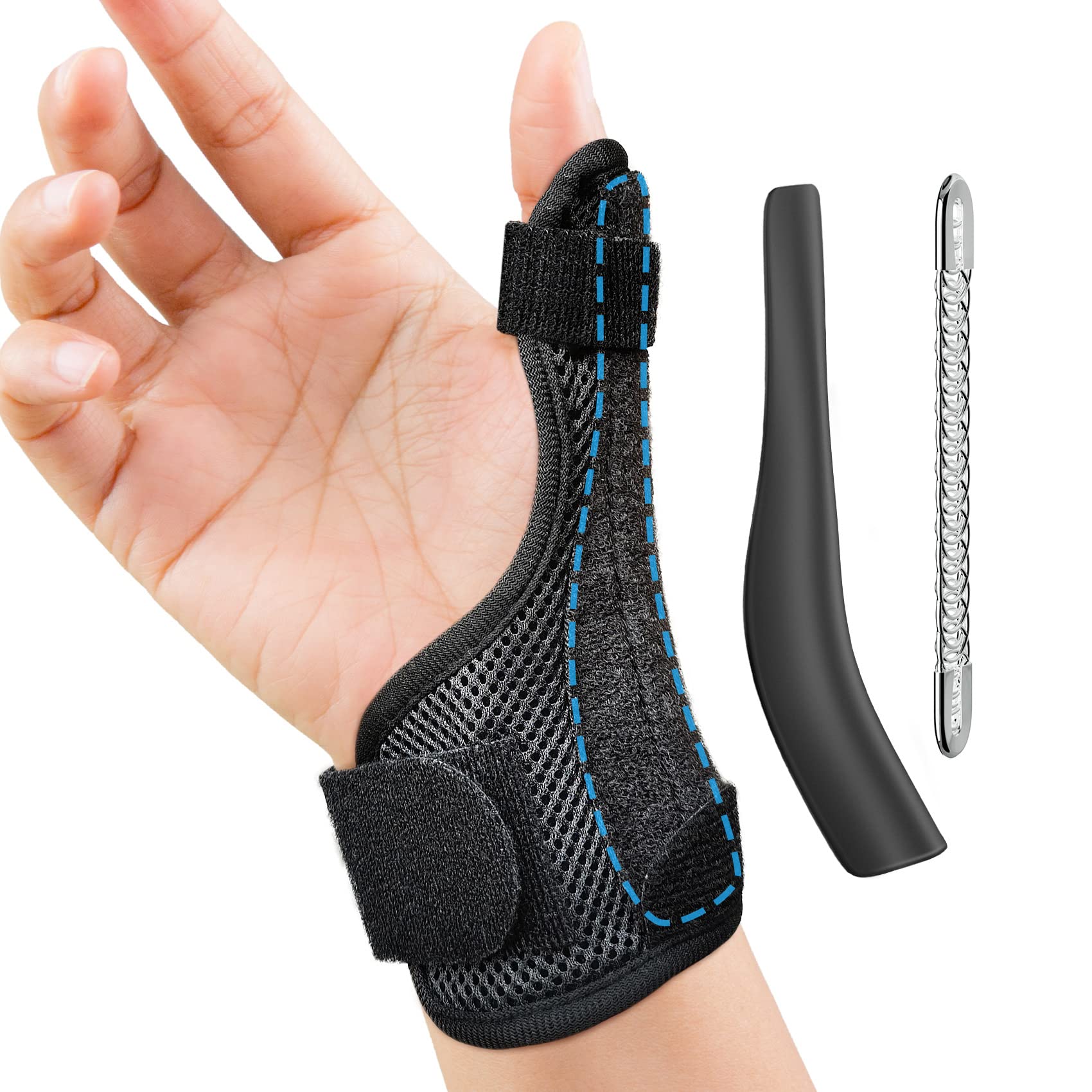
- Thumb Spica Splint: This splint immobilizes both the thumb and wrist, providing maximum support and rest for the inflamed tendons. It’s particularly effective for moderate to severe cases. King Brand and other companies manufacture this style of splint.
- Wrist Brace with Thumb Support: This option offers slightly more flexibility than a thumb spica splint, allowing for some thumb movement while stabilizing the wrist. It might be suitable for milder cases or for individuals who require more hand function for certain tasks. Check Amazon listings or specialized suppliers like OrthoMed (replace with actual link if available) for options.
Beyond Braces: Exploring Other Medical Interventions
In some cases, splints and braces may not be enough to manage De Quervain’s effectively. Other medical interventions may be necessary, such as:
- Iontophoresis: This procedure uses a mild electrical current to deliver anti-inflammatory medication directly through the skin to the affected area. It can be a valuable option for individuals who don’t respond well to oral medications or injections. Resources like OrthoInfo provide more details on this procedure.
- Therapeutic Ultrasound: Used in hand therapy, ultrasound waves create gentle vibrations that may promote tissue healing and reduce pain. While research suggests that TENS units may offer modest pain relief, it does not address the root cause of inflammation.
- Medication: Over-the-counter NSAIDs like ibuprofen or naproxen can provide temporary pain relief. For persistent inflammation, your doctor might recommend a corticosteroid injection directly into the tendon sheath. More guidance on these can often be found from healthcare providers like King Brand.
Choosing the Right Device and Treatment Strategy
Selecting the appropriate medical device and treatment strategy for De Quervain’s requires careful consideration of your individual needs and the severity of your symptoms.
Here’s a comparison table to help guide you:
| Device | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Thumb Spica Splint | Offers excellent support, restricts movement, helps reduce pain and swelling. | Can be bulky, may limit hand function for some tasks, and could feel uncomfortable with extended use. |
| Wrist Brace with Thumb Support | Less restrictive than a thumb spica splint, still provides support and compression. | May not provide enough immobilization for more serious cases of De Quervain’s, and might be less effective at reducing inflammation. |
Factors to consider when choosing a device:
- Severity of symptoms: Mild cases may respond well to a wrist brace, while more severe cases likely benefit from a thumb spica splint.
- Lifestyle: Consider your daily activities and occupation. If you frequently work with your hands, you might need a more flexible device.
- Comfort: The device should fit comfortably and not restrict circulation.
Consulting with a Healthcare Professional:
A healthcare professional, such as a doctor or hand therapist, can accurately diagnose De Quervain’s, assess the severity of your condition, and recommend the most appropriate device and treatment plan. They can also guide you on other treatment options, such as hand therapy exercises, activity modifications, and pain management techniques.
Is De Quervain’s Considered a Disability?
While De Quervain’s can significantly impact your ability to perform certain tasks, it rarely qualifies as a standalone disability. However, the severity of your condition and its impact on your daily life and work activities can influence a disability claim. For veterans, De Quervain’s falls under Diagnostic Code 5214 (Wrist Ankylosis) for VA disability claims. The rating depends on the degree of functional limitation. For long-term disability claims, substantial medical evidence and functional capacity evaluations are usually required. If you are struggling to get the VA disability benefits you deserve, find out more about how to win a sleep apnea VA claim. This resource offers valuable insights and guidance to help you navigate the process.
Living with De Quervain’s: Long-Term Management
Managing De Quervain’s often requires a multi-faceted approach. Beyond medical devices, consider these strategies:
- Hand Therapy: Targeted exercises can improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion, aiding in long-term recovery and preventing recurrence.
- Activity Modification: Avoiding aggravating activities and incorporating ergonomic principles into your daily routine can significantly reduce strain on your wrist and thumb.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers, ice, and heat therapy can help manage discomfort.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Proper posture, regular breaks, and stress management techniques can contribute to overall well-being and potentially lessen symptom flare-ups.
Remember, ongoing research continues to explore the complexities of De Quervain’s syndrome. Some studies suggest a genetic predisposition, while others are investigating the link between specific occupations and the condition. Your doctor or hand therapist can provide the most up-to-date information and personalized guidance for managing your specific case. With the right combination of medical devices, therapies, and lifestyle adjustments, you can effectively manage De Quervain’s and regain control of your hand.
- Georgia Platform: A Southern Strategy, 1850s - March 31, 2025
- How many weeks is 40 days: Quick Conversion Guide for Accurate Results - March 31, 2025
- How many feet is 300 meters? 984 Feet: Understand Length Conversions Easily - March 31, 2025